-
-
Save denisbrodbeck/635a644089868a51eccd6ae22b2eb800 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
| // License: MIT | |
| package main | |
| import ( | |
| "crypto/rand" | |
| "fmt" | |
| "math/big" | |
| ) | |
| // GenerateRandomASCIIString returns a securely generated random ASCII string. | |
| // It reads random numbers from crypto/rand and searches for printable characters. | |
| // It will return an error if the system's secure random number generator fails to | |
| // function correctly, in which case the caller must not continue. | |
| func GenerateRandomASCIIString(length int) (string, error) { | |
| result := "" | |
| for { | |
| if len(result) >= length { | |
| return result, nil | |
| } | |
| num, err := rand.Int(rand.Reader, big.NewInt(int64(127))) | |
| if err != nil { | |
| return "", err | |
| } | |
| n := num.Int64() | |
| // Make sure that the number/byte/letter is inside | |
| // the range of printable ASCII characters (excluding space and DEL) | |
| if n > 32 && n < 127 { | |
| result += string(n) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| func main() { | |
| length := 20 | |
| random, err := GenerateRandomASCIIString(length) | |
| if err != nil { | |
| panic(err) | |
| } | |
| fmt.Println(random) | |
| // Output: 0_tRSWiyJ=b4(x^6TE<q | |
| } |
| // License: MIT | |
| package main | |
| import ( | |
| "crypto/rand" | |
| "fmt" | |
| "math/big" | |
| "sort" | |
| "strings" | |
| "gonum.org/v1/plot" | |
| "gonum.org/v1/plot/plotter" | |
| "gonum.org/v1/plot/plotutil" | |
| "gonum.org/v1/plot/vg" | |
| ) | |
| const iterations = 1000 * 100 | |
| type generate func(int) (string, error) | |
| func GenerateRandomStringEven(length int) (pass string, err error) { | |
| for { | |
| if length <= lenString(pass) { | |
| return pass, nil | |
| } | |
| num, err := rand.Int(rand.Reader, big.NewInt(int64(127))) | |
| if err != nil { | |
| return "", err | |
| } | |
| n := num.Int64() | |
| if n > 32 && n < 127 { | |
| pass += string(n) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| //const letters = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz-" | |
| const letters = "!\"#$%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~" | |
| func GenerateRandomStringUneven(length int) (string, error) { | |
| bytes := make([]byte, length) | |
| if _, err := rand.Read(bytes); err != nil { | |
| return "", err | |
| } | |
| for i, b := range bytes { | |
| bytes[i] = letters[b%byte(len(letters))] | |
| } | |
| return string(bytes), nil | |
| } | |
| func main() { | |
| fmt.Println("Calculating even distribution of random characters…") | |
| even := measureDistribution(iterations, GenerateRandomStringEven) | |
| print(even) | |
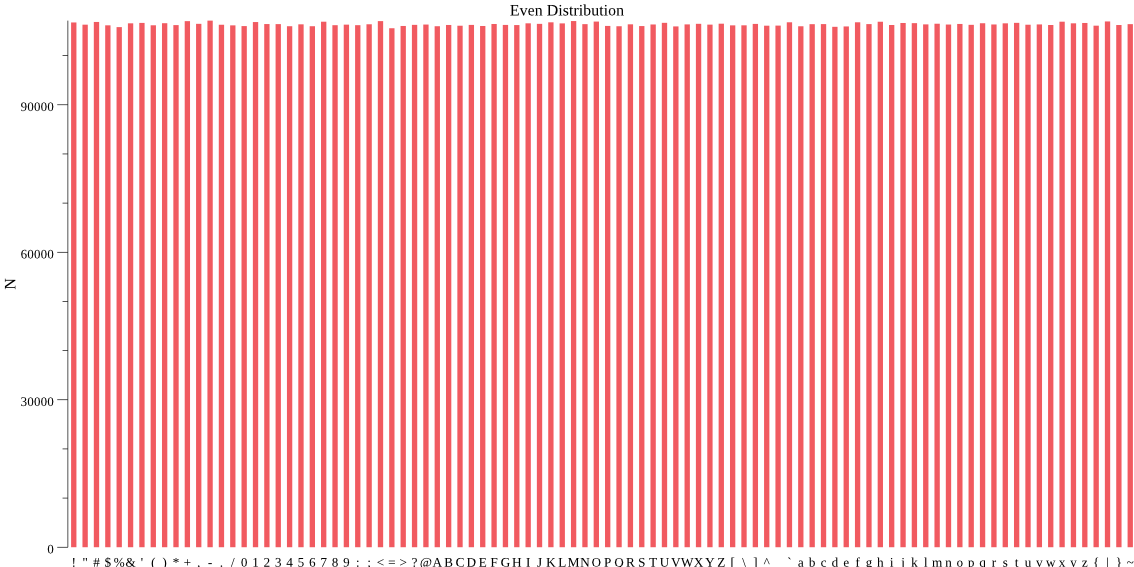
| draw(even, "Even Distribution", "dist-even.png") | |
| fmt.Println("\n\nCalculating uneven distribution of (nearly) random characters…") | |
| uneven := measureDistribution(iterations, GenerateRandomStringUneven) | |
| print(uneven) | |
| draw(uneven, "Uneven Distribution", "dist-uneven.png") | |
| } | |
| func measureDistribution(iterations int, fn generate) map[string]int { | |
| dist := make(map[string]int) | |
| for index := 1; index <= iterations; index++ { | |
| // status output to cli | |
| if index%1000 == 0 { | |
| fmt.Printf("\r%d / %d", index, iterations) | |
| } | |
| raw, err := fn(100) | |
| if err != nil { | |
| panic(err) | |
| } | |
| for _, s := range raw { | |
| c := string(s) | |
| i := dist[c] | |
| dist[c] = i + 1 | |
| } | |
| } | |
| return dist | |
| } | |
| func draw(distribution map[string]int, title, filename string) { | |
| keys, values := orderMap(distribution) | |
| group := plotter.Values{} | |
| for _, v := range values { | |
| group = append(group, float64(v)) | |
| } | |
| p, err := plot.New() | |
| if err != nil { | |
| panic(err) | |
| } | |
| p.Title.Text = title | |
| p.Y.Label.Text = "N" | |
| bars, err := plotter.NewBarChart(group, vg.Points(4)) | |
| if err != nil { | |
| panic(err) | |
| } | |
| bars.LineStyle.Width = vg.Length(0) | |
| bars.Color = plotutil.Color(0) | |
| p.Add(bars) | |
| p.NominalX(keys...) | |
| if err := p.Save(300*vg.Millimeter, 150*vg.Millimeter, filename); err != nil { | |
| panic(err) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| func orderMap(m map[string]int) (keys []string, values []int) { | |
| keys = []string{} | |
| values = []int{} | |
| for k := range m { | |
| keys = append(keys, k) | |
| } | |
| sort.Strings(keys) | |
| for _, key := range keys { | |
| values = append(values, m[key]) | |
| } | |
| return keys, values | |
| } | |
| func print(m map[string]int) { | |
| fmt.Println("\n\nCharacter Distribution") | |
| keys, values := orderMap(m) | |
| for i, key := range keys { | |
| fmt.Println(key, "\t", values[i]) | |
| } | |
| fmt.Println("\nAlphabet:", strings.Join(keys, "")) | |
| } | |
| // lenString returns the amount of valid characters instead of the number of bytes (like len()). | |
| func lenString(s string) int { | |
| return len([]rune(s)) | |
| } |
@fxkr You're totally right! And thank you for absolutely crushing the implementation 😄
I remember searching on the net for random string generation and putting together this example app as a future reminder to myself. Probably as a result of sleep deprivation and/or project deadlines I've screwed up my notes… and did not actually verify my code. Didn't expect for someone to stumble on this code, so devs naturally found/used/forked this. Oh no 😐
I took some time and rewrote this example using a more reliable approach (thanks for the hint).
There is a somewhat nice gist explaining the wrong usage of the output from getrandombytes (targeting nodejs — still the same underlying issue).
I wrote a comparison between the new and the previous approach, creating some graphs on the way, which show the already mentioned unbalanced distribution in the old implementation and an even distribution using the newer implementation.
Remind me to buy you a 🍺, should we ever meet 😄
if n > 32 && n < 127 {
is kind of wasteful, why not
r, _ := rand.Int(rander, big.NewInt(int64(len(letters))))
result = result + string(letters[r])
?
Actually you don't need a big.Int just to generate random numbers between 32 and 126.
You also don't want to pressurize the GC by doing a lot of s += string(i).
Even further, you don't want to do UTF-8 encoding each time by just calling string(i).
This is my implementation:
import "crypto/rand"
func GenerateRandomASCIIString(length int) (string, error) {
result := make([]byte, length)
_, err := rand.Read(result)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
result[i] &= 0x7F
for result[i] < 32 || result[i] == 127 {
_, err = rand.Read(result[i : i+1])
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
result[i] &= 0x7F
}
}
return string(result), nil
}

Disclaimer ahead: don't take my criticism too seriously. Just having fun ;-)
This is not perfect. With len(letters) == 63, 256 % len(letters) != 0 and therefore b%byte(len(letters)) is not evenly distributed. The first four characters, "0"/"1"/"2"/"3", will be a bit more common than the rest. The solution is simple, of course: add exactly one character to letters.
FYI, for arbitrary alphabet lengths, in general the safest way to implement this would be to draw random numbers and discard those that are too large.
edit: Of course, you shouldn't implement that yourself when there's a standard library function that does this for you.
And the GenerateRandomStringURLSafe implementation is just lazy (abusing a convenient encoding function when you could directly generate a string from an appropriate alphabet), inefficient (at least in memory usage per bit of security) and buggy (in the way that one would reasonably expect the result to be a string of length n) and besides redundant (GenerateRandomString already creates an URL-safe password and does a better job at it).
Don't roll your own crypto. That includes generating passwords :-)