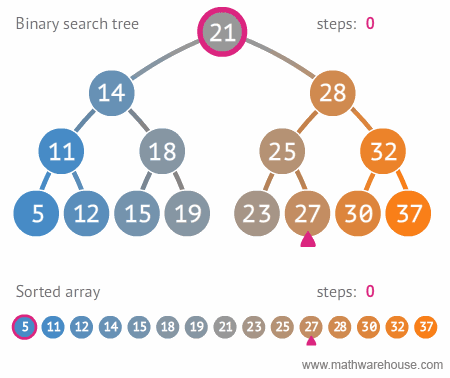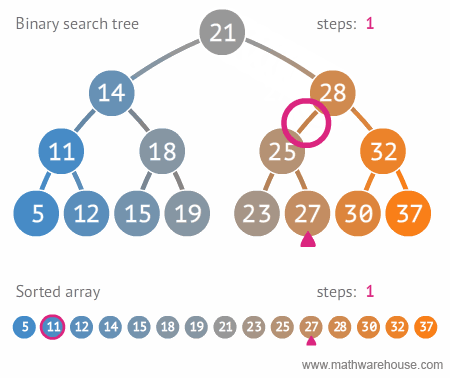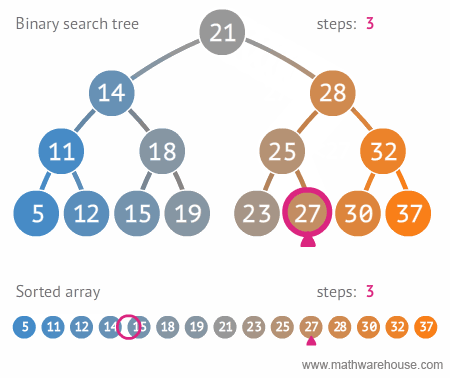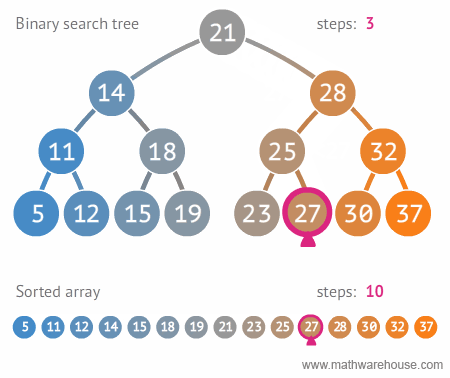
لیست پرداخت
select count(*) from payment
مقدار فروش هر کارمند
select staff_id,sum(amount) as total_amount from payment
group by staff_id
order by total_amount desc
یافتن ده کاربر برتر
table : payment > customer --> find :)
خب برای اینکه بتونیم ده کاربر برتر رو پیدا کنیم چه جوری شروع کنیم ؟
لیست پرداختی ها
select * from payment
در اینجا اگر دقت کنیم دوتا ستون پیدا میکنیم که خیلی به درد میخوره amount,customer_id
select customer_id , sum(amount)
from payment as pay
-- OPPS ://
error : column "pay.customer_id" must appear in the GROUP BY clause or be used in an aggregate function
-- current query
select customer_id , sum(amount)
from payment as pay
group by customer_id
تا اینجا اومدیم ببینم هر کاربر چند بار پرداخت داشته !
select customer_id , sum(amount) as total_amount , count(customer_id) as count_customer
from payment as pay
group by customer_id
حالا ما به ایدی کاربر دسترسی داریم اما کارفرما به گفته ایمیل و اسم کاربر رو به ما بده !
select customer_id , sum(amount) as total_amount , count(customer_id) as count_customer from payment as pay
join customer on customer.customer_id = pay.customer_id
group by customer_id
-- OPPS :/
-- ERROR: column reference "customer_id" is ambiguous
-- currect query :
select customer.customer_id , sum(amount) as total_amount , count(customer.customer_id) as count_customer from payment as pay
join customer on customer.customer_id = pay.customer_id
group by customer.customer_id
مرحله آخر
select customer.*,sum(amount) as total_amount from payment
inner join customer on customer.customer_id = payment.customer_id
group by customer.customer_id
order by total_amount desc
limit 10
خب تو اینجا همه اطلاعات کاربر رو داریم
دیدن این کوئری نیز خالی از لطف نیست
select concat(customer.first_name,' ',customer.last_name), email,sum(amount) as total_amount from payment
inner join customer on customer.customer_id = payment.customer_id
group by customer.customer_id
order by total_amount desc
limit 10
نکته : برای نوشتن کوئری ها بزرگ از کوئری های کوچولو که میشه فهمید استفاده کنید . لطفا از ریختن قیمه داخل ماست خود فرمایید.
پیدا کردن ده ژانر برتر
category > film_category > film > inventory > inventory > rental > customer >payment
خب خب برای اینکه جواب رو بیابیم بیاییم یکم با صورت سوال بازی کنیم مثلا اول ده تا کاربر برتر رو پیدا کنیم بعد که پیدا کردیم ، ده تا فیلم برتر را پیدا کنیم . شخصا وقتی با همچین کوئری هایی روبرو میشم که جوین خورش بالاست یا اینکه محاسبات داره میام ، کوئری کوچولو میکنم که بفهمم چی شد ! تاکید میکنم حواست باشه قیمه نره تو ماستا ، وقتی داده ها خیلی باشه ، این اشتباه ها ممکنه خیلی پیش بیاد که اشتباه محاسباتی پیش بیاد! حالا کی بفهمی و سوتی رو رفع کنی خدا داند .
select * from rental
select * from rental as rent
join inventory as inv on inv.inventory_id = rent.inventory_id
select inv.film_id,sum(amount) from rental as rent
join inventory as inv on inv.inventory_id = rent.inventory_id
join payment as pay on pay.rental_id = rent.rental_id
group by inv.film_id
order by sum(amount) desc
-- OR --
select inv.film_id,sum(amount) as total_amount from rental as rent
join inventory as inv on inv.inventory_id = rent.inventory_id
join payment as pay on pay.rental_id = rent.rental_id
group by inv.film_id
order by total_amount desc -- (desc/asc)
ده فیلم برتر
select inv.film_id,sum(amount) as total_amount from rental as rent
join inventory as inv on inv.inventory_id = rent.inventory_id
join payment as pay on pay.rental_id = rent.rental_id
group by inv.film_id
order by total_amount desc
limit 10
select inv.film_id,sum(amount) as total_amount from rental as rent
join inventory as inv on inv.inventory_id = rent.inventory_id
join payment as pay on pay.rental_id = rent.rental_id
join film_category on film_category.film_id = inv.film_id
group by inv.film_id
order by total_amount desc
limit 10
تازه رسیدیم به آیدی ژانرها!
select inv.film_id,sum(amount) as total_amount from rental as rent
join inventory as inv on inv.inventory_id = rent.inventory_id
join payment as pay on pay.rental_id = rent.rental_id
join film_category on film_category.film_id = inv.film_id
join category on category.category_id = film_category.category_id
group by inv.film_id
order by total_amount desc
limit 10
مرحله آخر یکم تغییرات ریز داریم و تامام
select category.category_id , category.name ,sum(amount) as total_amount from rental as rent
join inventory as inv on inv.inventory_id = rent.inventory_id
join payment as pay on pay.rental_id = rent.rental_id
join film_category on film_category.film_id = inv.film_id
join category on category.category_id = film_category.category_id
group by category.category_id
order by total_amount desc
limit 10
سوال : تعداد اجاره هر دسته را بیابید؟
سوال : میانگین فروش هر دسته ؟
select case
when rental_duration > date_part('day',return_date - rental_date) then 'returned early'
when rental_duration = date_part('day',return_date - rental_date) then 'returned on time'
else 'returned late'
end as status_of_return,
count(*) as total_number_films
from film
inner join inventory on film.film_id = inventory.film_id
inner join rental on inventory.inventory_id = rental.inventory_id
group by 1
order by 2 desc
کوئری بالا رو توضیح بدید ؟
select * from customer where customer.customer_id in (1,2)
select * From customer
where customer.customer_id in (
select customer_id from rental
)
نظرت در موردش چیه ؟
یافتن کاربری که بیشترین پرداخت را داشته است
select first_name , last_name
from customer
where customer_id in (
select customer_id from payment
group by customer_id
having sum(amount)=(
select sum(amount)
from payment
group by customer_id
order by sum(amount) desc limit 1
)
)
کدام فیلم تاکنون اجاره شده است
select title from film
where film_id in (
select distinct film_id from rental
join inventory on rental.inventory_id = inventory.inventory_id
)
select count(title),(select count(*) from film) as all_film
from film
where film_id in (
select distinct film_id from rental
join inventory on rental.inventory_id = inventory.inventory_id
)
result : 985 , 1000
select crental_film/all_film from (
select count(title) as rental_film,(select count(*) from film) as all_film
from film
where film_id in (
select distinct film_id from rental
join inventory on rental.inventory_id = inventory.inventory_id
)
)
-- ERROR: subquery in FROM must have an alias
-- currect query
select rental_film/all_film from (
select count(title) as rental_film,(select count(*) from film) as all_film
from film
where film_id in (
select distinct film_id from rental
join inventory on rental.inventory_id = inventory.inventory_id
)
) as foo
return result : 0
fix :
select rental_film::decimal /all_film from (
select count(title) as rental_film,(select count(*) from film) as all_film
from film
where film_id in (
select distinct film_id from rental
join inventory on rental.inventory_id = inventory.inventory_id
)
) as foo
Find customer first_names that starts with ‘P’ followed by any 5 letters.
select first_name from customer
where first_name similar to 'P[a-z]{5}'
A Postgres view is a virtual table in Postgres. It represents the result of a query to one or more underlying tables in Postgres. Views are used to simplify complex queries since these queries are defined once in the view, and can then be directly queried via the same.
postgres Definition : Instead, the query is run every time the view is referenced in a query. ref
CREATE VIEW sports AS
SELECT film.*
FROM film
join film_category on film_category.film_id = film.film_id
WHERE film_category.category_id = 15; -- sports = 15
run view :
select * from sports
-- OR
select * from sports where film_id = 10
-- OR
select * from sports
join inventory on inventory.film_id = sports.film_id
create [or replace] function function_name(param_list)
returns return_type
language plpgsql
as
$$
declare
-- variable declaration
begin
-- logic
end;
$$
sample : The following statement creates a function that counts the films whose length between the len_from and len_to parameters:
create function get_film_count(len_from int, len_to int)
returns int
language plpgsql
as
$$
declare
film_count integer;
begin
select count(*)
into film_count
from film
where length between len_from and len_to;
return film_count;
end;
$$;
usage :
select get_film_count(40,90);
-- OR --
select get_film_count(
len_from => 40,
len_to => 90
);
-- OR --
-- For backward compatibility postgres support :=
select get_film_count(
len_from := 40,
len_to := 90
);
PL/pgSQL support three parameter modes: in, out, and intout. By default, a parameter takes the in mode. Use the in mode if you want to pass a value to the function. Use the out mode if you want to return a value from a function. Use the inout mode when you want to pass in an initial value, update the value in the function, and return it updated value back.
PL/pgSQL Function Parameter Modes: IN, OUT, INOUT
How to return result of a SELECT inside a function in PostgreSQL?reference
function return id film that less than 11 :
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_object_fields()
RETURNS TABLE (
film_id int) AS
$func$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY
SELECT film_id
FROM film
WHERE film_id <=11;
END
$func$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
select * from get_object_fields();
-- OPPS
-- ERROR : column reference "film_id" is ambiguous
fix bug above function :
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_object_fields()
RETURNS TABLE (
film_id int
) AS
$func$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY
SELECT film.film_id
FROM film
WHERE film.film_id <=11;
END
$func$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
select * from get_object_fields();
function return id and title film that less than 11 :
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_object_fields()
RETURNS TABLE (
film_id int,
title varchar
) AS
$func$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY
SELECT film.film_id,film.title
FROM film
WHERE film.film_id <=11;
END
$func$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
run :
select get_object_fields();
-- OR --
select * from get_object_fields();
DROP FUNCTION get_object_fields();
A PostgreSQL trigger is a function invoked automatically whenever an event such as insert, update, or delete occurs. reference
A trigger function is similar to a regular user-defined function. a trigger function does not take any arguments and has a return value with the type trigger
To create a new trigger in PostgreSQL, you follow these steps:
-
First, create a trigger function using CREATE FUNCTION statement.
-
Second, bind the trigger function to a table by using CREATE TRIGGER statement.
syntax of creating trigger function :
CREATE FUNCTION trigger_function()
RETURNS TRIGGER
LANGUAGE PLPGSQL
AS $$
BEGIN
-- trigger logic
END;
$$
CREATE TRIGGER statement :
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
{BEFORE | AFTER} { event }
ON table_name
[FOR [EACH] { ROW | STATEMENT }]
EXECUTE PROCEDURE trigger_function
- Row-level trigger that is specified by the FOR EACH ROW clause.
- Statement-level trigger that is specified by the FOR EACH STATEMENT clause.
PostgreSQL CREATE TRIGGER example
A simple version of CREATE INDEX statement is as follows:
EXPLAIN ANALYZE select phone from address where phone ='14033335568'
-- result : Seq Scan on address (cost=0.00..15.54 rows=1 width=12) (actual time=0.013..0.069 rows=1 loops=1)
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name [USING method]
(
column_name [ASC | DESC] [NULLS {FIRST | LAST }],
...
);
sample :
CREATE INDEX idx_address_phone
ON address(phone);
EXPLAIN ANALYZE select phone from address where phone ='14033335568'
-- result : Index Only Scan using idx_address_phone on address (cost=0.28..8.29 rows=1 width=12) (actual time=0.056..0.056 rows=1 loops=1)
EXPLAIN ANALYZE select phone from address where phone LIKE '%568'
-- result : Seq Scan on address (cost=0.00..15.54 rows=12 width=12) (actual time=0.016..0.093 rows=4 loops=1)
-- OPPSSS :/
Index Columns for LIKE in PostgreSQL
DROP INDEX idx_address_phone;
question : Multiple indexes vs single index on multiple columns in postgresql
How to use indexes to optimize PostgreSQL queries?
An in-depth look at Database Indexing
first : install this package
pip install psycopg2
sample
import psycopg2
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
database="suppliers", # database name
user="postgres", # database user
password="1234" # database password
)
# create a cursor
cur = conn.cursor()
# execute a statement
print('PostgreSQL database version:')
cur.execute('SELECT version()')
# display the PostgreSQL database server version
db_version = cur.fetchone()
print(db_version)
cur.close()
cursor : Allows Python code to execute PostgreSQL command in a database session. Cursors are created by the connection.cursor() method: they are bound to the connection for the entire lifetime and all the commands are executed in the context of the database session wrapped by the connection. reference
run db.py
import psycopg2
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
database="dvdrental", # database name
user="postgres", # database user
password="1234" # database password
)
# create a cursor
cur = conn.cursor()
# execute a statement
print('PostgreSQL database version:')
cur.execute('SELECT version()')
# display the PostgreSQL database server version
db_version = cur.fetchone()
print(db_version)
# create sample table
table = """ CREATE TABLE parts (
part_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
part_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
)
"""
tb = cur.execute(table)
print(tb)
cur.close()
conn.commit()
important title for psycopg2
-
- fetchone()
- fetchall()
find duplicate row in one table
select insert
- LIKE operator
- %jen%
- %jen
- jen%
What is the difference between a "function" and a "procedure"?
Difference Between Trigger and Procedure
- Trigger and Procedure both perform a specified task on their execution. The fundamental difference between Trigger and Procedure is that the Trigger executes automatically on occurrences of an event whereas, the Procedure is executed when it is explicitly invoked.
more sample query for dvd rental more sample 2
بحث آزاد:
فرض کنید کارفرما ای به شما مراجعه کرده است ! و شما میخواهد برای او یک سایت فروشگاهی بزنید؟ چگونه بحث را شروع کنیم تا بتوانیم ساختار دیتابیس آن را پیاده سازی کنیم
نکته پایانی :بحث پایگاه داده بحثی به شدت گسترده و پیچیده ای می باشد، در این شبه جزوه سعی تا به شما دیدی دهیم که چگونه با مشکلات خود کنار بیایید و بتوانید جواب را پیدا کیند.
موفق و خوشگل باشید :)
author : mh sharifi
last update : 8/19/2022