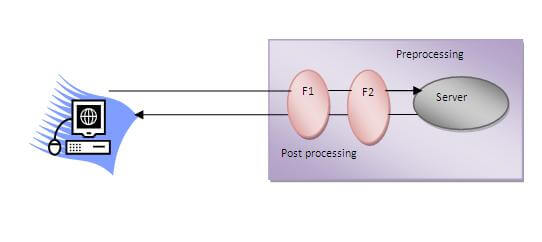
A filter is an object that is invoked at the preprocessing and postprocessing of a request.
- It is mainly used to perform filtering tasks such as conversion, logging, compression, encryption and decryption, input validation etc.
- The servlet filter is pluggable, i.e. its entry is defined in the web.xml file, if we remove the entry of filter from the web.xml file, filter will be removed automatically and we don't need to change the servlet.
- recording all incoming requests
- logs the IP addresses of the computers from which the requests originate
- conversion
- data compression
- encryption and decryption
- input validation etc.
- Filter is pluggable.
- One filter don't have dependency onto another resource.
- Less Maintenance
- Filter
For creating any filter, you must implement the Filter interface. Filter interface provides the life cycle methods for a filter.
- FilterChain
The object of FilterChain is responsible to invoke the next filter or resource in the chain.This object is passed in the doFilter method of Filter interface.
public class MyFilter implements Filter{ public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException {} public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { PrintWriter out=resp.getWriter(); out.print("filter is invoked before"); chain.doFilter(req, resp);//sends request to next resource out.print("filter is invoked after"); } public void destroy() {} } - FilterConfig