https://plantuml.com/ko/sitemap-language-specification
Gang of Four(Java Design Pattern)
Deatils
- Creational
- Structural
- Adapter
- Bridge
- Decorator (Wrapper)
- Filter
- Composite
- Facade
- Proxy
- Flyweight (Cache)
- Behavioral
- J2EE
- MVC
- Business Delegate
- Composite Entity
- Data Access Object (DAO)
- Front Controller
- Intercepting Filter
- Service Locator
- Transfer Object
Deatils
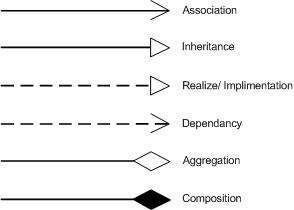
- Dependency
- Association
- Aggregation (Shared Aggregation)
- Composition
- Inheritance (Generalization)
http://butunclebob.com/ArticleS.UncleBob.PrinciplesOfOod
Deatils
- Single Responsibility Principle (단일 책임 원칙)
모든 클래스는 하나의 책임만 가지며, 클래스는 그 책임을 완전히 캡슐화해야 함
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EB%8B%A8%EC%9D%BC_%EC%B1%85%EC%9E%84_%EC%9B%90%EC%B9%99
- Open Closed Principle (개방 폐쇄 원칙)
소프트웨어 개체(클래스, 모듈, 함수 등등)는 확장에 대해 열려 있어야 하고, 수정에 대해서는 닫혀 있어야 한다.
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EA%B0%9C%EB%B0%A9-%ED%8F%90%EC%87%84_%EC%9B%90%EC%B9%99
- Liskov Substitution Principle (리스코프 치환 법칙)
q(x)를 자료형 T의 객체 x에 대해 증명할 수 있는 속성이라 하자. 그렇다면 S가 T의 하위형이라면 q(y)는 자료형 S의 객체 y에 대해 증명할 수 있어야 한다.
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EB%A6%AC%EC%8A%A4%EC%BD%94%ED%94%84_%EC%B9%98%ED%99%98_%EC%9B%90%EC%B9%99
- Interface Segregation Principle (인터페이스 분리 원칙)
클라이언트가 자신이 이용하지 않는 메서드에 의존하지 않아야 한다는 원칙.
인터페이스 분리 원칙은 큰 덩어리의 인터페이스들을 구체적이고 작은 단위들로 분리시킴으로써 클라이언트들이 꼭 필요한 메서드들만 이용할 수 있게 한다.
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%9D%B8%ED%84%B0%ED%8E%98%EC%9D%B4%EC%8A%A4_%EB%B6%84%EB%A6%AC_%EC%9B%90%EC%B9%99
- Dependency Inversion Principle (의존관계 역전 원칙)
첫째, 상위 모듈은 하위 모듈에 의존해서는 안된다. 상위 모듈과 하위 모듈 모두 추상화에 의존해야 한다.
둘째, 추상화는 세부 사항에 의존해서는 안된다. 세부사항이 추상화에 의존해야 한다.
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%9D%98%EC%A1%B4%EA%B4%80%EA%B3%84_%EC%97%AD%EC%A0%84_%EC%9B%90%EC%B9%99
Deatils
- Information Expert
- Creator
- Controller
- Low Coupling (Loose Coupling)
- High Cohesion
- Polymorphism
- Pure Fabrication
- Indirection
- Protected Variations
Deatils
- DRY Principle
Don't Repeat Yourself
- KISS Principle
Keep It Simple and Stupid
- YAGNI Principle
You Ain't Gonna Need It!
강한 응집력, 약한 결합력
Deatils
- UseCase Diagram
- Actor
- UseCase
- Class Diagram
- Class
- Attribute (= visibility attributeName : Type [multiplicity] = DefaultValue {property string})
- Operation (= visibility opertaionName (parameterName : Type) : ReturnType {property string})
- Class Relationship (#class-relationships)
- Sequence Diagram
- Lifeline
- Message (= "return = message (parameter: paremeterType) : returnType")
- Asynchronous Message
- Synchronous Message
- Response Message
- Found Message
- Lost Message
- Combined Fragments (alt, opt, loop, break, ...)
- Interaction Reference
- Activity Diagram
- Activity
- Controll Flow(Transition)
- Initial
- Final
- Decision Point
- Merge Point
- Fork Point
- Join Point
- Swinlanes
- Statechart Diagram
- State (= Entry Activity, Exit Activity, Do Activity)
- Transition (= Event[Guard]/Activity)
- Initial State
- Final State
- Composite State
- Orhtogonal State
- Shallow History State
- Deep History State
- Component Diagram
Deatils
- Waterfall Process (폭포수 프로세스)
- Spiral Process (나선형 프로세스)
- UP (Unified Process)
- Inception
- Elaboration
- Construction
- Transition
- Agile Process
https://mingrammer.com/translation-10-common-software-architectural-patterns-in-a-nutshell/
Deatils
- 계층화 패턴 (Layered pattern)
- 클라이언트-서버 패턴 (Client-server pattern)
- 마스터-슬레이브 패턴 (Master-slave pattern)
- 파이프-필터 패턴 (Pipe-filter pattern)
- 브로커 패턴 (Broker pattern, Publisher-Subscriber)
- 피어 투 피어 패턴 (Peer-to-peer pattern)
- 이벤트-버스 패턴 (Event-bus pattern)
- 모델-뷰-컨트롤러 패턴 (Model-view-controller pattern)
- 블랙보드 패턴 (Blackboard pattern)
- 인터프리터 패턴 (Interpreter pattern)
- Sonar
- Findbugs
- PMD
- Structure101
Deatils
- Logical View
- Process View
- Development View
- Physical View
- UseCase View
-
Module View
Decomposition, Class, Layered
- Class Diagram
-
Runtime View
C&C View : Component & Connector View
- Component Diagram
-
Allocation View
- Deployment Diagram
https://www.uml-diagrams.org/component-diagrams-reference.html
https://www.uml-diagrams.org/composite-structure-diagrams/connector.html
Deatils
An assembly connector is a connector between two or more parts or ports on parts that defines that one or more parts provide the services that other parts use.
A delegation connector is a connector that links the external contract of a component (as specified by its ports) to the realization of that behavior. It represents the forwarding of events (operation requests and events): a signal that arrives at a port that has a delegation connector to one or more parts or ports on parts will be passed on to those targets for handling.
A delegation connector is a declaration that behavior that is available on a component instance is not actually realized by that component itself, but by one or more instances that have “compatible” capabilities. These situations are modeled through a delegation connector from a Port to compatible Ports or Parts.