- mysql 학습 하면서 배운 내용을 적어 두었습니다.
- 아는 것은 기록하지 않는다.(책과 온라인 강의 등을 보고 있음)
- 정리는 나중에 리뷰 하면서 한 꺼번에 한다.
- 모르는 것, 새롭게 알게 된 것, 애매하게 알고 있는 것을 적는다.
- 아래와 같은 것을 새롭게 배웠다.
SELECT
orderNumber, status
FROM
orders
ORDER BY FIELD(status,
'In Process',
'On Hold',
'Cancelled',
'Resolved',
'Disputed',
'Shipped');
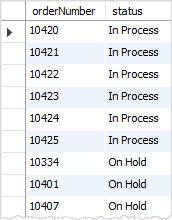
- 특정 칼럼을 지정하여 칼럼 내 값들을 임의대로 순서 조정 할 수 있다.
- 이렇게 하면 정렬을 자유자재로 할 수 있다.
SELECT
officeCode,
city,
phone,
country
FROM
offices
WHERE
country IN ('USA' , 'France');
SELECT
officeCode,
city,
phone
FROM
offices
WHERE
country = 'USA' OR country = 'France';
- In case the list has many values, you need to construct a very long statement with multiple OR operators. Hence, the IN operator allows you to shorten the query and make it more readable.
- 가독성의 중요성
SELECT
orderNumber,
customerNumber,
status,
shippedDate
FROM
orders
WHERE
orderNumber IN (SELECT
orderNumber
FROM
orderdetails
GROUP BY orderNumber
HAVING SUM(quantityOrdered * priceEach) > 60000);
- 구동방식은 아래와 같은 원리로 진행되었다.
SELECT
orderNumber,
customerNumber,
status,
shippedDate
FROM
orders
WHERE
orderNumber IN (10165,10287,10310);
- between 에서 not은 이렇게 사용한다.
select
productcode,
productname,
buyprice
From
products
where
buyprice not between 90 and 100;
- between은 경계 값에 대해 생각해보고 써야 한다.
- 예를 들면 시간 계산, 날짜 계산
- Q&A
-
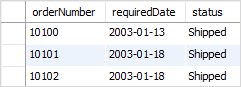
When you use the BETWEEN operator with date values, to get the best result, you should use the type cast to explicitly convert the type of column or expression to the DATE type.
-
For example, to get the orders whose required dates are from 01/01/2003 to 01/31/2003, you use the following query:
SELECT
orderNumber,
requiredDate,
status
FROM
orders
WHERE
requireddate BETWEEN
CAST('2003-01-01' AS DATE) AND
CAST('2003-01-31' AS DATE);
-
Because the data type of the required date column is DATE so we used the cast operator to convert the literal strings ‘2003-01-01 ‘ and ‘2003-12-31 ‘ to the DATE data type.
-
convert the literal strings ‘2003-01-01 ‘ and ‘2003-12-31 ‘ to the DATE data type.
SELECT
employeeNumber,
lastName,
firstName
FROM
employees
WHERE
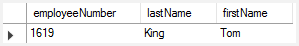
firstname LIKE 'T_m';
-
'T_M 이렇게 하면 Tom, Tim 등 일치하는 문자열 검색 가능
-
not like도 사용 가능
select
employeeNumber,
lastname,
firstname
from employees
where lastname not Like 'B%'
-
원래 ''만 되는 줄 알았다.(디폴트 값이다.)
-
그런데 escape를 지정하면 그 문자열도 지정할 수 있다.
-
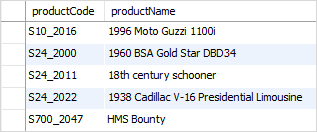
For example, if you want to find product whose product code contains string _20 , you can use the pattern %_20% as the following query:
SELECT
productCode,
productName
FROM
products
WHERE
productCode LIKE '%\_20%';
SELECT
productCode,
productName
FROM
products
WHERE
productCode LIKE '%$_20%' ESCAPE '$';
value IS NULL
If the value is NULL, the expression returns true. Otherwise, it returns false.
Note that MySQL does not have the built-in BOOLEAN type. It uses the TINYINT(1) to represent the BOOLEAN values i.e., true means 1 and false means 0.
SELECT 1 IS NULL, -- 0
0 IS NULL, -- 0
NULL IS NULL; -- 1
SELECT 1 IS NOT NULL, -- 1
0 IS NOT NULL, -- 1
NULL IS NOT NULL; -- 0
- http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-is-null/
- 위 부분이 이해가 잘 되지 않았다.
- 이해가 되면 업데이트 할 것
-
Introduction to MySQL EXISTS operator The EXISTS operator is a Boolean operator that returns either true or false. The EXISTS operator is often used the in a subquery to test for an “exist” condition.
-
where, update 등 다양하게 사용
-
서브쿼리 할 때 도 사용
select customernumber, customername
from customers
where
exists(
select 1
from orders
where orders.customernumber = customers.customernumber);
- sql 첫걸음 책에서도 본 내용이다. 두 개의 table에서 가져온 걸 비교할 때는 table0.column = table1.column
SELECT
employeenumber, firstname, lastname, extension
FROM
employees
WHERE
EXISTS( SELECT
1
FROM
offices
WHERE
city = 'San Francisco'
AND offices.officeCode = employees.officeCode);
- select 1 은 왜 쓸까?
Select 1 from table
위처럼 select 절에 1이 오는 것은 해당 테이블의 숫자만큼 1의 행을 만들어 낸다.
즉 table 의 데이터수가 N개면 1이 N행에 거쳐서 반환된다.
이것이 중요한 이유는 1은 TRUE의 다른 말이기 때문이다.
그래서 보통 WHERE 절의 (NOT) EXISTS 안의 내포 SELECT 문으로 사용된다.
또한 SELECT * FROM TABLE 이나 SELECT 1 FROM TABLE이나 논리식으로 사용될 때는 존재유무가 중요하기 때문에 보다 간단하게 사용하려면 SELECT 1 FROM TABLE을 사용하지만 접근에 대한 정확성은 떨어질 수 밖에 없다.
- exists 예제는 어려워서 링크로 대체한다.
- 핵심은 1을 반환하는 것이 True이며 결과에 매칭시킨다.
- http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-exists/
update employees
set extension = concat(extension,'1')
where
exists(
select 1
from offices
where
city = 'San Francisco'
and offices.officeCode = employees.officeCode);
select * from employees
inner join offices on offices.officeCode = employees.officeCode
- extension이라는 항목에 1을 추가 해야 하는데 exitsts를 이용하여 employees라는 항목에 1을 넣었다.
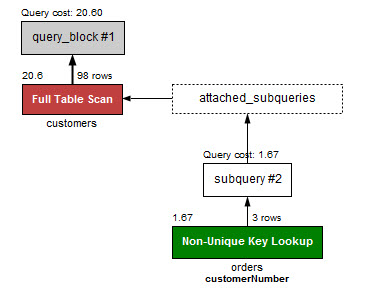
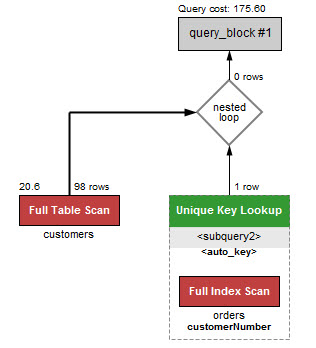
- exists(첫번째 그림), IN(두번째 그림)
- 하위 쿼리가 많을 수록 in이 느리다.
- 풀스캔해야 하기 때문이다.
- 적으면 in이 낫다.
- http://yahwang.tk/posts/35
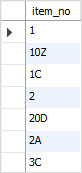
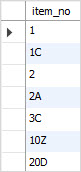
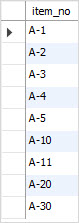
- 문자와 숫자가 함께 섞여 있는 경우의 정렬은 어떻게 하면 좋을까?
- 두번재 그림을 기대하였다.
SELECT
item_no
FROM
items
ORDER BY CAST(item_no AS UNSIGNED) , item_no;
- item_no의 데이터를 cast를 사용하여 부호없는 정수로 변환
- 그 다음 정렬
TRUNCATE TABLE items;
INSERT INTO items(item_no)
VALUES('A-1'),
('A-2'),
('A-3'),
('A-4'),
('A-5'),
('A-10'),
('A-11'),
('A-20'),
('A-30');
SELECT
item_no
FROM
items
ORDER BY item_no;
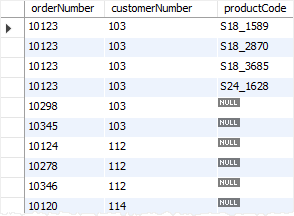
- truncate 후에 위의 쿼리를 날리면 아래와 같은 결과가 안 나온다...
뭐야..
- item_no의 문자열 길이를 반환한 다음에 길이별로 정렬
- 아이디어일뿐 해결책은 아님
SELECT
item_no
FROM
items
ORDER BY LENGTH(item_no), item_no;
SELECT
column1, column2,...
FROM
table
ORDER BY column1 DESC
LIMIT nth-1, count;
- offset첫 번째 행의 오프셋을 지정 반환한다. offset첫 번째 행의 0이 아닌 1이다.
- count최대 행 수를 반환하도록 지정합니다.
- using을 사용하면 같은 결과를 반환한다.(left, 마찬가지이다.)
SELECT
productCode,
productName,
textDescription
FROM
products t1
INNER JOIN
productlines t2 ON t1.productline = t2.productline;
SELECT
productCode,
productName,
textDescription
FROM
products
INNER JOIN
productlines USING (productline);
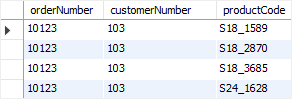
- join 에서 조건을 걸으면 결과가 다르게 나온다.
- where을 따로 거는 경우, left join에서 거는 경우
SELECT
o.orderNumber,
customerNumber,
productCode
FROM
orders o
LEFT JOIN
orderDetails USING (orderNumber)
WHERE
orderNumber = 10123;
SELECT
o.orderNumber,
customerNumber,
productCode
FROM
orders o
LEFT JOIN
orderdetails d ON o.orderNumber = d.orderNumber
AND o.orderNumber = 10123;
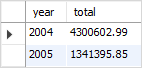
- 2018-03-03이라는 데이터가 있을 때 Year, Month, day를 쓰면 년, 월, 일을 추출할 수 있더라.
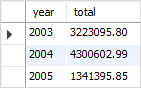
SELECT
YEAR(orderDate) AS year,
SUM(quantityOrdered * priceEach) AS total
FROM
orders
INNER JOIN
orderdetails USING (orderNumber)
WHERE
status = 'Shipped'
GROUP BY YEAR(orderDate);
SELECT
YEAR(orderDate) AS year,
SUM(quantityOrdered * priceEach) AS total
FROM
orders
INNER JOIN
orderdetails USING (orderNumber)
WHERE
status = 'Shipped'
GROUP BY YEAR
having year > 2003;
- group by 에서도 정렬을 할 수 있다.
SELECT
status, COUNT(*)
FROM
orders
GROUP BY status DESC;
- having을 쓰는 예를 더 적어보았다.
SELECT
ordernumber,
SUM(quantityOrdered) AS itemsCount,
SUM(priceeach*quantityOrdered) AS total
FROM
orderdetails
GROUP BY ordernumber
HAVING total > 1000 AND itemsCount > 600;
SELECT
a.ordernumber, status, SUM(priceeach*quantityOrdered) total
FROM
orderdetails a
INNER JOIN
orders b ON b.ordernumber = a.ordernumber
GROUP BY ordernumber, status
HAVING status = 'Shipped' AND total > 1500;
- http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-rollup/
- 기본서에 나오지 않은 내용이다.
- group by 결과가 있을 때 그 값의 총합을 구하는 것까지 하려면 어떻게 해야 할까?
- 합산 결과가 나오는 table 만들어서 union all?
- 그러면...
- The query is quite lengthy.
- The performance of the query may not be good since the database engine has to internally execute two separate queries and combine the result sets into one.
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
c1, c2, c3 WITH ROLLUP;
SELECT
productLine,
SUM(orderValue) totalOrderValue
FROM
sales
GROUP BY
productline WITH ROLLUP;
- the ROLLUP clause generates not only the subtotals but also the grand total of the order values.
오옷....짱이다
SELECT
productLine,
orderYear,
SUM(orderValue) totalOrderValue
FROM
sales
GROUP BY
productline,
orderYear
WITH ROLLUP;
- mysql 8.0.12 버전에서는 더 좋은 기능이 있으나 설치 안 해서 패스(rollup 링크 참조)
- local DB에 csv 파일을 넣을 때 한글이 깨지는 경우가 발생한다.
- 그럴 때 생성하는 table에 명령어를 추가하면 쉽게 문제를 해결 할 수 있다.
create table 'DB name'.'table name' (
'table_name_1' INT(11) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT 'hihihihi',
'table_name_2' INT(11) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT 'hihihihi',
'table_name_3' VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL COMMENT 'hihihihi'
) DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
- 한글이 잘 들어가는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
- 쿼리를 만들 때 현재 날짜와 관련하여 어떤 것을 사용해야 할까?
- 날짜만 필요하면 current_date(), 쿼리 날리는 시각의 변화가 불필요하면 now(), 같은 쿼리를 날리는 중에도 변화가 있으면 sysdate()
mysql> select now(), sysdate(), current_date(), sleep(5), now(), sysdate();
+---------------------+---------------------+----------------+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
| now() | sysdate() | current_date() | sleep(5) | now() | sysdate() |
+---------------------+---------------------+----------------+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
| 2019-05-21 03:11:57 | 2019-05-21 03:11:57 | 2019-05-21 | 0 | 2019-05-21 03:11:57 | 2019-05-21 03:12:02 |
+---------------------+---------------------+----------------+----------+---------------------+---------------------+
1 row in set (5.02 sec)