本文原载于我的独立博客 https://lutaonan.com/blog/effective-graphql-and-antd/
在过去的几年,不论是面向内部的系统,还是面向外部的产品,我们都大量地使用了 Ant.Design —— 一个基于 React 的 UI 组件库。
在做内部系统时,Ant.Design 解决了几乎 60% 的问题。剩下的问题在业务逻辑和代码组织的复杂度。我见过很多内部系统因为滥用状态管理而使代码变得复杂,他们之所以使用状态管理库,并不是因为应用的状态复杂,而是因为需要一个状态树来管理网络请求的状态、接口返回的数据等等这些和接口相关的状态。
真的需要状态管理库吗?在之前,我没有信心回答这个问题。但在使用了 GraphQL (Apollo) 后,我确信,在大多数场景,你不再需要状态管理。
这篇文章的目标就是让你认识 GraphQL / Apollo, 以及在 Ant.Design 里如何高效地使用他。你不必担心 GraphQL 会给你带来负担,学习和使用 GraphQL 都是令人愉快的过程。你会发现以往让你感到厌烦的需要重复编写的逻辑,可以不必再写了。
Keep frontend code lean and straight.
—— Randy Lu
本文的前端代码在 CodeSandbox https://codesandbox.io/s/pwmrnjz2km
本文使用大量 ES6+ 特性,请在阅读本文前熟悉 ES6+ 语法。
GraphQL 是一个查询语言,和 SQL 是同等概念的。
举个例子,在 RESTful 的场景里,我们查询一个资源是通过命令式地进行网络请求:
const posts = await fetch('/api/v1/posts')而使用 GraphQL, 是声明式地查询:
query {
posts {
title, body, id
}
}写数据时,命令式地 POST:
const response = await fetch('/api/v1/posts', { method: 'POST', body: { title: "foo", body: "content" } } )使用 GraphQL, 声明式地触发 mutation:
mutation {
createPost(post: { title: "foo", body: "content" })
}你也许会疑惑,这些 GraphQL 语句怎么执行?其实这些语句需要被转换,而转换的工具就是接下来要介绍的 Apollo.
Apollo 是一系列的 GraphQL 工具链,从客户端(不同的前端框架)到服务器端都提供了使用和搭建 GraphQL 的工具。
下面会通过一个简单的例子,让你从前端到服务器端对 GraphQL 有个初步的了解。
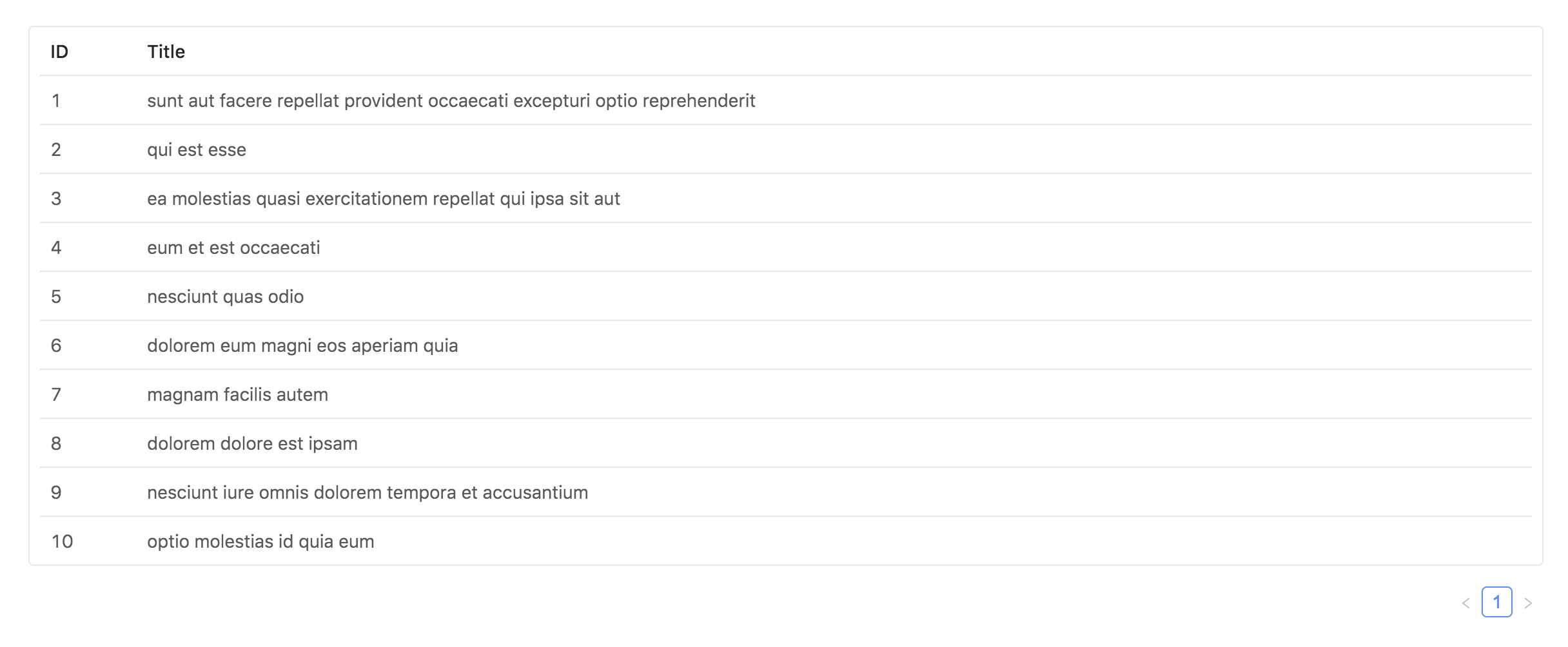
想象有这样一个需求:用表格展示一组数据。
后端告诉你,有如下接口:
这个接口可以获取所有 Post, 返回的格式如下:
interface Post {
userId: number,
id: number,
title: string,
body: string
}第一步我们需要搭建一个 GraphQL 服务器。
搭建一个 GraphQL 服务器不难,Apollo Server 对主流的 Node.js Web 框架都有封装,本文不赘述如何搭建一个 GraphQL 服务器,只介绍 GraphQL 后端编写的一些概念。
用 Apollo Server 编写 GraphQL 服务器有两个主要概念,typeDefs 和 resolvers.
typeDefs 指的是类型定义。GraphQL 是一个有类型系统的查询语言,因此在编写 GraphQL 服务时,要先对查询的数据类型进行定义。
我们已经知道 Post 的数据类型是怎样的,就可以编写 Post 的类型定义:
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Post {
userId: Int!
id: Int!
title: String!
body: String!
}
`另外,我们需要对 Query 进行定义,来定义有哪些查询操作:
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Post {
userId: Int!
id: Int!
title: String!
body: String!
}
+ type Query {
+ posts: [Post]
+ }
`在 官方文档 详细了解 GraphQL 的类型系统。
这样一来,外界就可以通过
query {
posts {
id, title
}
}这样的查询语句查询到 posts 了。
光是类型定义还不够,因为服务器还不知道「查询 posts」这个操作到底应该做什么。这里就是 resolvers 要做的事了。在 resolvers 里定义查询的实际行为:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
async posts() {
const res = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts')
return res.json()
}
}
}在 官方文档 详细了解
resolvers的用法。
最后,通过 Apollo Server 把 typeDefs 和 resolvers 连起来,一个 GraphQL 服务器就成功搭起来了。
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers })
server.listen().then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`Ready at ${url}`)
})我在本文用到的 GraphQL 服务器源码在 https://github.com/djyde/graphql-jsonplaceholder , 通过 https://graphql-jsonplaceholder.now.sh 可以访问 Playground.
你也可以通过 Apollo Launchpad 在线上快速搭建一个测试用的 GraphQL 服务.
有了 GraphQL 服务后,我们开始编写前端组件。首先要创建一个 ApolloClient 实例。最简单的方法是通过 apollo-boost:
import ApolloClient from "apollo-boost";
const apolloClient = new ApolloClient({
// GraphQL 服务器地址
uri: "https://graphql-jsonplaceholder.now.sh"
});ApolloClient 可以命令式地进行查询:
const result = await apolloClient.query({
query: gql`
query {
posts {
id, title, body
}
}
`
})不过,更高效的做法是用 <Query /> 和 <Mutation /> 组件进行声明式的查询。因为它们用了 Function as Child Components
的模式,把 loading 状态,返回的数据 data 都通过参数传递。你不需要手动去管理请求的状态。
import { Query, ApolloProvider } from 'react-apollo'
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
import { Table } from 'antd'
const GET_POSTS = gql`
query GetPosts {
posts {
id, title
}
}
`
const App = () => {
return (
<Query
query={GET_POSTS}
>
{({ loading, data }) => {
const columns = [
{
title: "ID",
dataIndex: "id"
},
{ title: "Title", dataIndex: "title" }
]
const dataSource = data.posts || []
return (
<Table
size="small"
loading={loading}
dataSource={dataSource}
columns={columns}
/>
);
}}
</Query>
)
}
export default () => {
return (
<ApolloProvider client={apolloClient}>
<App />
</ApolloProvider>
)
}
<ApolloProvider />的作用是向所有子组件里的<Query />和<Mutation />传递ApolloClient实例.
我们希望通过一个下拉框 <Select /> 选择需要获取的 Post 数量:
我们可以让 posts 查询接受一个 limit 参数:
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Post {
userId: Int!
id: Int!
title: String!
body: String!
}
type Query {
+ posts(limit: Int): [Post]
}
`然后在 resolvers 里拿到参数,进行处理:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
async posts(root, args) {
// 每个 resolver 的第二个参数就是查询参数
const { limit } = args
const res = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', {
params: {
_limit: limit
}
})
return res.json()
}
}
}在前端,<Query /> 的 variables props 可以传递参数:
import * as React from "react";
import { Table, Select } from "antd";
import { Query } from "react-apollo";
import gql from "graphql-tag";
const GET_POSTS = gql`
query GetPosts($limit: Int) {
posts(limit: $limit) {
id, title
}
}
`
export default class Limit extends React.Component {
state = {
limit: 5
};
onChangeLimit = limit => {
this.setState({ limit });
};
render() {
return (
<div style={{ padding: "2rem" }}>
<Query
query={GET_POSTS}
variables={{ limit: this.state.limit }}
>
{({ loading, data }) => {
const columns = [
{
title: "ID",
dataIndex: "id"
},
{ title: "Title", dataIndex: "title" }
];
const dataSource = data.posts || [];
return (
<React.Fragment>
<div style={{ marginBottom: "12px" }}>
<Select
onChange={this.onChangeLimit}
value={this.state.limit}
style={{ width: "100px" }}
>
<Select.Option value={5}>5</Select.Option>
<Select.Option value={10}>10</Select.Option>
<Select.Option value={15}>15</Select.Option>
</Select>
</div>
<Table
rowKey={record => record.id}
size="small"
loading={loading}
dataSource={dataSource}
columns={columns}
/>
</React.Fragment>
);
}}
</Query>
</div>
);
}
}在 官方文档 详细了解 GraphQL 查询变量定义
接下来实现创建一篇 Post:
当我们需要操作数据的时候,就要用到 Mutation. 还用到一个特殊的数据类型 Input. 通常用来在 Mutation 的参数里传一整个对象。
const typeDefs = gql`
input CreatePostInput {
title: String!
body: String!
}
Mutation {
createPost(post: CreatePostInput!): Post!
}
`然后在为 createPost 这个 mutation 创建一个 resolver:
const resolvers = {
Mutation: {
async createPost(root, args) {
const {
post
} = args
const res = await http.post('/posts', {
data: post
})
const now = Date.now()
const id = Number(now.toString().slice(8, 13))
return {
...res.data.data,
id,
userId: 12
}
}
}
}前端结合 Ant.Design 的 <Modal />, <Form /> 组件和 react-apollo 提供的 <Mutation /> 组件,就可以完成整个「新建 Post」动作:
const GET_POSTS = gql`
query GetPost($limit: Int) {
posts(limit: $limit) {
id, title
}
}
`;
// 「新建 Post」 的 Muation
const CREATE_POST = gql`
mutation CreatePost($post: CreatePostInput!) {
createPost(post: $post) {
id, title
}
}
`
class CreatePost extends React.Component {
state = {
modalVisible: false
};
showModal = () => {
this.setState({ modalVisible: true });
};
closeModal = () => {
this.setState({ modalVisible: false });
};
// Modal 的 onOk 事件
onCreatePost = createPost => {
const { form } = this.props;
form.validateFields(async (err, values) => {
if (!err) {
// `createPost` 是 `<Mutation />` 组件传给 children 的 mutation 方法
await createPost({ variables: { post: values } });
this.closeModal();
form.resetFields();
}
});
};
render() {
const { form } = this.props;
return (
<div style={{ padding: "2rem" }}>
<Query query={GET_POSTS} variables={{ limit: 5 }}>
{({ loading, data }) => {
const columns = [
{
title: "ID",
dataIndex: "id"
},
{ title: "Title", dataIndex: "title" }
];
const dataSource = data.posts || [];
return (
<React.Fragment>
<Mutation mutation={CREATE_POST}>
{(createPost, { loading, data }) => {
return (
<Modal
onOk={e => this.onCreatePost(createPost)}
onCancel={this.closeModal}
title="Create Post"
confirmLoading={loading}
visible={this.state.modalVisible}
>
<Form>
<Form.Item label="Title">
{form.getFieldDecorator("title", {
rules: [{ required: true }]
})(<Input />)}
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item label="Body">
{form.getFieldDecorator("body", {
rules: [{ required: true }]
})(<Input.TextArea />)}
</Form.Item>
</Form>
</Modal>
);
}}
</Mutation>
<div style={{ marginBottom: "12px" }}>
<Button onClick={this.showModal} type="primary">
New Post
</Button>
</div>
<Table
rowKey={record => record.id}
size="small"
loading={loading}
dataSource={dataSource}
columns={columns}
/>
</React.Fragment>
);
}}
</Query>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Form.create()(CreatePost);和 <Query /> 一样,<Mutation /> 把请求状态都传递给了 children.
在 官方文档 详细了解
<Mutation />的用法
成功「新建 Post」以后,通常我们会更新数据列表。react-apollo 有两种方法实现。
<Mutation /> 有 update 这个 props. 在 mutation 执行成功后回调,并且带有 cache 和 mutation 的响应数据。我们可以通过更新 cache 来实现更新数据列表。
例如,在获取数据列表的 <Query /> 中,是通过 GET_POSTS 来查询的:
query={GET_POSTS} variables={{ limit: 5 }}那么,在 update 回调里,我们可以得到 GET_POSTS 对应的 cache, 然后更新这个 cache. 更新 cache 后,通过 GET_POSTS (以及相同的 variables) 查询的组件,会自动 rerender:
const update = (cache, { data: { createPost } }) => {
// 取得 `GET_POSTS` 对应的 cache
// 注意要和你要更新的组件的 query 和 variables 都要一致
const { posts } = cache.readQuery({ query: GET_POSTS, variables: { limit: 5 } })
// 用 mutation 的响应数据更新 cache
// 同样,query 和 variables 都要一致
cache.writeQuery({
query, GET_POSTS,
variables: { limit: 5 },
data: { posts: [createPost].concat(posts) }
})
}有时我们想要直接重新请求数据列表而不是手动更新 cache. 我们可以使用 refetchQueries 返回一个你要重新查询的查询数组:
const refetch = () => {
return [
{ query: GET_POSTS }
]
}这样,所有 query 是 GET_POSTS 的组件都会重新执行查询并 rerender.
Ant.Design 的 Table 组件可以通过 Pagination 很容易地实现分页异步加载.
首先先让 GraphQL 接口支持分页:
const typeDefs = gql`
type Post {
userId: Int!
id: Int!
title: String!
body: String!
}
+ type Meta {
+ total: Int!
+ }
+ type PostResultWithMeta {
+ metadata: Meta!
+ data: [Post]!
+ }
type Query {
posts(page: Int, limit: Int): [Post]
+ postsWithMeta(page: Int, limit: Int!): PostResultWithMeta!
}
`const resolvers = {
Query: {
async postsWithMeta(root, args) {
const {
page, limit
} = args
const res = await http.get('/posts', {
params: {
+ _page: page,
_limit: limit
}
})
return {
+ metadata: {
+ total: res.headers['x-total-count']
+ },
+ data: res.data
}
}
},
}前端就可以传 limit 和 page 实现分页:
const GET_POSTS = gql`
query GetPosts($limit: Int!, $page: Int) {
postsWithMeta(limit: $limit, page: $page) {
metadata {
total
},
data {
id, title
}
}
}
`;
export default class Pagination extends React.Component {
// 传给 Ant.Design Table 的 pagination 信息
state = {
pagination: {
pageSize: 10,
current: 1,
total: 0
}
};
// Query 完成后,给 pagination 设置数据总数
onCompleteQuery = ({
postsWithMeta: {
metadata: { total }
}
}) => {
const pagination = { ...this.state.pagination };
pagination.total = total;
this.setState({ pagination });
};
handleTableChange = pagination => {
const pager = { ...pagination };
pager.current = pagination.current;
this.setState({ pagination });
};
render() {
return (
<div style={{ padding: "2rem" }}>
<Query
onCompleted={this.onCompleteQuery}
query={GET_POSTS}
variables={{
// 在 pagination 信息中得到 `limit` 和 `page`
limit: this.state.pagination.pageSize,
page: this.state.pagination.current
}}
>
{({ loading, data }) => {
const columns = [
{
title: "ID",
dataIndex: "id"
},
{ title: "Title", dataIndex: "title" }
];
const dataSource = data.postsWithMeta ? data.postsWithMeta.data : [];
return (
<Table
pagination={this.state.pagination}
onChange={this.handleTableChange}
rowKey={record => record.id}
size="small"
loading={loading}
dataSource={dataSource}
columns={columns}
/>
);
}}
</Query>
</div>
);
}
}GraphQL 比 RESTful 的优势在于,GraphQL 让你专注于你想做什么,想获取什么。「查询语言」是声明式的,而「HTTP 请求」是命令式的。声明式可以让复杂度转移给运行时,就像 GraphQL 语句最终执行的 HTTP 请求可以交给像 Apollo 这样的封装去处理。
当你不再需要自己管理这么多 HTTP 请求的状态时,你就要仔细考虑你的应用到底需不需要状态管理工具了。尤其在开发中后台类的管理系统应用时,往往不会涉及复杂的数据流。Local state is fine.