Benefit of deploying a Heroku free dyno and using Mongo Atlas for your MongoDB is that you are not required to use a credit card during the sign up. The process of setting up a DB cluster with Mongo Atlas takes a bit longer than it would be if you are using the Heroku's MLab add-on (free sandbox).
This is a life saver as 'd tried a countless times to no avail
npm install -g heroku
heroku --version
# heroku/7.0.0 (darwin-x64) node-v8.0.0
heroku login- Select New >>> Create new app >>> Choose region - Europe >>> Create app.
- After you create the app, you should be redirected to the app's dashboard.
- Select the Deploy section.
While in the server root directory, in the terminal run :
# Commit the most recent work and merge it to the master branch
git add .
git commit -m 'Update xyz.js with new middleware'
git push origin <branch-name>
# Checkout to the master branch
git checkout master
# Add heroku remote
heroku git:remote -a <name-of-the-newly-created-app>
# Check the remotes available
git remote -v
# Make some changes to the code and deploy them to Heroku using Git.
git add .
git commit -m 'Make it better'
git push heroku masterSESSION_SECRET=cookies-and-milk
-
Open your project in the VSCode, and open the terminal.
-
We will work from the root directory of your project.
heroku --versionheroku login# Add heroku remote
heroku git:remote -a <name-of-the-app>
# Check the remotes available
git remote -v
# Make some changes to the code and deploy them to Heroku using Git.
git add .
git commit -m 'Make it better'
git push heroku masterhttps://www.mongodb.com/atlas-signup-from-mlab
- Sign Up for Mongo Atlas - enter the email, password, first name, last nae
- Select >>> Starter Clusters
- In the drop-down Cloud Provider & Region select:
- Europe Region with "FREE TIER AVAILABLE" flag
- In the drop-down "Cluster Tier" make sure to select:
- M2 Sandbox
- Click the button Create Cluster
-
In the sidebar select SECURITY -> Database Access
-
Click on + ADD NEW USER to create a new user
- Select Read and write to any database - User Privileges
- Set the Username and Password
- Create New User
-
In the sidebar select SECURITY -> Network Access
-
Click on + ADD IP ADDRESS
- Click on ALLOW ACCESS FROM ANYWHERE
- Confirm
-
Connect To Your Cluster: Click on the gray button CONNECT
-
Select Connect Your Application option
-
Choose Your driver version: DRIVER: Node.js
-
Copy the Connection String Only
-
-
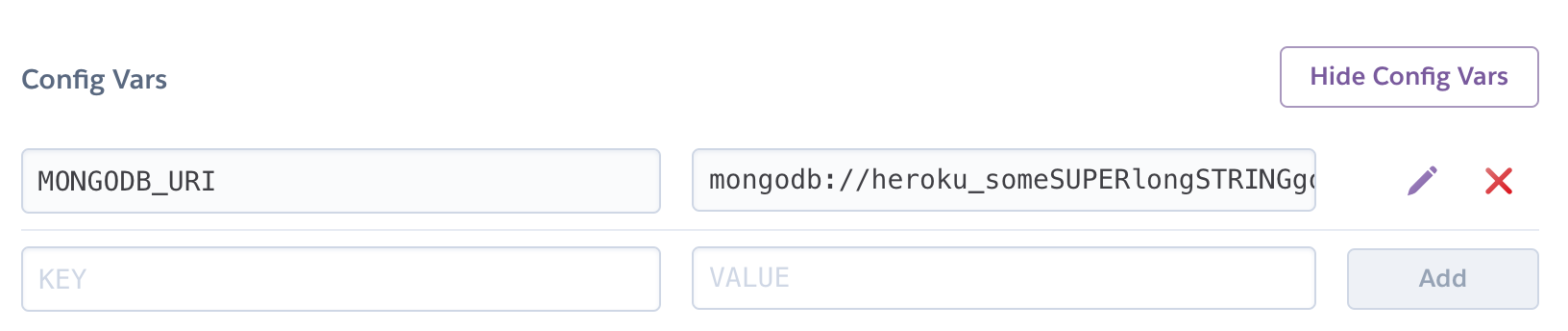
In the Heroku app Dashboard >> Settings:
- Create tne new Config Var KEY - MONGODB_URI
- Set the value to be the previously copied Connection String from Mongo Atlas.
- Remember to add the
<password>to the Connection String you copy/pasted.
-
Update also the
.envfile in your project, which is used for development:-
Change the name from DB_NAME (or whatever you called it) to MONGODB_URI
-
MONGODB_URI value should include the complete URI including the database name, like:
MONGODB_URI=mongodb://localhost:27017/deployment-db-name
-
-
Update the
app.jsandbin/seed.js.
// app.js AND bin/seed.js
// ...
require('dotenv').config(); // <--- ADD
mongoose
.connect(process.env.MONGODB_URI, {useNewUrlParser: true}) // <--- UPDATE
.then((x) => console.log('Connected to the DB', x.connections[0].name))
.catch(err => console.error('Error while trying to connect to MongoDB',err));
// ...
// ...
// ...- Commit the changes and push to remote on GitHub (
origin) and Heroku (heroku)
git add .
git commit -m 'Update .env variables and add MONGODB_URI'
git push origin master
git push heroku masterDouble-check that the config variable process.env.MONGODB_URI is available (set by the same name) in your Heroku app **Settings **:
Heroku app Dashboard >> Settings >> Config Vars >> Reveal Config Vars
node --version"engines": {
"node": "12.x"
}# Make some changes to the code and deploy them to Heroku using Git.
git add .
git commit -m 'Production deployment v1'
git push heroku master
heroku open
heroku logsThe logs command retrieves 100 log lines by default.
You can specify the number of log lines to retrieve (up to a maximum of 1,500 lines) by using the --num (or -n) option.
heroku logs -n 200
heroku logs -t
We can open the terminal instance on the Heroku container (dyno) in order to run custom scripts or see the files included in the instance.
# Open the terminal in the app dyno in Heroku
heroku run bash
# We may then run the seed file
~$~$ node bin/seed.js