- Event driven system - serverless function usually glue the services together and work properly.
- Serverless function was called service bus in the past.
- The features of serverless function:
- short-lived
- not a daemon
- stateful
- execute in few second
- make use of existing services
Further reading:
- introducing-functions-as-a-service
- AWS re:Invent 2017: GitHub to AWS Lambda
- Local Testing and Deployment Best Practices for Serverless Applications
- Building a Pipeline for Your Serverless Application
- AWS Lambda (Part 1): Introduction
- AWS CodeStar: Develop, Build, and Deploy applications on AWS
- Serverless Architecture Patterns and Best Practices
- Load balancers distribute incoming client requests to computing resources:
- application (web app)
- database
- Load balancers tasks include:
- Prevent requests to unhealthy services
- Prevent overloading of the service
- Eliminating signle point failure
- SSL Termination (Remove the need to install certification to each server)
- Session persistent
- Route traffic algorithm
- Round-Robin
- Least Load
- Random
- Layer 4 (transport layer) load balancer: NAT
- Layer 7 (application layer) load balancer: Nginx, HAProxy, ...
- Layer 7 load balancer redirect traffic to the service, for example:
- video stream to video streamming server
- billing request to another security server
- Load balancer could be bottleneck (disadvantage)
- Horizontal Scaling (scale out)
- Advantage: Load balancer helps horizontal scaling
- Disadvantage:
- Increase system complexity
- Server should be stateless
- Downstream servers such as caches and databases need to handle more simultaneous connections as upstream servers scale out
- Vertical scaling (scale up): Upgrade the hardware to a single machine
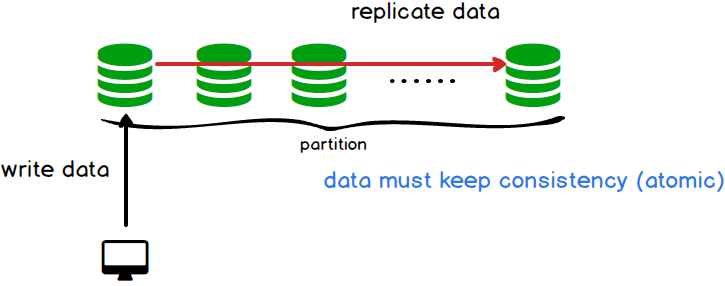
- Consistency - A read is guaranteed to return the most recent write for a given client
- Availability - A non-failing node will return a reasonable response within a resonable amount of time (no error or timeout)
- Partition Tolerance - The system will continue to function when network partitions occur
Further reading:
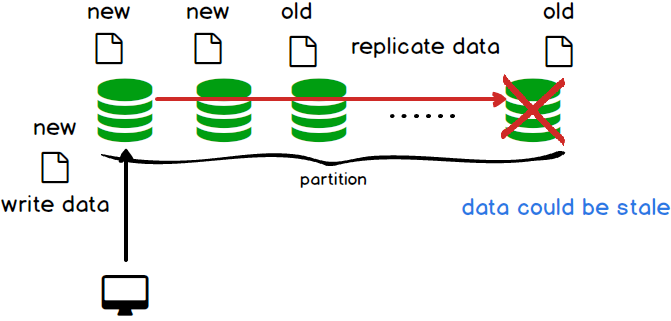
- Weak consistency: After a write, reads may or may not see it.
- Eventual consistency: After a write, reads will eventually see it. Data is replicated asynchronously
- Strong consistency: After a write, reads will see it. Data is replicated synchronously.
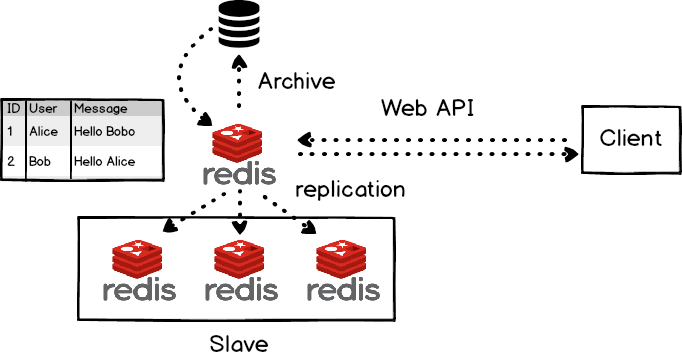
- Redis in memory store,
- A key-value store
- Redis is a data structure serve, no query language.
- 2 options for persistent
- regular snapshotting
- append-only files.
- Use cases:
- Show latest items listings in your home page
- Order by user votes and time
- Implement expires on items
- Counting stuff
- Pub/Sub
- Queues
- Caching
Use case:
- Chat or Twitter
- Cache pattern
Further reading:
- ACID is a set of properties of relational database transactions.
- Atomicity - Each transaction is all or nothing
- Consistency - Any transaction will bring the database from one valid state to another
- Isolation - Executing transactions concurrently has the same results as if the transactions were executed serially
- Durability - Once a transaction has been committed, it will remain so
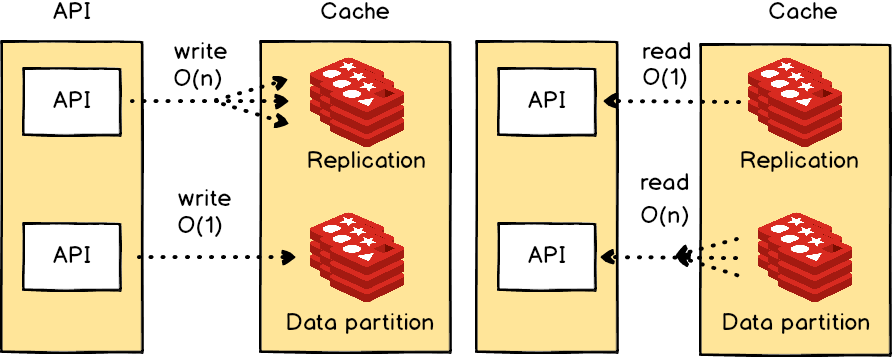
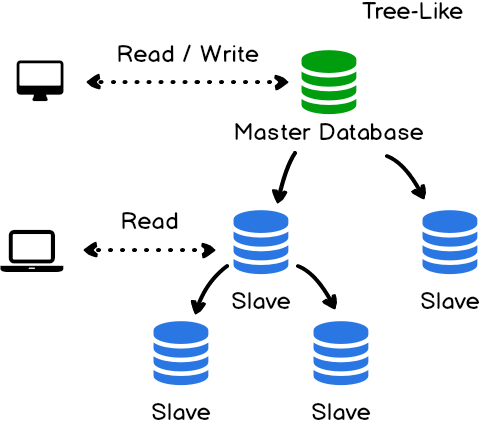
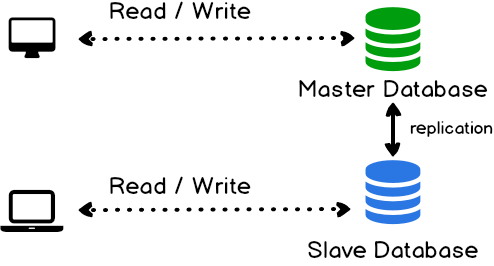
- Scale a relational database
- master-slave replication
- master-master replication
- federation: Federation (or functional partitioning) splits up databases by function. For example, instead of a single, monolithic database, you could have several databases
- sharding: Sharding distributes data across different databases such that each database can only manage a subset of the data
- denormalization: Denormalization attempts to improve read performance at the expense of some write performance. Redundant copies of the data are written in multiple tables to avoid expensive joins
- key-value store
- document-store
- wide column store
- graph database
Most NoSQL stores lack true ACID transactions and favor eventual consistency. In comparison with the CAP Theorem, BASE chooses availability over consistency
BASE is often used to describe the properties of NoSQL databases.
- Basically available - the system guarantees availability
- Soft state - the state of the system may change over time, even without input
- Eventual consistency - the system will become consistent over a period of time, given that the system doesn't receive input during that period
Futher reading:
- Asynchronous workflows help reduce request times for expensive operations
- Workflow:
- An application publishes a job to the queue, then notifies the user of job status
- A worker picks up the job from the queue, processes it, then signals the job is complete
- The user is not blocked and the job is processed in the background
- Message queue project:
- Redis
- RabbitMQ
- Amazon SQS
- Disadvantage:
- Introducing queues can add delays and complexity
- Back pressure
- If queue growth too quick which exceed the system loading, introducing a back-pressure (the limitation of queue) can eliminate system loading. Once the queue fills up, the system can reponse a busy error code such as HTTP 503 to ask client try again later.
Futher reading:
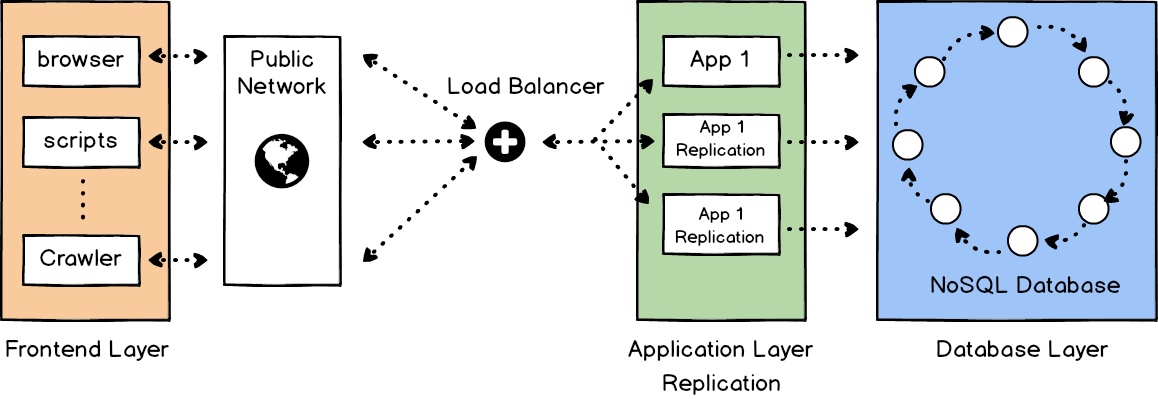
- Strengths:
- Rich frontend framework
- Scalable (the benefit comes from stateless of app)
- Scalable data (usually use NoSQL database)
- State in the middle tier (Since apps usually stateless)
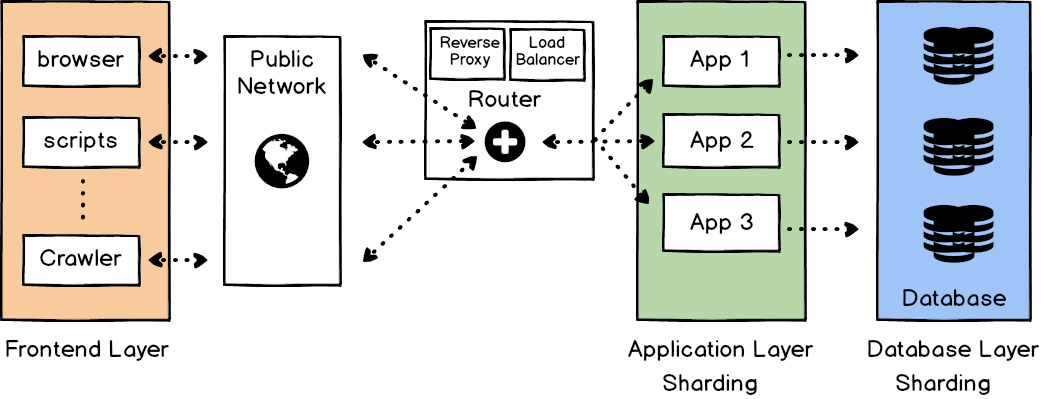
- Strengths:
- Client isolation is easy
- Simple technology
- Weekness
- Complexity
- Hard to understand data
- Oversize shard (redundent shard)
- Example:
- Slack (apps, channels)