Created
May 16, 2020 00:10
-
-
Save csaybar/7ef67cd88276086d7da4463dd4815bd7 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| [](https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/actions) | |
| [](https://www.repostatus.org/#active) | |
| [](https://codecov.io/gh/r-spatial/rgee) | |
| [](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0) | |
| [](https://www.tidyverse.org/lifecycle/#maturing) | |
| [](https://cran.r-project.org/package=rgee) | |
| # Google Earth Engine for R | |
| <a href="http://r-spatial.github.io/rgee"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/r-spatial/rgee/master/man/figures/logo.png" align="left" hspace="10" vspace="0" width="15%"></a> | |
| `rgee` is a binding package for calling [Google Earth Engine | |
| API](https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/) from within R. | |
| Additionally, several functions have been implemented to make simple the connection with the R spatial ecosystem. The current version of rgee has been built considering the | |
| [earthengine-api 0.1.221](https://pypi.org/project/earthengine-api/0.1.221/). | |
| **Note that access to Google Earth Engine is only available to [registered users](https://earthengine.google.com/)**. | |
| #### More than 250+ examples using Google Earth Engine with R are available [here](http://csaybar.github.io/rgee-examples/) | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/FeatureCollection/search_by_buffer_distance.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_01_search_by_buffer_distance.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/image/convolutions.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_02_convolutions.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/FeatureCollection/idw_interpolation.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_03_idw_interpolation.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/image/spectral_unmixing.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_04_spectral_unmixing.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Algorithms/CloudMasking/sentinel-2.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_05_sentinel2.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/image/canny_edge_detector.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_06_canny_edge_detector.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/image/cumulative_cost_mapping.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_07_cumulative_cost_mapping.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/image/zero_crossing.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_08_zero_crossing.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples//Visualization/hillshade.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_09_hillshade.png" height="100" hspace="5"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Visualization/styled_layer_descriptors.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_10_styled_layer_descriptors.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Visualization/terrain_visualization.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_11_terrain_visualization.png" height="100" hspace="5"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Datasets/Vectors/us_census_counties.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_12_us_census_counties.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Datasets/Vectors/global_power_plant_database.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_13_global_power_plant_database.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Datasets/Vectors/landsat_wrs2_grid.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_14_landsat_wr2_grid.png" height="100" hspace="4"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Datasets/Water/jrc_metadata.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_15_jrc_metadata.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples//Visualization/visualizing_geometries.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_16_visualizing_geometries.png" height="100" hspace="1"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Algorithms/center_pivot_irrigation_detector.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_17_center_pivot_irrigation_detector.png" height="100" hspace="2"/></a> | |
| <a href="https://github.com/r-spatial/rgee/blob/examples/Visualization/image_color_ramp.R"><img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ryali93/rgee_readme_icons/master/images/img_18_image_color_ramp.png" height="100"/></a> | |
| ## What is Google Earth Engine? | |
| [Google Earth Engine](https://earthengine.google.com/) is a cloud-based platform that allows users to have an easy access to a petabyte-scale archive of remote sensing data and run geospatial analysis on Google’s infrastructure. Currently, Google offers support only for Python and JavaScript. `rgee` will fill the gap **starting to provide support to R\!**. Below you will find the comparison between the syntax of `rgee` and the two Google-supported client libraries. | |
| <table> | |
| <tr> | |
| <th> JS (Code Editor) </th> | |
| <th> Python </th> | |
| <th> R </th> | |
| </tr> | |
| <tr> | |
| <td> | |
| ``` javascript | |
| var db = 'CGIAR/SRTM90_V4' | |
| var image = ee.Image(db) | |
| print(image.bandNames()) | |
| #> 'elevation' | |
| ``` | |
| </td> | |
| <td> | |
| ``` python | |
| import ee | |
| ee.Initialize() | |
| db = 'CGIAR/SRTM90_V4' | |
| image = ee.Image(db) | |
| image.bandNames().getInfo() | |
| #> [u'elevation'] | |
| ``` | |
| </td> | |
| <td> | |
| ``` r | |
| library(rgee) | |
| ee_Initialize() | |
| db <- 'CGIAR/SRTM90_V4' | |
| image <- ee$Image(db) | |
| image$bandNames()$getInfo() | |
| #> [1] "elevation" | |
| ``` | |
| </td> | |
| </tr> | |
| </table> | |
| **Quite similar, isn’t it?**. However, there are additional smaller changes that you must consider when you use Google Earth Engine with R. Please check the [consideration section](https://r-spatial.github.io/rgee/articles/considerations.html) before start coding\! | |
| ## Installation | |
| Install the `rgee` package from GitHub is quite simple, you just have to run in your R console as follows: | |
| ``` r | |
| remotes::install_github("r-spatial/rgee") | |
| ``` | |
| **`rgee` depends on [sf](https://github.com/r-spatial/sf)**. Therefore, it is necessary to install its external libraries, follow the installation steps specified [here](https://github.com/r-spatial/sf#installing). | |
| #### Docker image | |
| docker pull csaybar/rgee | |
| docker run -d -p 8787:8787 -e USER=rgee -e PASSWORD=rgee --name rgee-dev csaybar/rgee | |
| After that, in your preferred browser, run: | |
| 127.0.0.1:8787 | |
| ## Requirements | |
| Prior to using `rgee` you will need to install a **Python version higher than 3.5** in your system. `rgee` counts with an installation module (ee_install_*) which helps you to deal with the external dependencies of `rgee`: | |
| ```r | |
| library(rgee) | |
| # 1. Initialize rgee with ee_Initialize(). If there is no any Python environment, miniconda | |
| # will be installed by default. | |
| ee_Initialize() | |
| # 2. Create a Python environment, e.g. ee. | |
| pyenv <- ee_install_create_pyenv(py_env = "ee") | |
| # Find others Python environments in the system. | |
| # ee_install_discover_pyenvs() | |
| # 3. Set a Python environment (e.g. ee) and restart R to see changes. | |
| ee_install_set_pyenv(pyenv, install = TRUE) | |
| # 4. Install Python package dependencies and restart R to see changes. | |
| ee_install_python_packages() | |
| # 5. Initialize rgee again! | |
| ee_Initialize() | |
| ``` | |
| Additionally, you might use the functions below for checking the status of rgee, delete credentials, and install (or upgrade) Python packages. | |
| ```r | |
| ee_check() # Check non-R dependencies | |
| ee_clean_credentials() # Remove credentials of a specific user | |
| ee_clean_pyenv() # Remove reticulate system variables | |
| ee_install_earthengine_upgrade() # it's a wrapper around py_install("earthengine-api") | |
| ``` | |
| Also, consider looking at the [setup section](https://r-spatial.github.io/rgee/articles/setup.html) for major information to customizing Python installation. | |
| ## Package Conventions | |
| - All `rgee` functions have the prefix ee\_. Auto-completion is | |
| your friend :). | |
| - Full access to the Earth Engine API with the prefix | |
| [**ee$…:**](https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/). | |
| - Authenticate and Initialize the Earth Engine R API with | |
| [**ee\_Initialize:**](https://r-spatial.github.io/rgee/reference/ee_Initialize.html), you just will need to do it once by session!. | |
| - `rgee` is “pipe-friendly”, we re-exports %\>%, but `rgee` does | |
| not require its use. | |
| - Wrap your R function using `ee_utils_pyfunc` before passing them to the | |
| Earth Engine Web REST API. This is not compulsory, but it will help | |
| reduce possible [bugs](https://r-spatial.github.io/rgee/articles/considerations.html#the-map-message-error) :bug:. | |
| ## Quick Demo | |
| ### 1. Compute the trend of night-time lights ([JS version](https://github.com/google/earthengine-api)) | |
| Authenticate and Initialize the Earth Engine R API. | |
| ``` r | |
| library(rgee) | |
| ee_Initialize() | |
| #ee_reattach() # reattach ee as a reserve word | |
| ``` | |
| Adds a band containing image date as years since 1991. | |
| ``` r | |
| createTimeBand <-function(img) { | |
| year <- ee$Date(img$get('system:time_start'))$get('year')$subtract(1991L) | |
| ee$Image(year)$byte()$addBands(img) | |
| } | |
| ``` | |
| Map the time band creation helper over the [night-time lights collection](https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/NOAA_DMSP-OLS_NIGHTTIME_LIGHTS). | |
| ``` r | |
| collection <- ee$ | |
| ImageCollection('NOAA/DMSP-OLS/NIGHTTIME_LIGHTS')$ | |
| select('stable_lights')$ | |
| map(createTimeBand) | |
| ``` | |
| Compute a linear fit over the series of values at each pixel, visualizing the y-intercept in green, and positive/negative slopes as red/blue. | |
| ``` r | |
| col_reduce <- collection$reduce(ee$Reducer$linearFit()) | |
| col_reduce <- col_reduce$addBands( | |
| col_reduce$select('scale')) | |
| ee_print(col_reduce) | |
| ``` | |
| Create a interactive visualization\! | |
| ``` r | |
| Map$setCenter(9.08203, 47.39835, 3) | |
| Map$addLayer( | |
| eeObject = col_reduce, | |
| visParams = list( | |
| bands = c("scale", "offset", "scale"), | |
| min = 0, | |
| max = c(0.18, 20, -0.18) | |
| ), | |
| name = "stable lights trend" | |
| ) | |
| ``` | |
| 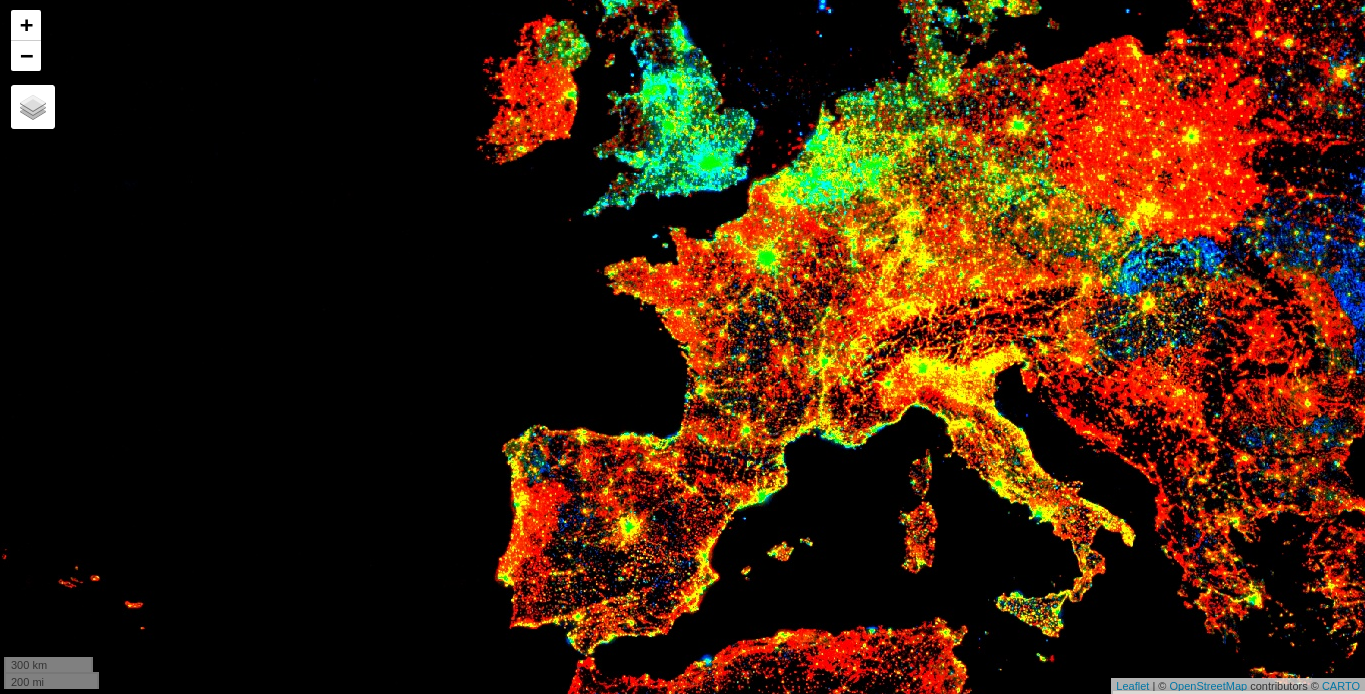 | |
| ### 2. Extract precipitation values | |
| Load `sf` and authenticate and initialize the Earth Engine R API. | |
| ``` r | |
| library(tidyverse) | |
| library(rgee) | |
| library(sf) | |
| # ee_reattach() # reattach ee as a reserve word | |
| ee_Initialize() | |
| ``` | |
| Read the `nc` shapefile. | |
| ``` r | |
| nc <- st_read(system.file("shape/nc.shp", package = "sf"), quiet = TRUE) | |
| ``` | |
| Map each image from 2001 to extract the monthly precipitation (Pr) from the [Terraclimate | |
| dataset](https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/IDAHO_EPSCOR_TERRACLIMATE) | |
| ``` r | |
| terraclimate <- ee$ImageCollection("IDAHO_EPSCOR/TERRACLIMATE")$ | |
| filterDate("2000-01-01", "2001-01-01")$ | |
| map(function(x) x$select("pr")) | |
| ``` | |
| Extract monthly precipitation values from the Terraclimate ImageCollection through `ee_extract`. `ee_extract` works | |
| similar to `raster::extract`, you just need to define: the | |
| ImageCollection object (x), the geometry (y), and a function to | |
| summarize the values (fun). | |
| ``` r | |
| ee_nc_rain <- ee_extract(x = terraclimate, y = nc, fun = ee$Reducer$max(), sf = FALSE) | |
| colnames(ee_nc_rain) <- sprintf("%02d", 1:12) | |
| ee_nc_rain$name <- nc$NAME | |
| ``` | |
| Use ggplot2 to generate a beautiful static plot! | |
| ``` r | |
| ee_nc_rain %>% | |
| pivot_longer(-name, names_to = "month", values_to = "pr") %>% | |
| ggplot(aes(x = month, y = pr, group = name, color = pr)) + | |
| geom_line(alpha = 0.4) + | |
| xlab("Month") + | |
| ylab("Precipitation (mm)") + | |
| theme_minimal() | |
| ``` | |
| <p align="center"> | |
| <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/16768318/81945044-2cbd8280-95c3-11ea-9ef5-fd9f6fd5fe89.png" width=80%> | |
| </p> | |
| ### 3. Create an NDVI-animation ([JS version](https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/tutorials/community/modis-ndvi-time-series-animation)) | |
| Load sf and authenticate and initialize the Earth Engine R API. | |
| ``` r | |
| library(rgee) | |
| library(sf) | |
| ee_Initialize() | |
| # ee_reattach() # reattach ee as a reserve word | |
| ``` | |
| Define the regional bounds of animation frames and a mask to clip the NDVI data by. | |
| ``` r | |
| mask <- system.file("shp/arequipa.shp", package = "rgee") %>% | |
| st_read(quiet = TRUE) %>% | |
| sf_as_ee() | |
| region <- mask$geometry()$bounds() | |
| ``` | |
| Retrieve the MODIS Terra Vegetation Indices 16-Day Global 1km dataset as an `ee.ImageCollection` | |
| and select the NDVI band. | |
| ``` r | |
| col <- ee$ImageCollection('MODIS/006/MOD13A2')$select('NDVI') | |
| ``` | |
| Group images by composite date | |
| ``` r | |
| col <- col$map(function(img) { | |
| doy <- ee$Date(img$get('system:time_start'))$getRelative('day', 'year') | |
| img$set('doy', doy) | |
| }) | |
| distinctDOY <- col$filterDate('2013-01-01', '2014-01-01') | |
| ``` | |
| Define a filter that identifies which images from the complete collection match the DOY | |
| from the distinct DOY collection. | |
| ``` r | |
| filter <- ee$Filter$equals(leftField = 'doy', rightField = 'doy'); | |
| ``` | |
| Define and Apply the join; convert the resulting FeatureCollection to an ImageCollection. | |
| ``` r | |
| join <- ee$Join$saveAll('doy_matches') | |
| joinCol <- ee$ImageCollection(join$apply(distinctDOY, col, filter)) | |
| ``` | |
| Apply median reduction among matching DOY collections. | |
| ``` r | |
| comp <- joinCol$map(function(img) { | |
| doyCol = ee$ImageCollection$fromImages( | |
| img$get('doy_matches') | |
| ) | |
| doyCol$reduce(ee$Reducer$median()) | |
| }) | |
| ``` | |
| Define RGB visualization parameters. | |
| ``` r | |
| visParams = list( | |
| min = 0.0, | |
| max = 9000.0, | |
| bands = "NDVI_median", | |
| palette = c( | |
| 'FFFFFF', 'CE7E45', 'DF923D', 'F1B555', 'FCD163', '99B718', '74A901', | |
| '66A000', '529400', '3E8601', '207401', '056201', '004C00', '023B01', | |
| '012E01', '011D01', '011301' | |
| ) | |
| ) | |
| ``` | |
| Create RGB visualization images for use as animation frames. | |
| ```r | |
| rgbVis <- comp$map(function(img) { | |
| do.call(img$visualize, visParams) %>% | |
| ee$Image$clip(mask) | |
| }) | |
| ``` | |
| Define GIF visualization parameters. | |
| ```r | |
| gifParams <- list( | |
| region = region, | |
| dimensions = 600, | |
| crs = 'EPSG:3857', | |
| framesPerSecond = 10 | |
| ) | |
| ``` | |
| Render the GIF animation in the console. | |
| ```r | |
| print(rgbVis$getVideoThumbURL(gifParams)) | |
| browseURL(rgbVis$getVideoThumbURL(gifParams)) | |
| ``` | |
| <p align="center"> | |
| <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/16768318/77121867-203e0300-6a34-11ea-97ba-6bed74ef4300.gif"> | |
| </p> | |
| ## How does rgee work? | |
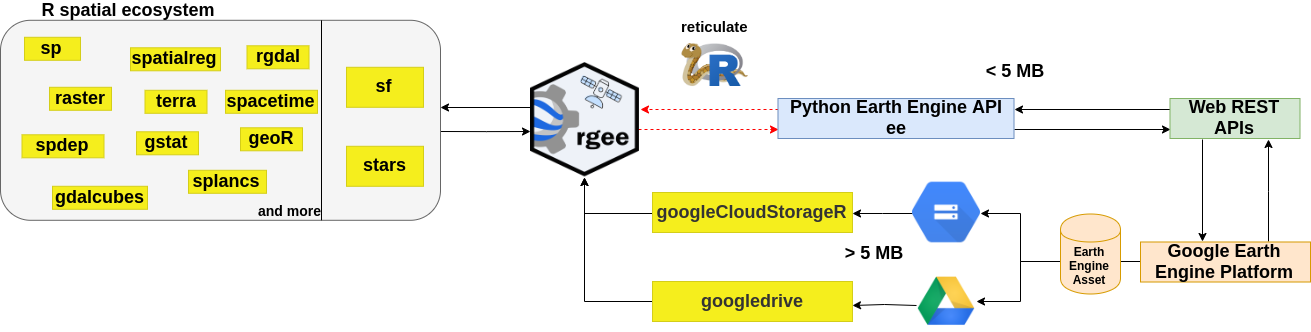
| `rgee` is **not** a native Earth Engine API like the Javascript or Python client, to do this would be extremely hard, especially considering that the API is in [active development](https://github.com/google/earthengine-api). So, how is it possible to run Earth Engine using R? the answer is [reticulate](https://rstudio.github.io/reticulate/). `reticulate` is an R package designed to allow a seamless interoperability between R and Python. When an Earth Engine **request** is created in R, `reticulate` will transform this piece of code to Python. Once the Python code is obtained, the `Earth Engine Python API` transform the request to a `JSON` format. Finally, the request is received by the Google Earth Engine Platform thanks to a Web REST API. The **response** will follow the same path. If you are searching a way to interact with the Earth Engine Asset (EEA), `rgee` offers also functions to batch [upload](https://r-spatial.github.io/rgee/reference/sf_as_ee.html)([download](https://r-spatial.github.io/rgee/reference/ee_as_sf.html)) spatial objects. Additionally, you could easily manage EEA through the [ee\_manage\_\*](https://r-spatial.github.io/rgee/reference/ee_manage-tools.html) interface. | |
|  | |
| ## Code of Conduct | |
| Please note that the `rgee` project is released with a [Contributor Code | |
| of Conduct](CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md). By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms. | |
| ## Contributing Guide | |
| 👍 Thanks for taking the time to contribute\! 🎉👍 Please review our [Contributing Guide](CONTRIBUTING.md). | |
| ## Share the love ❤️ | |
| Think **rgee** is useful? Let others discover it, by telling them in | |
| person via Twitter or a blog post. | |
| Using **rgee** for a paper you are writing? Consider citing it | |
| ``` r | |
| citation("rgee") | |
| #> | |
| #> WORKING ON THIS :) | |
| ``` | |
| ## Credits :bow: | |
| First off, we would like to offer an **special thanks** :raised_hands: :clap: to [**Justin Braaten**](https://github.com/jdbcode) for his wise and helpful comments in the whole development of **rgee**. As well, we would like to mention the following third-party R/Python packages for contributing indirectly to the develop of rgee: | |
| - **[gee\_asset\_manager - Lukasz Tracewski](https://github.com/tracek/gee_asset_manager)** | |
| - **[geeup - Samapriya Roy](https://github.com/samapriya/geeup)** | |
| - **[geeadd - Samapriya Roy](https://github.com/samapriya/gee_asset_manager_addon)** | |
| - **[cartoee - Kel Markert](https://github.com/KMarkert/cartoee)** | |
| - **[geetools - Rodrigo E. Principe](https://github.com/gee-community/gee_tools)** | |
| - **[landsat-extract-gee - Loïc Dutrieux](https://github.com/loicdtx/landsat-extract-gee)** | |
| - **[earthEngineGrabR - JesJehle](https://github.com/JesJehle/earthEngineGrabR)** | |
| - **[sf - Edzer Pebesma](https://github.com/r-spatial/sf)** | |
| - **[stars - Edzer Pebesma](https://github.com/r-spatial/stars)** | |
| - **[gdalcubes - Marius Appel](https://github.com/appelmar/gdalcubes)** | |
| #### Readme template obtained from [dbparser](https://github.com/Dainanahan/dbparser) |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment