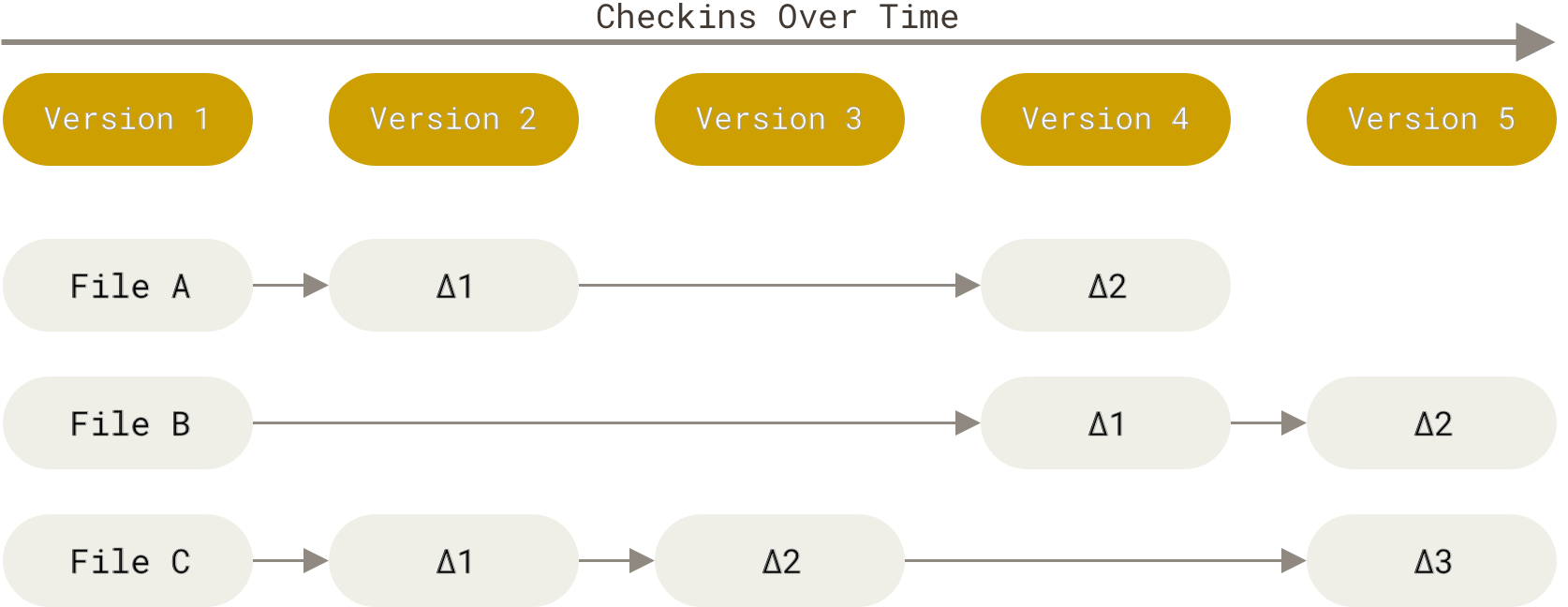
- Traditional VCS, like Subversion, CVS etc. are Centralized VCS based on where they store data
- They are also Delta Version Control Systems (VCS) based on how they store data.
- base version of the file is created when it was added to VCS for tracking
- changes are stored as a list of changes (i.e. diffs or deltas) per tracked file.
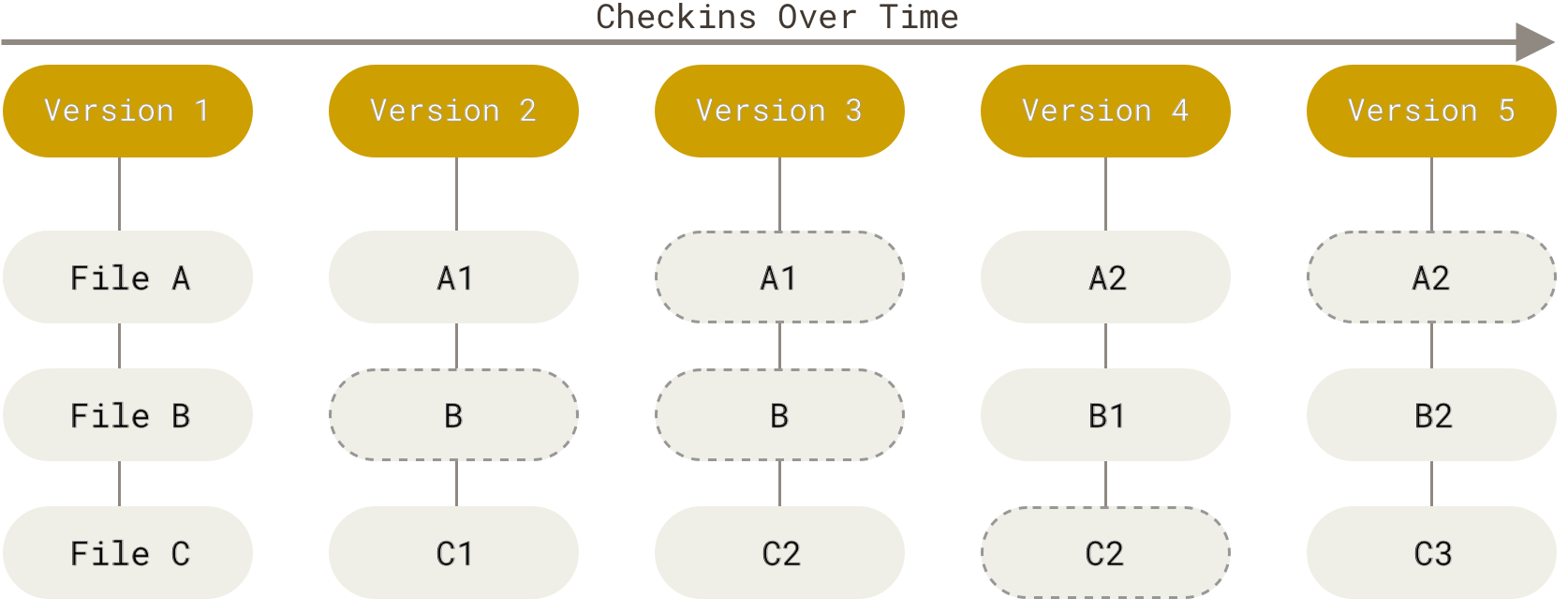
- Git is a Snapshot VCS
- think of the git repository as a miniature file system
- after each commit, i.e. a logical unit of change in 1 or more files, a snapshot of the complete miniature file system is created. The snapshot includes
- the complete file, which changed in that commit
- a link to the file in the previous snapshot, if it did not change.
- thus changes are preserved as series of snapshots and the entire filesystem can be generated for any needed snapshot
- snapshots are checksummed with SHA-1 hash. Any further (unauthorized/backdoored) changes to the snapshot will invalidate the checksum, providing integrity to commits.
-
Local Respository
- hidden .git sub-directory in the directory created when a repository is cloned
- it contains metadata and snapshots for all changes ever committed to the repository
- it also contains details about all branches available locally
-
Working Tree
- A single checkout of one entire snapshot of the directory.
- the snapshot is extracted from the .git director, usually the last snapshot on the checkedout branch.
-
Staging area (also called Index)
- sad
- sdfsdf
- Three States of a file tracked by git - SINGLE MOST IMPORTANT CONCEPT TO UNDERSTAND
- Modified : Tracked file in working directory with changes
.gitignoreand.git/info/excludecan be used to ignore untracked files. If file was ever tracked this method will not work (see below)- Use
.gitignoreto exclude files universally for all contributers. This file is checked into the repo. - Use
.git/info/excludein case a file needs to be excluded only in the local repo of an individul. This is never checked in the repo
- Use
- To ignore tracked files refer to the
git update-indexcommand- The
skip-worktreeandassume-ungangedoptions help in this case--assume-unchangedassumes that a developer shouldn’t change a file. This flag is meant for improving performance for not-changing folders like SDKs.--skip-worktreeis useful when you instruct git not to touch a specific file ever because developers should change it. For example, if the main repository upstream hosts some production-ready configuration files and you don’t want to accidentally commit changes to those files, --skip-worktree is exactly what you want.
- Refer: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13630849/git-difference-between-assume-unchanged-and-skip-worktree
- Refer: https://fallengamer.livejournal.com/93321.html
- The
Rebase helps get updates from the master branch into the feature branch. While starting a new feature development we will create a feature branch from master. Over time master branch will move ahead due to commits from other team members. To get the feature branch updated with the changes (so that we do not have a giant conflict later) we should periodically rebase the feature branch to master.
git checkout master
git pull # get changes from origin to local master
So now our repository will be in the state below
A---B---C feature
/
D---E---F---G master
To rebase
git checkout feature
git rebase master
Will cause the repo to be in
A'--B'--C' topic
/
D---E---F---G maste
# Show local branches, the remote they track and behind/ahead information between the two
git branch -vv
# Nice colored and compact git log
git log --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit
git remote update origin --prune # Will make local branch refs current with remote refs. Remove dangling local refs
git branch -vv # list local branches and corresponding tracked remote branches
git checkout old_name
git branch -m new_name # Rename local branch from old_name -> new_name
git push origin :old_name new_name # deletes old_branch on remote + push the new local branch
git push origin -u new_name # set upstream for the new branchgit checkout local_branch_name # Checkout an existing local branch
git chechout --track origin/remote_branch # Checkout a local branch called remote_name and set corresponding remote branch to track it
- BFG Repo Cleaner Helps clean publich repo if some confidential information is inadvertanatly pushed to origin. Also useful in case very large files are pushed in.