git - 简明指南
一张图看明白Git的四个区五种状态
99%的时间在使用的Git命令
blob object # 数据对象
tree object # 树对象
commit object # 提交对象
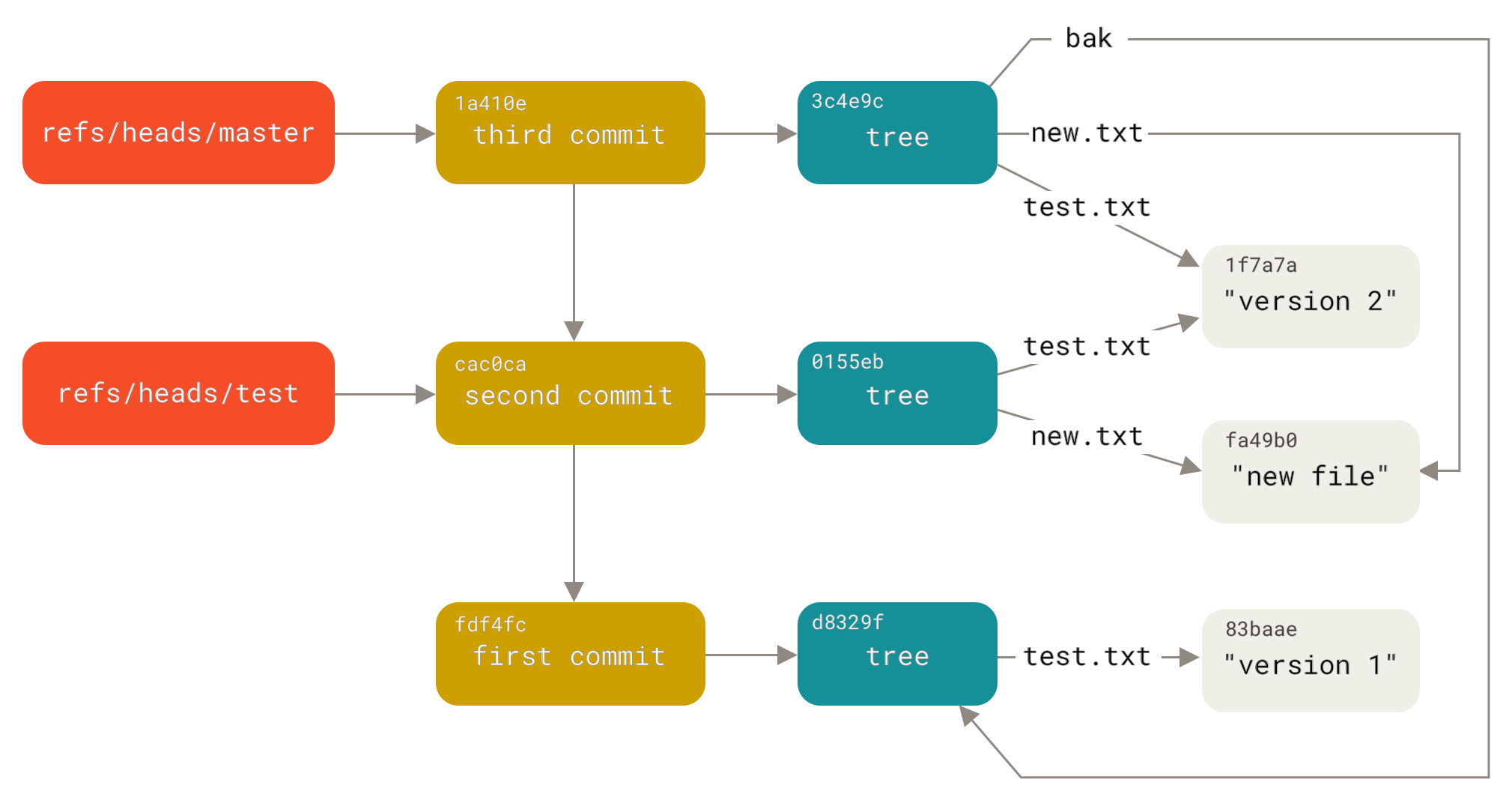
tag object # 标签对象.git/refs/heads/master # 本地master引用,即本地master分支,内容为master分支对应的最后提交的commit对象的SHA-1值
.git/refs/heads/branch # 本地branch引用,即本地branch分支,内容为branch分支对应的最后提交的commit对象的SHA-1值
.git/HEAD # HEAD引用,内容类似于ref: refs/heads/master,指向当前使用的分支
.git/refs/remotes/origin/master # 远程master引用,内容为最近一次与服务器通信时本地远程 master 分支所对应的 SHA-1 值
.git/refs/remotes/origin/HEAD # 远程HEAD引用,内容类似于ref: refs/remotes/origin/masterman git中关于tree-ish和commit-ish等术语的定义
-
tree-ishIndicates a tree, commit or tag object name. A command that takes atree-ishargument ultimately wants to operate on atreeobject but automatically dereferencescommitandtagobjects that point at atree. -
commit-ish
Indicates a commit or tag object name. A command that takes acommit-ishargument ultimately wants to operate on acommitobject but automatically dereferencestagobjects that point at acommit.
更多git术语可以通过git help glossary命令查看
$ git diff # 比较working tree的文件与已暂存(staged)的文件有哪些不同
$ git diff --cached # 比较已暂存的文件(staged)和已提交对象(commit)的文件有哪些不同,不指定commit对象则默认使用HEAD
$ git diff HEAD # 比较working tree和已提交对象(commit)的文件有哪些不同
$ git diff HEAD -- ./test # 只比较working tree中的test文件与已提交对象(commit)中test文件的不同
$ git diff HEAD HEAD^ # 比较最后一次提交对象和它之前一次提交对象的不同$ git show [options] <object>… # <object>可以是blobs,tags,trees和commits
$ git show # 查看$ git log --prety=oneline myfile.txt # 查看myfile.txt的提交历史,并复制<commit object name>。比如92e20281
$ git checkout 92e20281 myfile.txt # 恢复myfile.txt到92e20281的提交版本
$ git checkout master myfile.txt # 恢复myfile.txt到master分支的提交版本
$ git checkout HEAD myfile.txt # 恢复myfile.txt到最新的提交版本
# 如果某个文件正好与分支同名,比如有个文件叫master,对这个文件使用checkout命令时,需要加上[--]选项来区分分支名
$ git checkout master # 切换到master分支
$ git checkout -- master # 恢复工作目录下的master文件到最新的提交版本$ git stash # 工作区修改暂存
$ git pull # 更新分支
$ git stash pop # 暂存修改恢复到工作区$ git remote -v # 查看你已经配置的远程仓库服务器
$ git remote add <remote-name> <url> # 添加远程仓库
$ git fetch [remote-name] # 拉取远程仓库
必须注意 git fetch 命令会将数据拉取到你的本地仓库,它并不会自动合并或修改你当前的工作,你必须手动将其合并入你的工作。
$ git push [remote-name] [branch-name] # 推送到远程仓库
$ git push origin master
$ git remote show origin # 查看远程仓库
$ git remote rename <old-name> <new-name> # 重命名远程仓库
$ git remote rm <remote-name> # 删除远程仓库# 创建新分支hotfix
$ git branch hotfix
$ git checkout hotfix
# 与上面两句等价
$ git checkout -b hotfix
# 将hotfix分支合并到master分支
$ git checkout master
$ git merge hotfix
# 合并后可以将hotfix分支从本地删除
$ git branch -d hotfix远程分支以remote/branch的形式命名
# 列出远程引用
$ git ls-remote [origin]
# 列出远程引用详细信息
$ git remote show [origin]
# 添加一个新的远程引用
$ git remote add teamone https://git.team1.ourcompany.com
# 抓取远程分支
$ git fetch origin
# 将新的远程分支合并到当前分支
$ git merge origin/new-branch
# 或者创建一个跟踪远程分支的本地分支,即跟踪分支(也叫做上游分支)
$ git checkout -b local-branch origin/branch
$ git checkout --track origin/branch
# 设置当前本地分支跟踪到远程分支
$ git branch -u origin/branch
# 查看设置的所有跟踪分支
$ git branch -vv
# 推送到远程分支,形式为本地分支:远程分支
$ git push origin local-branch:remote-branch
# 推送到与本地分支名相同的远程分支,如果没有找到,则创建一个同名远程分支,参考git push --help
$ git push origin local-branch
# 从服务器删除远程分支
$ git push origin --delete remote-branch
# 同上面的命令,删除远程分支
$ git push origin :remote-branch