Word Blanks
You will need to use string operators to build a new string, result,
using the parameters: myNoun, myAdjective, myVerb, and myAdverb.
Parameters are variables that represent the values that get passed into your function from the function call.
Notice how the variables level and score in the function definition addScore are called parameters.
However, when we invoke the function like in:
addScore(3, 10) or addScore(6, 20)
the values are called arguments. Here is an important lesson:
You define a function with parameters, you call a function with arguments.
Another example of this:
function hello(fName, uName) {
return "Hello " + fName + " " + uName + ", How is your day?";
}
hello("Joseph", "@revisualize"); // "Hello Joseph @revisualize, How is your day?"
hello("Bella", "@bellaknoti"); // "Hello Bella @bellaknoti, How is your day?"
hello("Andy", "@dirn"); // "Hello Andy @dirn, How is your day?"You can use the fName and uName parameters just like a variable inside of your function.
Other important things to remember:
A function can have zero parameters. You still have to use the parentheses to define it.
A function might have no return statements. In this case we say that the function returns undefined.
When you have the function declaration of:
function wordBlanks(myNoun, myAdjective, myVerb, myAdverb) { }and you make the function call of:
wordBlanks("dog", "big", "ran", "quickly");
The parameter myNoun gets the first argument from the function call of a string "dog"
The parameter myAdjective gets the second argument from the function call of a string "big"
The parameter myVerb gets the third argument from the function call of a string "ran"
The parameter myAdverb gets the second argument from the function call of a string "quickly"
Parameters are treated like variables that represent the values that get passed into your function from the function call (arguments).
You will need to use string operators to build a new string, result,
using the parameters: myNoun, myAdjective, myVerb, and myAdverb.
You will also need to use additional strings, which will not change,
and must be in between all of the provided words.
The output should be a complete sentence.
Hint: Concatenating Strings with Plus Operator https://www.freecodecamp.com/challenges/concatenating-strings-with-plus-operator Concatenating Strings with the Plus Equals Operator https://www.freecodecamp.com/challenges/concatenating-strings-with-the-plus-equals-operator
function wordBlanks(myNoun, myAdjective, myVerb, myAdverb) {
var result = "";
// Your code below this line
// Your code above this line
return result;
}
// Change the words here to test your function
wordBlanks("dog", "big", "ran", "quickly");
// should contain all of the passed in words separated by non-word characters (and any additional words in your madlib).
wordBlanks("cat", "little", "hit", "slowly");
// should contain all of the passed in words separated by non-word characters (and any additional words in your madlib).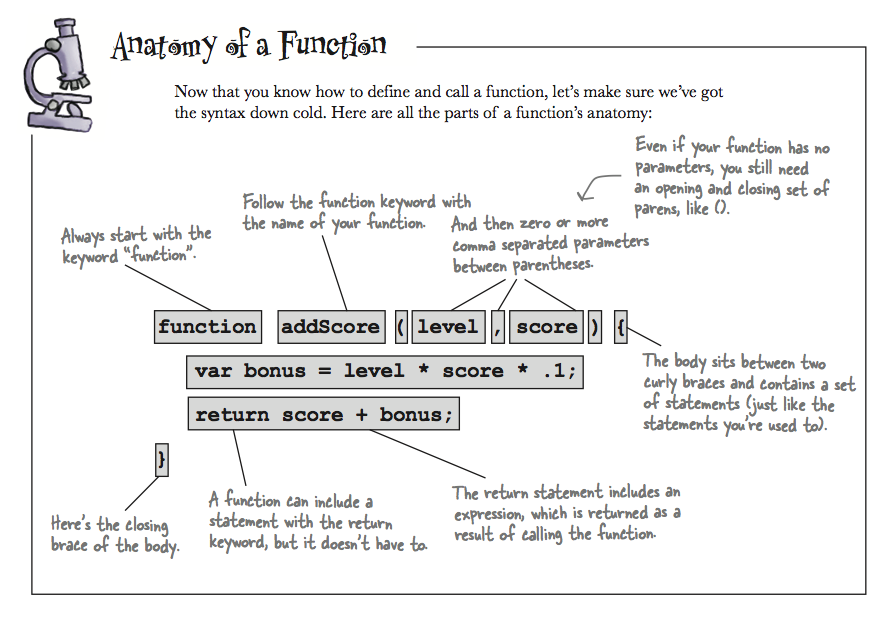
Parameters are values that get passed into your function from the function call.
https://cs.wellesley.edu/~cs110/lectures/L16/images/function-anatomy.png
Notice how the variables
levelandscorein the function definitionaddScoreare called parameters.However, when we invoke the function like in:
addScore(3, 10)oraddScore(6, 20)the values are called arguments. Here is an important lesson:
You define a function with parameters, you call a function with arguments.
Another example of this:
You can use the
fNameanduNameparameters just like a variable inside of your function.Other important things to remember:
* A function can have zero parameters. You still have to use the parentheses to define it.
* A function might have no return statements. In this case we say that the function returns undefined.