Ref : stackoverflow
The best solution in my opinion is to use the unittest command line interface which will add the directory to the sys.path so you don't have to (done in the TestLoader class).
For example for a directory structure like this:
new_project
├── antigravity.py
└── test_antigravity.py
You can just run:
$ cd new_project
$ python -m unittest test_antigravity
For a directory structure like yours:
new_project
├── antigravity
│ ├── __init__.py # make it a package
│ └── antigravity.py
└── test
├── __init__.py # also make test a package
└── test_antigravity.py
And in the test modules inside the test package, you can import the antigravity package and its modules as usual:
# import the package
import antigravity
# import the antigravity module
from antigravity import antigravity
# or an object inside the antigravity module
from antigravity.antigravity import my_object
Running a single test module:
To run a single test module, in this case test_antigravity.py:
$ cd new_project
$ python -m unittest test.test_antigravity
Just reference the test module the same way you import it.
Running a single test case or test method:
Also you can run a single TestCase or a single test method:
$ python -m unittest test.test_antigravity.GravityTestCase
$ python -m unittest test.test_antigravity.GravityTestCase.test_method
Running all tests:
You can also use test discovery which will discover and run all the tests for you, they must be modules or packages named test*.py (can be changed with the -p, --pattern flag):
$ cd new_project
$ python -m unittest discover
This will run all the test*.py modules inside the test package.
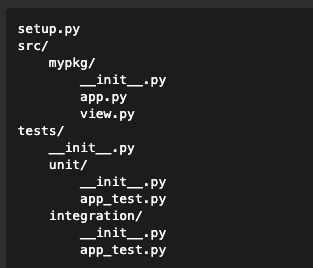
You need to add
__init__.pyto thetestsdirectory, If you have other subdirectories in thetestsdirectory you also need to add the__init__.pyso python can know that those are modules, not just directories.then run: