About this codelab
- Last updated 6月 18, 2020
- Written by Hoi Lam (revamping author), Yash Katariya (original author)
このベータ版コードラボではTensorFlow Lite Model MakerとAndroid Studio 4.1 Beta 1以降を使った最新のツールを紹介します。また動作を確認するのに物理的なAndroid端末が必要になります。安定版のコードラボを試したい場合はこちらを参照ください。
TensorFlowは多目的機械学習フレームワークです。クラウド内で複数のクラスタをまたがった巨大なモデルの訓練からスマートフォンのような組み込みシステムでのローカルなモデルの実行まで、幅広い用途に使用することができます。
このコードラボでは、TensorFlow Liteを使ってAndroid端末で画像認識モデルを実行します。
- TensorFlow Lite Model Makerを使用したカスタム画像分類器の訓練方法
- Android StudioでTensorFlow Liteモデルをインポートし、CameraXを使用してカスタムモデルをAndroidアプリに導入する方法
- スマートフォンでGPUを使用してモデルを高速化する方法
TensorFlowの画像分類プログラムを実行して花を分類する簡単なカメラアプリを作ります。
Colabを開いてみましょう。TensorFlow Lite transfer learningを使って、Kerasで分類器を訓練して花を認識する方法を確認します。
先に進む前に、
- 訓練されたモデル(model.tflite)をダウンロードして、
- FlowerModel.tfliteのファイル名を変更
したことを確認してください。
一部のブラウザではダウンロードがブロックされます:
Colabがファイルをダウンロードすることを許可する必要がある場合があります:
以下のコマンドでこのコードラボで必要なファイルが含まれるGitリポジトリをcloneします。
git clone https://github.com/hoitab/TFLClassify.git次に、cloneしたディレクトリに移動します。ここでこのコードラボの残りの手順を行います。
cd TFLClassifyまだインストールしていない場合は、AndroidStudio 4.1 Beta 1以降をインストールしてください。
以下の手順でAndroid Studioでプロジェクトを開きます。
- Android Studioを起動する。ロードが終わったら、以下のポップアップから"Open an Existing project"を選択する
- ファイル選択で、作業ディレクトリ内のTFLClassify/build.gradleを選ぶ。
このプロジェクトには、
startとfinishの2つのモジュールがあります。作業に行き詰まった場合はfinishを参照してヒントにしましょう。
- 初回はgradle wrapperの使用に関する"Gradle Sync"ポップアップが表示されます。「OK」をクリックします。
-
まだの場合はスマートフォンの開発者モードとUSBデバッグを有効にします。これは1回限りのセットアップです。設定するにはこの手順に従ってください。
-
プロジェクトとスマートフォン両方の設定が終わったら、実際に端末で動かしてみましょう。
TFL_Classify.startを選択してツールバーのrunボタンをクリックします。
- Tensorflow Demoにカメラへのアクセスを許可します。
- 結果が表示される場所にランダムな数値が入った以下の画面が端末に表示されるはずです。
- 画面左側のプロジェクトエクスプローラーから
startモジュールを選択します。
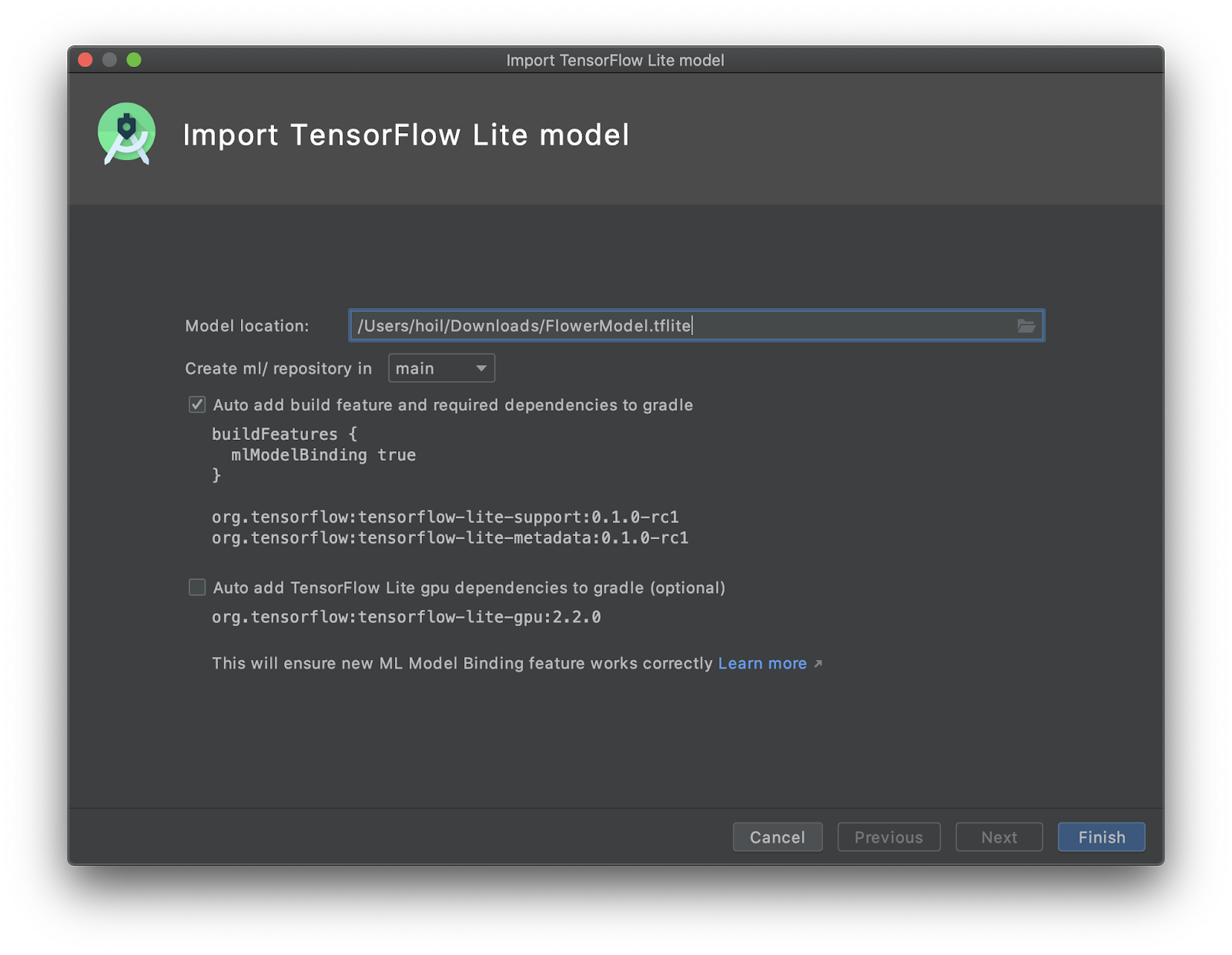
startモジュールを右クリック、またはFileからNew>Other>TensorFlow Lite Modelを選択します
- 先程ダウンロードした、訓練済みの
FlowerModel.tfliteのパスを選択します。
このツールを使うと、自動的に
build.gradleにML Model bindingや依存が挿入されモジュールの依存設定が行われます。
-
Finishをクリックします。 -
最後に以下のような画面が表示されるはずです。
FlowerModel.tfliteのインポートが成功して、入出力などモデルに関する高レベルな情報がサンプルコードとともに表示されます。
- (任意)TODOリストを使う
コードラボの更新に必要な場所へピンポイントで遷移するには、TODOリストが便利です。またAndroidプロジェクトで将来的に変更が必要な箇所を覚えておくのにも使えます。TODO項目を追加するにはコメントとTODOキーワードを使用します。TODOの一覧を確認するには以下の方法があります。
- やることを確認するにはTODOリストを表示するのが良いでしょう。画面上部のメニューから
View>Tool Windows>TODOを選択します。
- 初期設定ではすべてのモジュールのTODOを表示するので、すこし分かりづらいかもしれません。TODOパネル端のgroup byボタンをクリックして
Modulesを選択することでstartのTODOのみに絞り込むことができます。
- startモジュール内の項目を展開します。
- TODOリストのTODO 1をクリックするかMainActivity.ktファイルを開いてTODO 1を探し、以下の行を追加してモデルの初期化を行います。
private class ImageAnalyzer(ctx: Context, private val listener: RecognitionListener) :
ImageAnalysis.Analyzer {
...
// TODO 1: Add class variable TensorFlow Lite Model
private val flowerModel = FlowerModel.newInstance(ctx)
...
}- CameraX Analyzerのanalyzeメソッドの中ではカメラからの入力の
ImageProxyをBitmapに変換し、TensorImageオブジェクトを生成して、推論プロセスに使用します。
このツールでは画像の入力は
Bitmap形式である必要があります。
- これはつまり
ImageProxyではなくファイルを入力として使う場合、fromBitmapメソッドに直接Bitmapとして流し込むことができます。ImageProxyがどうBitmapに変換されているかについては、toBitmapメソッドとYuvToRgbConverterを参照ください。またこれは将来的なTensorImageのImageProxy対応までの暫定的なメソッドです。
override fun analyze(imageProxy: ImageProxy) {
...
// TODO 2: Convert Image to Bitmap then to TensorImage
val tfImage = TensorImage.fromBitmap(toBitmap(imageProxy))
...
}- 画像を処理して、結果に対し以下の操作を行います。
- 属性スコアを使って確立の高い順に結果をソートする
MAX_RESULT_DISPLAYで定義される上位k個の結果取得する。この値を任意のものに差し替えて結果の数を変更することもできます。
override fun analyze(imageProxy: ImageProxy) {
...
// TODO 3: Process the image using the trained model, sort and pick out the top results
val outputs = flowerModel.process(tfImage)
.probabilityAsCategoryList.apply {
sortByDescending { it.score } // Sort with highest confidence first
}.take(MAX_RESULT_DISPLAY) // take the top results
...
}- ソートしてフィルタした結果をデータオブジェクト
Recognitionに変換して、Data Bindingを使ってRecyclerViewに流し込めるようにします。
override fun analyze(imageProxy: ImageProxy) {
...
// TODO 4: Converting the top probability items into a list of recognitions
for (output in outputs) {
items.add(Recognition(output.label, output.score))
}
...
}- 以前表示されていたプレースホルダーの結果を生成する以下の行をコメントアウトもしくは削除します。
// START - Placeholder code at the start of the codelab. Comment this block of code out.
for (i in 0..MAX_RESULT_DISPLAY-1){
items.add(Recognition("Fake label $i", Random.nextFloat()))
}
// END - Placeholder code at the start of the codelab. Comment this block of code out.TFL_Classify.startを選択してツールバーのrunボタンをクリックして、実際の端末でアプリを起動してみます。
- 以下の画面が表示され、ランダムな値の代わりに実際の結果が表示されるようになります。
TensorFlow Liteは複数のハードウェアアクセラレータに対応し、モバイル端末での推論を高速化することができます。GPUも利用できるアクセラレータのひとつで、デリゲート機能を使って比較的簡単に使用することができます。
startモジュールのbuild.gradleを開くか、TODOリストのTODO 5を選択して、以下の依存を追加します。
// TODO 5: Optional GPU Delegates
implementation 'org.tensorflow:tensorflow-lite-gpu:2.2.0'- MainActivity.ktファイルに戻るかTODOリストのTODO 6を選択して以下のモデルオプションを初期化します。
private class ImageAnalyzer(ctx: Context, private val listener: RecognitionListener) :
ImageAnalysis.Analyzer {
...
// TODO 6. Optional GPU acceleration
private val options = Model.Options.Builder().setDevice(Model.Device.GPU).build()
...
}- 引数に
optionsを追加してモデルの初期化処理を変更します。
private class ImageAnalyzer(ctx: Context, private val listener: RecognitionListener) :
ImageAnalysis.Analyzer {
...
// TODO 1: Add class variable TensorFlow Lite Model
private val flowerModel = FlowerModel.newInstance(ctx, options)
...
}TFL_Classify.startを選択した上でツールバーのrunボタンをクリックして、実機でアプリを実行します。
ハイ・ミドルレンジの端末では、CPUよりもGPUのほうが格段に高速です。一方でエントリー機には遅いGPUが搭載されていることが多く、機種によって推論の高速化度合いが異なります。
以下のリンクをたどってみましょう
- TFLiteについてもっと学ぶにはtensorflow.orgのドキュメントやコードリポジトリがあります。
- 音声ホットワード検知器やスマート返信のオンデバイス版など、予め訓練されたTFLiteモデルを試してみましょう。
- Getting startedの資料でTensorFlow全般について学んでみましょう。