- to set up FreeBSD by Vagrant on macOS
- to execute provisioning with sudo required
The box of FreeBSD on Vagrant Cloud
% mkdir -p ~/tmp/vagrant-freebsd-test
% cd ~/tmp/vagrant-freebsd-test
% vagrant init freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-STABLE
A `Vagrantfile` has been placed in this directory. You are now
ready to `vagrant up` your first virtual environment! Please read
the comments in the Vagrantfile as well as documentation on
`vagrantup.com` for more information on using Vagrant.
% ls
Vagrantfilethen,
% vagrant up
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Importing base box 'freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-STABLE'...
No base MAC address was specified. This is required for the NAT networking
to work properly (and hence port forwarding, SSH, etc.). Specifying this
MAC address is typically up to the box and box maintainer. Please contact
the relevant person to solve this issue.hmm... :thinking_face:
This problem is referenced from official Vagrantfile
(though even base_mac is copied & pasted)
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.guest = :freebsd
config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", id: "vagrant-root", disabled: true
config.vm.box = "freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-STABLE"
config.ssh.shell = "sh"
config.vm.base_mac = "080027D14C66"
config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb|
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--memory", "1024"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--cpus", "1"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--hwvirtex", "on"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--audio", "none"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--nictype1", "virtio"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--nictype2", "virtio"]
end
end% vagrant up
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Importing base box 'freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-STABLE'...
==> default: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> default: Checking if box 'freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-STABLE' is up to date...
==> default: Setting the name of the VM: vagrant-freebsd-test_default_1509123869695_7924
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
default: Adapter 1: nat
==> default: Forwarding ports...
default: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
==> default: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> default: Booting VM...
==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
default: SSH username: vagrant
default: SSH auth method: private key
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
default: Warning: Connection reset. Retrying...
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
default: Warning: Connection reset. Retrying...
#
# so many times repeated
#
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
default: Warning: Connection reset. Retrying...
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
default: Warning: Connection reset. Retrying...
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
default:
default: Vagrant insecure key detected. Vagrant will automatically replace
default: this with a newly generated keypair for better security.
default:
default: Inserting generated public key within guest...
default: Removing insecure key from the guest if it is present...
default: Key inserted! Disconnecting and reconnecting using new SSH key...
==> default: Machine booted and ready!
==> default: Checking for guest additions in VM...
default: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
default: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
default: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
default: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
default: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
default: your host and reload your VM.
default:
default: Guest Additions Version: 5.2.0
default: VirtualBox Version: 5.1Though there were many retrying for ssh connection, as it says Machine booted and ready!, let's try ssh now.
% vagrant ssh
FreeBSD 10.4-STABLE (GENERIC) #0 r324749: Thu Oct 19 15:55:47 UTC 2017
Welcome to FreeBSD!
Release Notes, Errata: https://www.FreeBSD.org/releases/
Security Advisories: https://www.FreeBSD.org/security/
FreeBSD Handbook: https://www.FreeBSD.org/handbook/
FreeBSD FAQ: https://www.FreeBSD.org/faq/
Questions List: https://lists.FreeBSD.org/mailman/listinfo/freebsd-questions/
FreeBSD Forums: https://forums.FreeBSD.org/
Documents installed with the system are in the /usr/local/share/doc/freebsd/
directory, or can be installed later with: pkg install en-freebsd-doc
For other languages, replace "en" with a language code like de or fr.
Show the version of FreeBSD installed: freebsd-version ; uname -a
Please include that output and any error messages when posting questions.
Introduction to manual pages: man man
FreeBSD directory layout: man hier
Edit /etc/motd to change this login announcement.
"man firewall" will give advice for building a FreeBSD firewall
-- David Scheidt <[email protected]>
vagrant@:~ % uname -a
FreeBSD 10.4-STABLE FreeBSD 10.4-STABLE #0 r324749: Thu Oct 19 15:55:47 UTC 2017 [email protected]:/usr/obj/usr/src/sys/GENERIC amd64
vagrant@:~ %
vagrant@:~ % echo "Hello, FreeBSD!"
Hello, FreeBSD!
vagrant@:~ %It works at least ssh.
Let's destroy, to make it reproducible.
% vagrant destroy
default: Are you sure you want to destroy the 'default' VM? [y/N] y
==> default: Forcing shutdown of VM...
==> default: Destroying VM and associated drives...
% ls
Vagrantfile
%Then, edit Vagrantfile
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.guest = :freebsd
config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", id: "vagrant-root", disabled: true
config.vm.box = "freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-STABLE"
config.ssh.shell = "sh"
config.vm.base_mac = "080027D14C66"
config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb|
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--memory", "1024"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--cpus", "1"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--hwvirtex", "on"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--audio", "none"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--nictype1", "virtio"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--nictype2", "virtio"]
end
+
+ config.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo hello"
+
endlike this, and
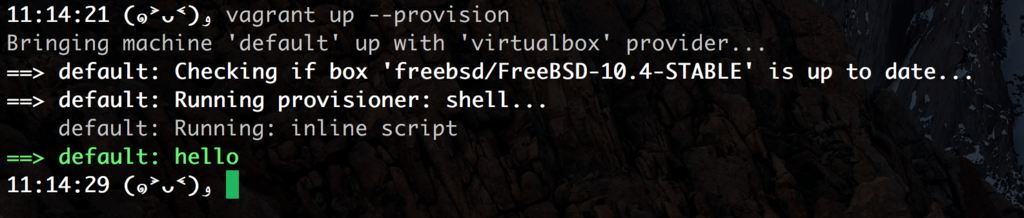
% vagrant up
# tl;dr
==> default: Running provisioner: shell...
default: Running: inline script
The SSH command responded with a non-zero exit status. Vagrant
assumes that this means the command failed. The output for this command
should be in the log above. Please read the output to determine what
went wrong.
%Vagrant assumes that this means the command failed.
I can't believe echo failed.
% vagrant ssh --command "echo hgoeeee"
hgoeeee
Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed.
%It's not because of echo itself.
To get debug logs,
% vagrant destroy -f && vagrant up --debug
Followings are some parts of debug logs.
DEBUG virtualbox_5_1: - [1, "ssh", 2222, 22, "127.0.0.1"]
DEBUG ssh: Checking key permissions: /Users/otiai10/tmp/vagrant-freebsd-test/.vagrant/machines/default/virtualbox/private_key
DEBUG ssh: Re-using SSH connection.
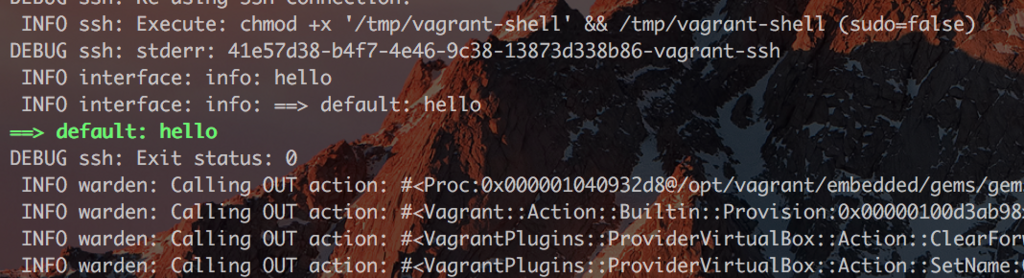
INFO ssh: Execute: chown -R vagrant /tmp/vagrant-shell (sudo=true)
DEBUG ssh: stderr: Segmentation fault
DEBUG ssh: Exit status: 139
DEBUG ssh: Uploading: /var/folders/__/xxcbtw6j0tb681fjv1lbnlg40000gn/T/vagrant-shell20171028-68133-1nvns04.ps1 to /tmp/vagrant-shell
DEBUG ssh: Re-using SSH connection.
INFO interface: detail: Running: inline script
INFO interface: detail: default: Running: inline script
default: Running: inline script
DEBUG ssh: Re-using SSH connection.
INFO ssh: Execute: chmod +x '/tmp/vagrant-shell' && /tmp/vagrant-shell (sudo=true)
DEBUG ssh: stderr: Segmentation fault
DEBUG ssh: Exit status: 139
Segmentation fault
humm...
- https://forums.freebsd.org/threads/62311/
- it's kind of a problem of sudo?
Let's try sudo=false in Vagrantfile
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--nictype2", "virtio"]
end
- config.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo hello"
+ config.vm.provision "shell", inline: "echo hello", privileged: false
endand
% vagrant destroy -f && vagrant up --debugthen,
It is clear that this is because sudo privilege.
Read carefully
- https://forums.freebsd.org/threads/62311/
- https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/vagrantfile/ssh_settings.html
Seems like sudo will segfault on official FreeBSD STABLE (but not RELEASE) Vagrant boxes if a hostname isn't set. Problem is Vagrant uses sudo to set any hostname specified in the Vagrantfile or run any shell commands.
Setting it manually worked for me:
ah-han?
% vagrant ssh
vagrant@:~ % su
root@:/home/vagrant # sysrc hostname=myhost.local (modifies rc.conf)
root@:/home/vagrant # halt -p
% vagrant up --provisionIt works, but I don't wanna vagrant ssh, you know. It's not "automated".
Seems like sudo will segfault on official FreeBSD STABLE (but not RELEASE) Vagrant boxes if a hostname isn't set.
Really? I'll try -RELEASE.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.guest = :freebsd
config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", id: "vagrant-root", disabled: true
- config.vm.box = "freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-STABLE"
+ config.vm.box = "freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-RELEASE"
config.ssh.shell = "sh"
config.vm.base_mac = "080027D14C66"and
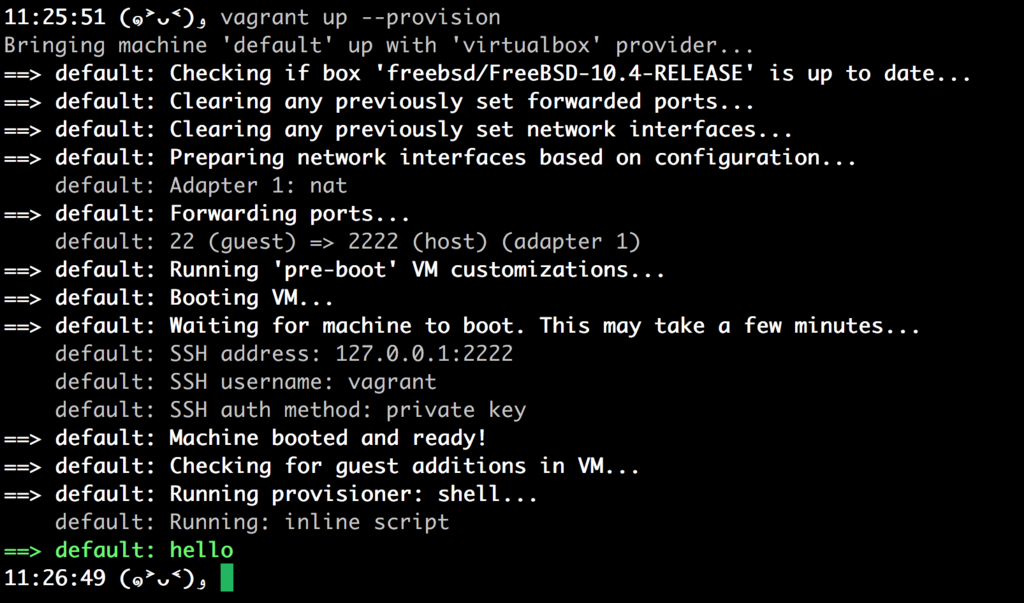
% vagrant destroy -f && vagrant upDEBUG virtualbox_5_1: - [1, "ssh", 2222, 22, "127.0.0.1"]
DEBUG ssh: Checking key permissions: /Users/otiai10/tmp/vagrant-freebsd-test/.vagrant/machines/default/virtualbox/private_key
DEBUG ssh: Re-using SSH connection.
INFO ssh: Execute: chown -R vagrant /tmp/vagrant-shell (sudo=true)
DEBUG ssh: stderr: Segmentation fault
DEBUG ssh: Exit status: 139
DEBUG ssh: Uploading: /var/folders/__/xxcbtw6j0tb681fjv1lbnlg40000gn/T/vagrant-shell20171028-72476-1wwln9a.ps1 to /tmp/vagrant-shell
DEBUG ssh: Re-using SSH connection.
INFO interface: detail: Running: inline script
INFO interface: detail: default: Running: inline script
default: Running: inline script
DEBUG ssh: Re-using SSH connection.
INFO ssh: Execute: chmod +x '/tmp/vagrant-shell' && /tmp/vagrant-shell (sudo=true)
DEBUG ssh: stderr: Segmentation fault
the same segmentation fault. To make it sure, try the same way in which it worked before: ssh and set hostname manually.
% vagrant ssh
vagrant@:~ % su
root@:/home/vagrant # sysrc hostname=testtest.local
root@:/home/vagrant # halt -p
Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed by remote host.
Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed.
% vagrant up --provisionOh... it works perfectly.
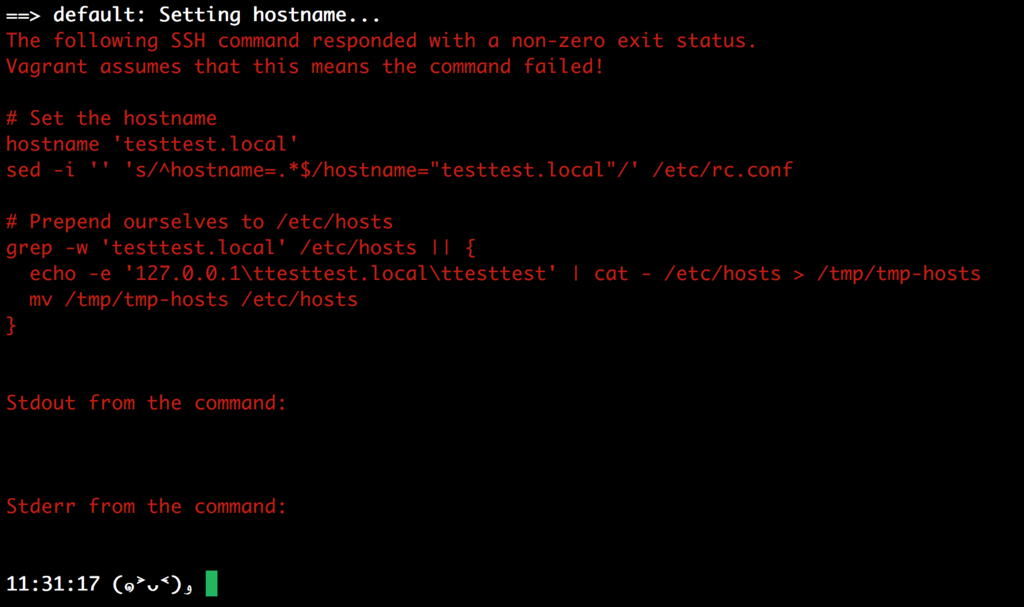
Is it possible to set hostname in Vagrantfile?
config.vm.hostname - The hostname the machine should have. Defaults to nil. If nil, Vagrant will not manage the hostname. If set to a string, the hostname will be set on boot.
great
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.guest = :freebsd
config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", id: "vagrant-root", disabled: true
config.vm.box = "freebsd/FreeBSD-10.4-RELEASE"
config.ssh.shell = "sh"
config.vm.base_mac = "080027D14C66"
+
+ config.vm.hostname = "testtest.local"
+then...
I can get the same segmentation fault error.
- when it tries
sudo, it causessegmentation fault - it can be solved by entering with ssh and set
hostnamemanually - it's 100% reproducible