- VCS = Version Control System
- You can use it to save your work and create save points that you can reference at a later date.
- Thus you can "go back in time".
- Makes it easier to work collaboratively on a project.
- Multiple branches or saves can be created, so different individuals can work at the same time and then merge the files together to create a final file.
- Can view who actually made each change.
- Everything on Git is local, so we use online git repository hosting services like GitHub to share repos.
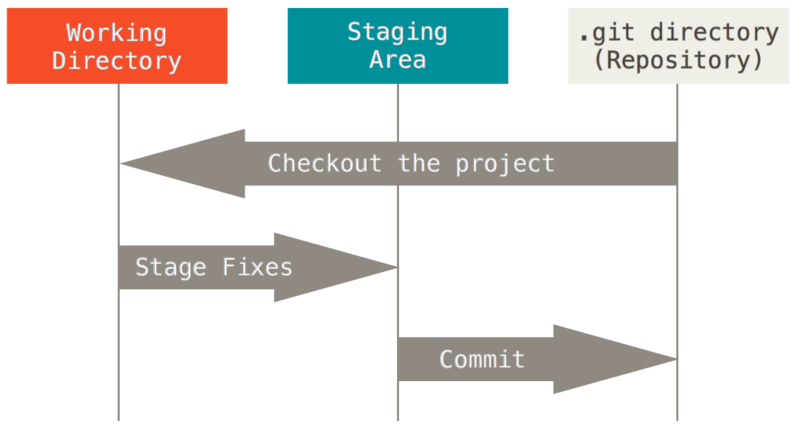
- Repository (or repo) is a place that stores your work and commits.

- Start tracking a directory (folder) with
git init.
- You need to do this once per project.
- Only need to be done in the base folder where all of the files are housed.
- Use
git status frequently throughout to check where you are currently at in the steps.
- Once the file is tracked, you will want to move it to the staging area. Add a file to track with
git add <file name>.
- This takes a snapshot of the current file.
- Then you will need to complete the initial commit using
git commit -m <'message'>.
- This takes the file from the staging area and stores in the local repository.
- On your first commit, you will want to always use 'Initial Commit'.
- For any commits after, you will create your own message representing any changes made to the file.
- If you add any future changes to the file, for example adding additional text. Then you will want to complete steps 2-4 after the changes to your file have been saved.
- Before adding changes to the staging area. Use
git diff <file name>, because it shows the differences between your original file and the updated version.
samanthafreeman~/git_example$ git init
Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/samanthafreeman/git_example/.git/
samanthafreeman~/git_example$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
git_example.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
samanthafreeman~/git_example$ git add git_example.txt
samanthafreeman~/git_example$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: git_example.txt
samanthafreeman~/git_example$ git commit -m 'Initial Commit'
[master (root-commit) 52757b2] Initial Commit
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 git_example.txt