These parameters are largely undocumented and unsupported by VMware. Always backup your .vmx files before making changes and test in non-production environments first.
| #!/bin/sh | |
| # The chip info can be found via sensors-detect in lm_sensors | |
| # Driver `to-be-written': | |
| # * ISA bus, address 0xa40 | |
| # Chip `ITE IT8686E Super IO Sensors' (confidence: 9) | |
| # Driver `it87': | |
| # * ISA bus, address 0xa60 | |
| # Chip `ITE IT8792E Super IO Sensors' (confidence: 9) |
Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) is one of the computer memory design methods used in multiprocessor systems, and the time to access the memory varies depending on the relative position between the memory and the processor. In the NUMA architecture, when a processor accesses its local memory, it is faster than when it accesses the remote memory. Remote memory refers to memory that is connected to another processor, and local memory refers to memory that is connected to its own processor. In other words, it is a technology to increase memory access efficiency while using multiple processors on one motherboard. When a specific processor runs out of memory, it monopolizes the bus by itself, so other processors have to play. , and designate 'access only here', and call it a NUMA node.
lspci | grep -i nvidia
01:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation TU106 [GeForce RTX 2060 12GB] (rev a1)- https://ionutbalosin.com/2020/01/hotspot-jvm-performance-tuning-guidelines/
- Which Version of JDK Should I Use? -
whichjdk.com - JDK Distributions -
sdkman.io/jdks https://jdk.dev
As you can see on the AdoptOpenJDK blog
OpenJ9 builds
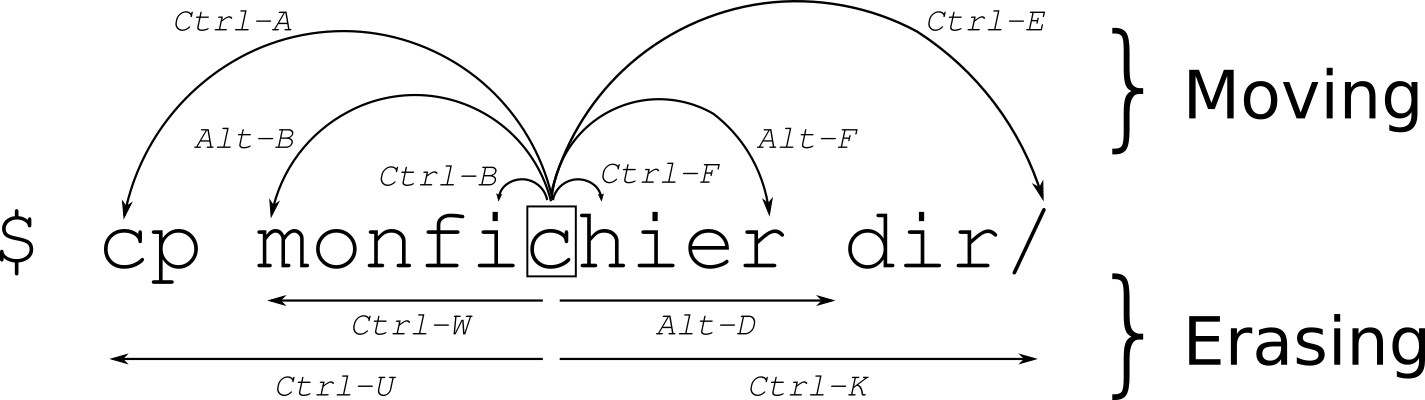
Copied from: Moving efficiently in the CLI
| #!/bin/bash | |
| # ========================================================================= | |
| # Source: https://gist.github.com/lucaspar/27f5e108b80524b315be10b2a9049817 | |
| # ========================================================================= | |
| # This script will compile and install a static FFmpeg build with | |
| # support for NVENC in Ubuntu. Updated for Ubuntu 24.04.2, | |
| # with NVIDIA Drivers v535.183.01 and CUDA v12.2 with a GPU | |
| # with CUDA capability 8.6 (RTX 3080). Set ccap below if using | |
| # a different GPU. | |
| # It assumes NVIDIA drivers are installed and that you have a |
| # /etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.conf | |
| # NVIDIA Linux modprobe.d Configuration | |
| # | |
| # Memory and Performance Enhancements: | |
| # | |
| # - NVreg_UsePageAttributeTable=1 (Default: 0) | |
| # Activates the Page Attribute Table (PAT) for improved memory management. | |
| # PAT creates a partition table at a fixed register-mapped address, potentially enhancing CPU performance. | |
| # |