- What is the purpose of unit testing in JavaScript development? How does it contribute to the overall quality of a software application?
- Explain the difference between manual testing and automated testing. What are the advantages of using automated testing in JavaScript projects?
- What is a test suite, and how does it relate to test cases in JavaScript testing? Provide an example of a test suite and its corresponding test cases.
- Describe the concept of test-driven development (TDD) in JavaScript. How does TDD influence the development process and help in writing robust and reliable code?
- What are the popular testing frameworks and libraries available for JavaScript? Compare and contrast two of them, highlighting their key features and use cases.
-
-
Save halitbatur/5e0f845b8ec30da545ce58b91d46fdb1 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
Omid Kayhani | Houzifa Haboo | Ftma Zehra Aydın | Abdurrahman Abuzaid
-
Unit testing in JavaScript development involves writing and running tests for individual parts of code, like functions or modules. It helps catch bugs early, making it easier to fix them. Unit tests act as documentation, making code easier to understand. They prevent regressions and enable collaboration among developers. Unit tests also support continuous integration and delivery, ensuring code quality and stability. Overall, unit testing contributes to better software quality and maintainability.
-
In manual testing, a human performs the tests step by step, without test scripts. In automated testing, tests are executed automatically via test automation frameworks, along with other tools and software. The biggest pro of automation testing over manual testing is that it allows you to do more testing in less time. It increases productivity and expands how much you can test.
-
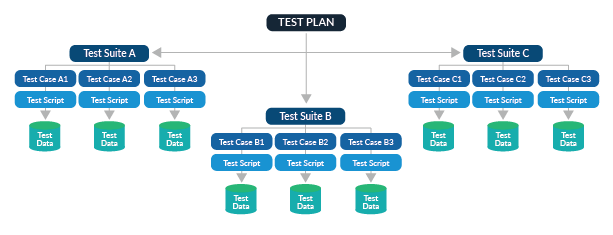
A test suite in JavaScript testing is a collection of related test cases that are grouped together for a specific purpose. It represents a logical unit of testing, such as a module, a class, or a feature of an application. A test suite encompasses multiple test cases that verify different aspects or scenarios of the functionality being tested. For example, a test suite for a JavaScript shopping cart module may include test cases for adding items to or removing them from the cart, calculating the total price, and applying discounts. Each test case within the suite would focus on testing a specific behavior or scenario, such as checking if the correct item is added or removed or verifying the accuracy of the calculated price.
-
Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development approach where tests are written before the code. It follows the "Red-Green-Refactor" cycle: write a failing test, implement code to make it pass, and then refactor the code.
TDD influences the development process by improving code quality, enabling regression testing, guiding code design, facilitating faster debugging, providing confidence in refactoring, promoting collaboration, and acting as executable documentation. It helps in writing robust and reliable JavaScript code by ensuring that code behavior is defined, catching bugs early, and promoting incremental and disciplined development.
- Jest and Mocha are among the most popular testing frameworks in JS.
Jest is a comprehensive testing framework with built-in assertions, mocking, snapshot testing, and code coverage, making it an excellent choice for JavaScript projects, particularly those using React or Vue. On the other hand, Mocha offers more flexibility and customizability, allowing developers to choose their preferred assertion and mocking libraries. It excels in handling asynchronous code and is suitable for a wide range of JavaScript projects, including frontend and backend applications.
Team: @fatimaali200 , @TasneemAkkad, @mohamadAid , Ahmad ramin
1-JavaScript unit testing allows you to test small, self-contained units of JavaScript code, which are part of a web page or web application or to isolate written code to test and determine if it works as intended.Good unit tests create testable code, which improves quality. That code will have fewer defects, which means fewer bug fixes, for faster project completion.
2-In manual testing, a human performs the tests step by step, without test scripts. In automated testing, tests are executed automatically via test automation frameworks, along with other tools and software.
a)Automated Testing Saves Time and Money
b)Vastly Increases Your Test Coverage:Automated software testing can increase the depth and scope of tests to help improve software quality.
3-In software development, a test suite, less commonly known as a validation suite, is a collection of test cases that are intended to be used to test a software program to show that it has some specified set of behaviors.
an ex code of a test suit
const mathFunctions = {
add: (a, b) => a + b,
};
module.exports = mathFunctions;
const mathFunctions = require('./mathFunctions');
describe('Math Functions', () => {
test('Addition', () => {
expect(mathFunctions.add(2, 3)).toBe(5);
expect(mathFunctions.add(-1, 1)).toBe(0);
});
4-Test-driven development (TDD) is a coding practice where you write the result you want your program to produce before creating the program. In other words, TDD requires you to pre-specify the output your intended program must produce to pass the test of functioning the way you envisioned.TDD helps you to develop the logic in your code
For example, here is a possible test suite and its corresponding test cases for testing a function that checks whether a value is an integer number1:
// isInteger.js
module.exports = (value) => !isNaN(parseInt(value, 10));
// isInteger.test.js
const isInteger = require('./isInteger');
describe('isInteger function', () => {
// Test suite for isInteger function
test('should return true for integer numbers', () => {
// Test case for integer numbers
expect(isInteger(42)).toBe(true); // Assertion
expect(isInteger(-5)).toBe(true); // Assertion
});
test('should return false for non-integer numbers', () => {
// Test case for non-integer numbers
expect(isInteger(3.14)).toBe(false); // Assertion
expect(isInteger(NaN)).toBe(false); // Assertion
});
test('should return false for non-numeric values', () => {
// Test case for non-numeric values
expect(isInteger('hello')).toBe(false); // Assertion
expect(isInteger(true)).toBe(false); // Assertion
});
});