- Java Identifiers
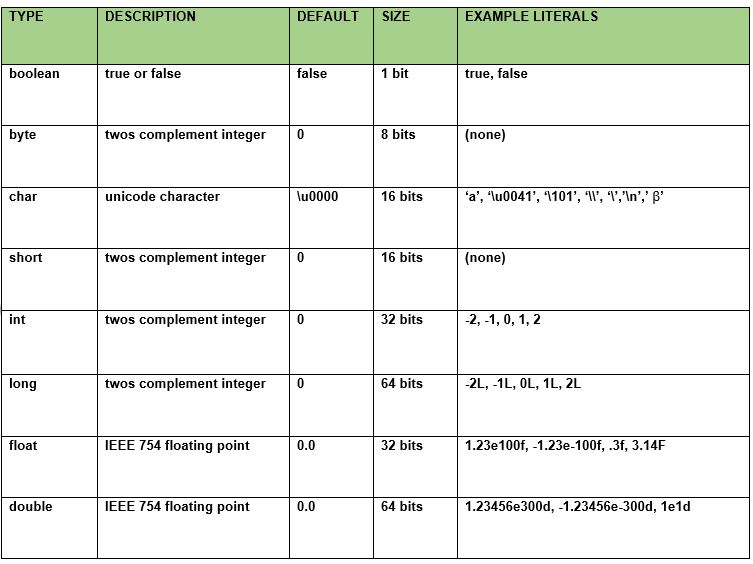
- Data types
- How to define our own data type in java(enum)
- Variables
- Scope of Variables
- Loops in Java(Practice)
- For-each loop in Java
- For Loop in Java | Important points
- Decision Making(if, if-else, switch, break, continue, jump)(Practice)
- Switch Statement in Java(Practice)
- String in Switch Case in Java
- Forward declarations
- Widening Primitive Conversion
- Type conversion in Java
- Comments in Java
- Does Java support goto?
- Interesting facts about null in Java
- Using underscore in Numeric Literals
- class name
- method name
- variable name
- label
- The only allowed characters are ([A-Z],[a-z],[0-9]), ‘$‘(dollar sign) and ‘_‘ (underscore)
- Identifiers should not start with digits([0-9])
- case-sensitive
- no limit on the length
- Reserved words can't be used as an identifier
- Statically typed language (Java)
- each variable and expression type is already known at compile time
- once a variable is declared to be of a certain data type, it cannot hold values of their data types
- Dynamically typed language (Python, Ruby)
- these languages can receive different data types over the time
Java = statically typed and a strongly typed language - each type of data is predefined as part of the programming language - all constants or variables defined for a given program must be described with one of the data types
Java:
- Primitive data
- Object data (programmer created type)
Enumerations serve the purpose of representing a group of named constants in a programming language.
Enums are used when we know all possible values at compile time, such as choices on a menu, rounding modes, command line flags, etc. It is not necessary that the set of constants in an enum type stay fixed for all time.
The main objective of enum is to define our own data types(Enumerated Data Types).
Enum declaration can be done outside a Class or inside a Class but not inside a Method.
// A simple enum example where enum is declared
// outside any class (Note enum keyword instead of
// class keyword)
enum Color
{
RED, GREEN, BLUE;
}
public class Test
{
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Color c1 = Color.RED;
System.out.println(c1);
}
}
or
// enum declaration inside a class.
public class Test
{
enum Color
{
RED, GREEN, BLUE;
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Color c1 = Color.RED;
System.out.println(c1);
}
}
- First line inside enum should be list of constants and then other things like methods, variables and constructor.
- According to Java naming conventions, it is recommended that we name constant with all capital letters
- Every enum internally implemented by using Class.
/* internally above enum Color is converted to
class Color
{
public static final Color RED = new Color();
public static final Color BLUE = new Color();
public static final Color GREEN = new Color();
}*/
- Every enum constant represents an object of type enum.
- enum type can be passed as an argument to switch statement.
// A Java program to demonstrate working on enum
// in switch case (Filename Test. Java)
import java.util.Scanner;
// An Enum class
enum Day
{
SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY,
THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY;
}
// Driver class that contains an object of "day" and
// main().
public class Test
{
Day day;
// Constructor
public Test(Day day)
{
this.day = day;
}
// Prints a line about Day using switch
public void dayIsLike()
{
switch (day)
{
case MONDAY:
System.out.println("Mondays are bad.");
break;
case FRIDAY:
System.out.println("Fridays are better.");
break;
case SATURDAY:
case SUNDAY:
System.out.println("Weekends are best.");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Midweek days are so-so.");
break;
}
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "MONDAY";
Test t1 = new Test(Day.valueOf(str));
t1.dayIsLike();
}
}
- Every enum constant is always implicitly public static final.
- Since it is static, we can access it by using enum Name.
- Since it is final, we can’t create child enums.
- We can declare main() method inside enum. Hence we can invoke enum directly from the Command Prompt.
// A Java program to demonstrate that we can have
// main() inside enum class.
enum Color
{
RED, GREEN, BLUE;
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Color c1 = Color.RED;
System.out.println(c1);
}
}
- All enums implicitly extend java.lang.Enum class. As a class can only extend one parent in Java, so an enum cannot extend anything else.
- toString() method is overridden in java.lang.Enum class, which returns enum constant name.
- enum can implement many interfaces.
- These methods are present inside java.lang.Enum.
- values() method can be used to return all values present inside enum.
- Order is important in enums. By using ordinal() method, each enum constant index can be found, just like array index.
- valueOf() method returns the enum constant of the specified string value, if exists.
- enum can contain constructor and it is executed separately for each enum constant at the time of enum class loading.
- We can’t create enum objects explicitly and hence we can’t invoke enum constructor directly.
- enum can contain concrete methods only i.e. no any abstract method.
// Java program to demonstrate that enums can have constructor
// and concrete methods.
// An enum (Note enum keyword inplace of class keyword)
enum Color
{
RED, GREEN, BLUE;
// enum constructor called separately for each
// constant
private Color()
{
System.out.println("Constructor called for : " +
this.toString());
}
// Only concrete (not abstract) methods allowed
public void colorInfo()
{
System.out.println("Universal Color");
}
}
public class Test
{
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Color c1 = Color.RED;
System.out.println(c1);
c1.colorInfo();
}
}
Output:
Constructor called for : RED
Constructor called for : GREEN
Constructor called for : BLUE
RED
Universal Color