- Starter Repositories
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
- Reverse Proxy
- Password encryption using Bcrypt
- Frontend > https://github.com/cpe207-2568/lecture19-2568-frontend-starter
- Backend > https://github.com/cpe207-2568/lecture19-2568-backend-starter
- Many web applications rely on 3rd-party resources from different
domains- APIs, fonts, data or videos
- Imagine that a web page from
https://www.domain1.comuses JavaScript to fetch data fromhttps://api.weather.com.- By default, the
api.weather.comserver does not allow requests from differntoriginorport
- By default, the
CORSallows your application to safely access resources on different domain- The
api.weather.comserver checks itsCORSconfiguration ifhttps://www.domain1.comis allowed. - Prevent malicious websites from sending requests to other sites without permission
- The
- Enables secure cross-domain data transfers by having the server explicitly permit requests
Install the cores package
pnpm install cores
pnpm install -D @types/coresImport and use cors middleware
import express from 'express';
import cors from 'cors';
const app = express();
// Enable CORS for all origins
app.use(cors());
// Your routes and other middleware go here
app.get('/api/data', (req, res) => {
res.json({ message: 'This is CORS-enabled for all origins!' });
});
const PORT = 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});In a production environment, it is best practice to restrict CORS to only the specific orgins.
We can achieve this by passing and options object with whitelist or origin property.
import cors from 'cors';
const allowedOrigins = ['http://localhost:3000', 'https://your-frontend-domain.com'];
const corsOptions: cors.CorsOptions = {
origin: allowedOrigins
};
app.use(cors(corsOptions));
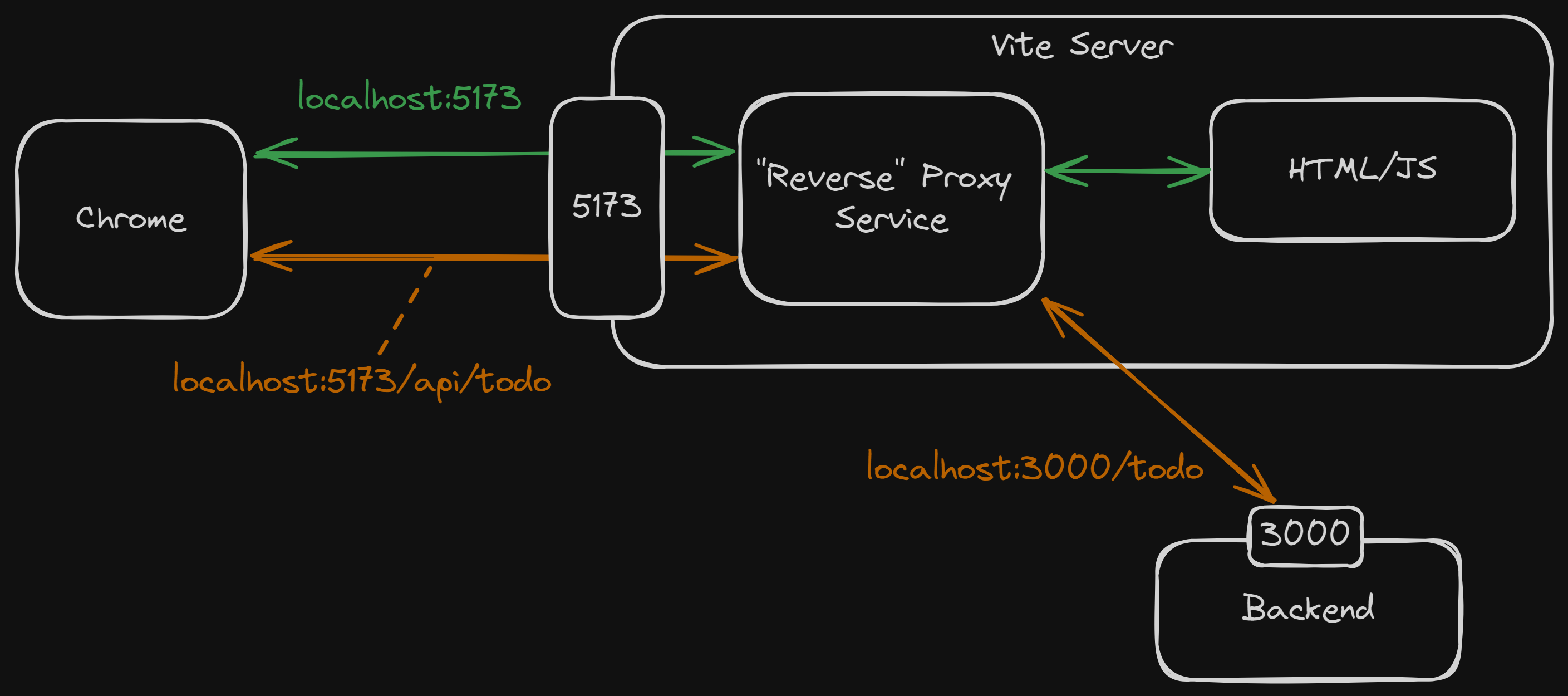
...- An intermediary server that sits in front of one or more web (frontend or backend) servers.
- Intercepting client requests and forwarding them to the appropriate server.
- Enahnce security by hinding the identity of backend servers.
- Vite has a built-in revere proxy functionality.
- For an API service which are not designed to serves other external applications.
Open vite.config.js located in the root of your Vite project. Add server.proxy configuration. For example,
// vite.config.js
import { defineConfig } from 'vite';
import react from '@vitejs/plugin-react';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [react()],
server: {
proxy: {
// Proxying API requests
'/api': {
target: 'http://localhost:3000', // Your backend server address
changeOrigin: true, // Changes the origin of the host header to the target URL
rewrite: (path) => path.replace(/^\/api/, ''), // Rewrites the path by removing '/api'
},
// You can add more proxy rules for other paths
'/auth': {
target: 'http://localhost:3001',
changeOrigin: true,
},
},
},
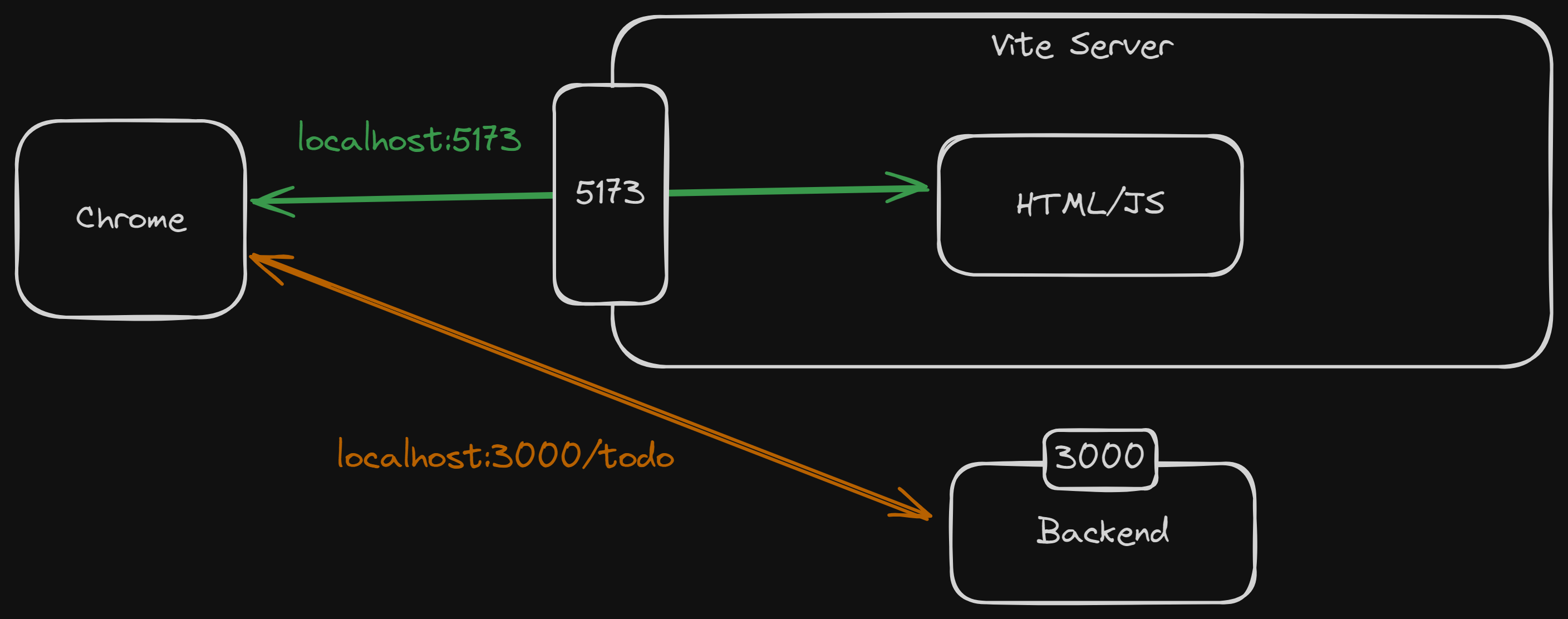
});- A frontend web application make an API request to the URL
http://localhost:5173/api/v2/users. - Vite's reverse proxy take a look at the request found that there is
/apiin the URL. - Vite's reverse proxy then forwards the request to the URL
http://localhost:3000/v2/users.
- Note that the
/apiwas removed from the URL.
- A frontend web application make an API request to the URL
http://localhost:5173/auth/login. - Vite's reverse proxy take a look at the request found that there is
/authin the URL. - Vite's reverse proxy then forwards the request to the URL
http://localhost:3001/auth/login.
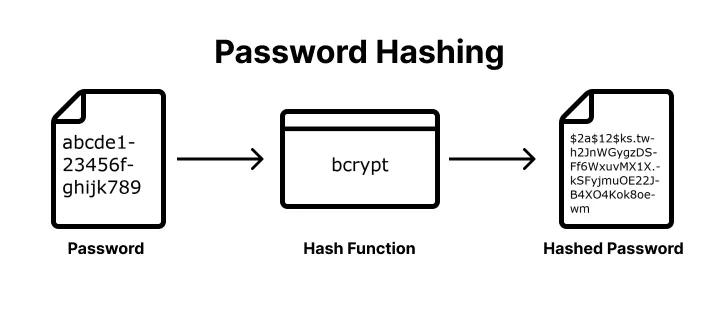
- Bcrypt is an adaptive
password-hashing functionHashingconverts input text into a unique fixed-length string (138-bit) that cannot be reversedSalting, a unique random string (128-bit) is attached each string before hashing to protect against rainbow table attack- The higher adaptive
costparameter makes the process more computationally intensive and slow
- Securely scrambles a plaintext password into unreadable string that is resistant to
brute-forceandrainbow tableattacks
Install the bcrypt package
pnpm install bcrypt
pnpm install -D @types/bcryptWe can now use bcrypt to a hashed password when a user create a new password.
Create the hashPassword() function in src/utils/hash.ts file with the following code.
import Debug from "debug";
import bcrypt from "bcrypt";
const debug = Debug("app:hash");
export const hashPassword = async (plainPassword: string, saltRounds: number): Promise<string> => {
// const salt = await bcrypt.genSalt(saltRounds);
// const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(plainPassword, salt);
const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(plainPassword, saltRounds);
return hashedPassword;
};
async function main() {
for (let i = 1; i < 16; i++) {
const hashedPassword = await hashPassword("1234", i);
debug(`saltRounds=${i}, hash=${hashedPassword}`);
}
}
main();Next, create the comparePassword() function in src/utils/compare.ts file with the following code.
import Debug from "debug";
import bcrypt from "bcrypt";
const debug = Debug("app:compare");
export const comparePassword = async (password: string, hash: string): Promise<boolean> => {
const isMatch = await bcrypt.compare(password, hash);
return isMatch;
};
const hashes = [
"$2b$04$eTJZhao.xVbwO0Nk6r0QR.rXidUh6Q7VQyOXEfOiI.f.1kWKr5GE.",
"$2b$04$F0diMVVp8QayoVYbpAvlDulU7YHNtkD8Uj11zX3kRfcSYQXkf3g0C",
"$2b$04$x/qMWRLQC7ZkLaIS81haw.6cP8hhipS1bFcs6BVP90NEUSkb1wl2a",
"$2b$04$QfAO3rT.rpLg5rMLpVBqgedjekS.GLhT6Sp610myj0SEZLOOE0tj6",
"$2b$05$427rfEYlN/76vMjck5n2bOUOM1rzL/FyIzn26PvyCxhsSE62fX.5G",
"$2b$06$7tlphrVyFNgZv11q5zF2pexp7DReAnISEVGzN3ZLw/u.sCMiHuJcS",
"$2b$07$i6EGvfaYbWBeecVya0bTK.7hOwy3kwMDiG1Ro4Eu362z7/z3L39sW",
"$2b$08$X1HV7IRxckH.RgqG1jjIYOsRyCQMUiLoawaBfb05uzwQVDgwBVMX2",
"$2b$09$8RTZjy80LBgrU0i4VRdGbuQQjleozkb7W47K7fqt64m9uM4PktRhS",
"$2b$10$BuyRls5Tgok0JVFsPZiTU./TUrcGM3jHkTkf.3/Y.5ecY6d/NIJ8a",
"$2b$11$Cqs1JJ660dzqgipEapnjF.gBeF2b9ONEDV3tyun2Rk/myW8K/yl3.",
"$2b$12$zXDDP70MIfSsw9HysFcV9uj78i5pK6zWfFTPCvrEC4DBlKqeARh76",
"$2b$13$dmzM28M74S8WlE9kzCrkWO5x9.M9YoXCAKBxHZvnZtvCPv2s99H9K",
"$2b$14$GAdDkSvWT.sW4cgMNA5sd.npyWE5s8doMNS2lB4VxVtjJ6V3.4CYu",
"$2b$15$iZTgg3w.dsuotW4JYTB3S.XhnOWzKPnOOW0NJVWs0nqAYidulJ5Ge",
];
async function main() {
for (let hash of hashes) {
const isMatch = await comparePassword("1234", hash);
debug(isMatch);
}
}
main();Enable DEBUG information to print in console:
// For PowerShell
$env:DEBUG = "*"
// For macOS
export DEBUG="*"Now you can test the bcrypt hash and compare function with following commands.
npx tsx src/utils/hash.ts
npx tsx src/utils/compare.ts