Motivation - Holes are good. They let you go places.
-
Download Blender 2.93. Do NOT use the Windows Store Version!
-
Download Metaforce and extract your ISO. This can take 1hr+. Do not use an extraction filepath longer than what is shown below:
-
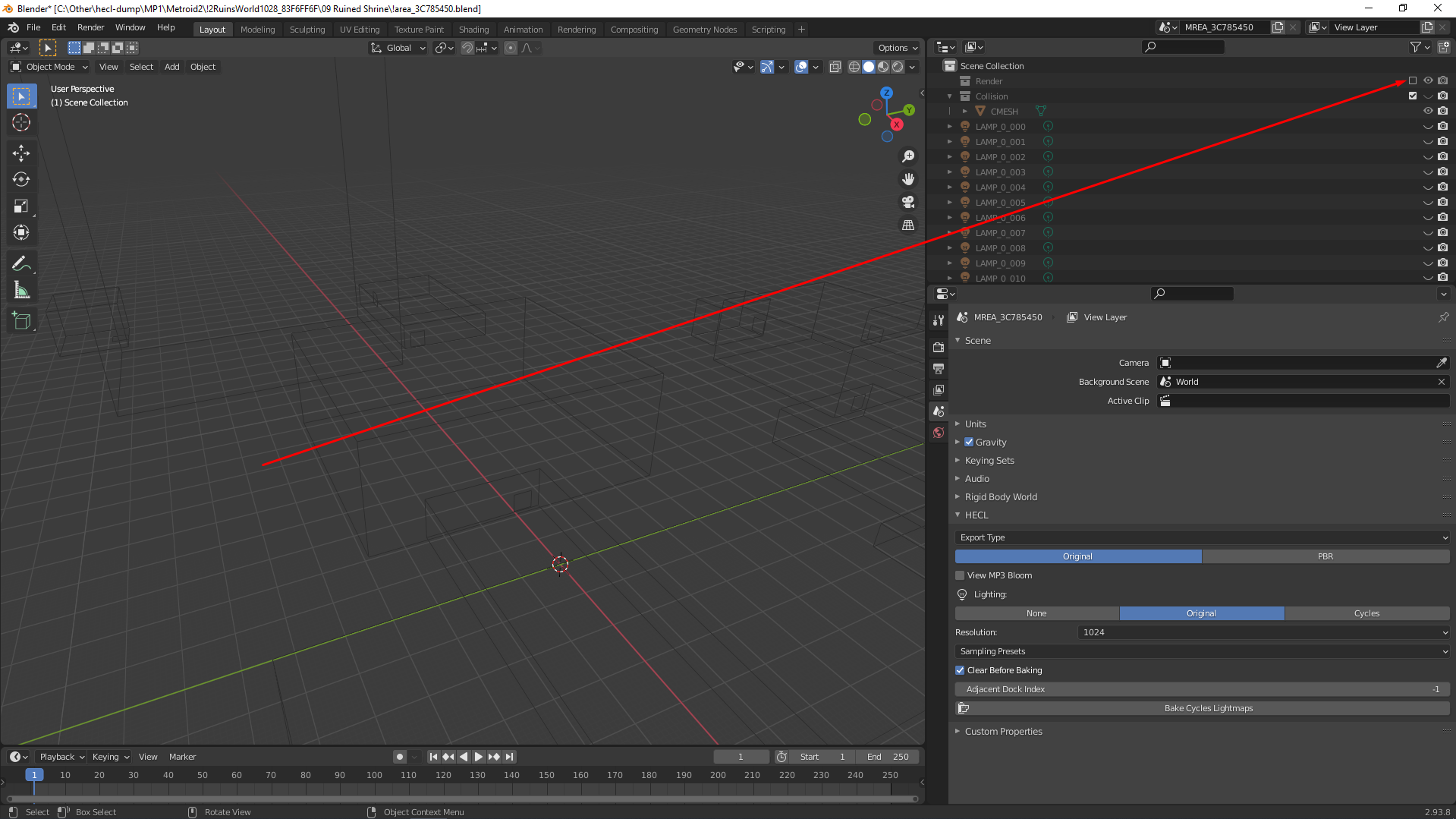
Find the
.blendfile for the area you would like to analyze and open it in blender. e.g.MP1\Metroid1\!1IntroLevel1027_158EFE17\00 Exterior Docking Hangar\!area_D1241219.blend -
Uncheck the
Rendergroup:
This is stuff you can see in-game but not neccessarily collide with.
- Ensure the
Collision/CMESHis checked and the hidden "eye" is open.
This is just the collision data.
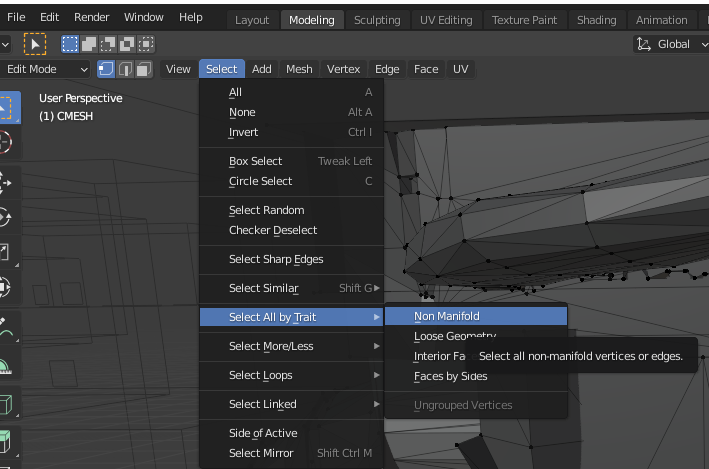
- In the modelling workspace, select all "Non-Manifold" edges:
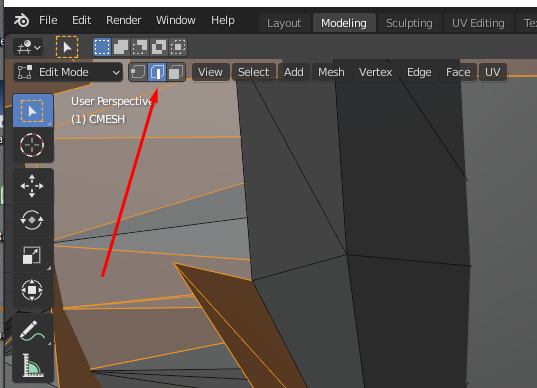
- Switch to "Edge Select":
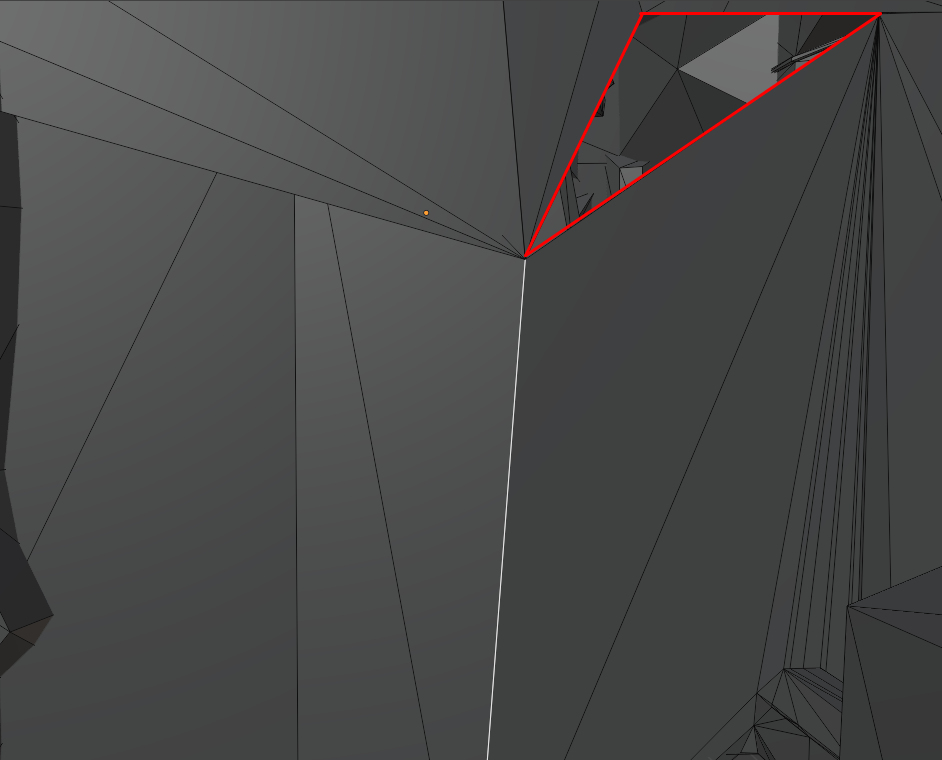
- Single-click one of the non-manifold edges and press
gto distort it around and look for holes:
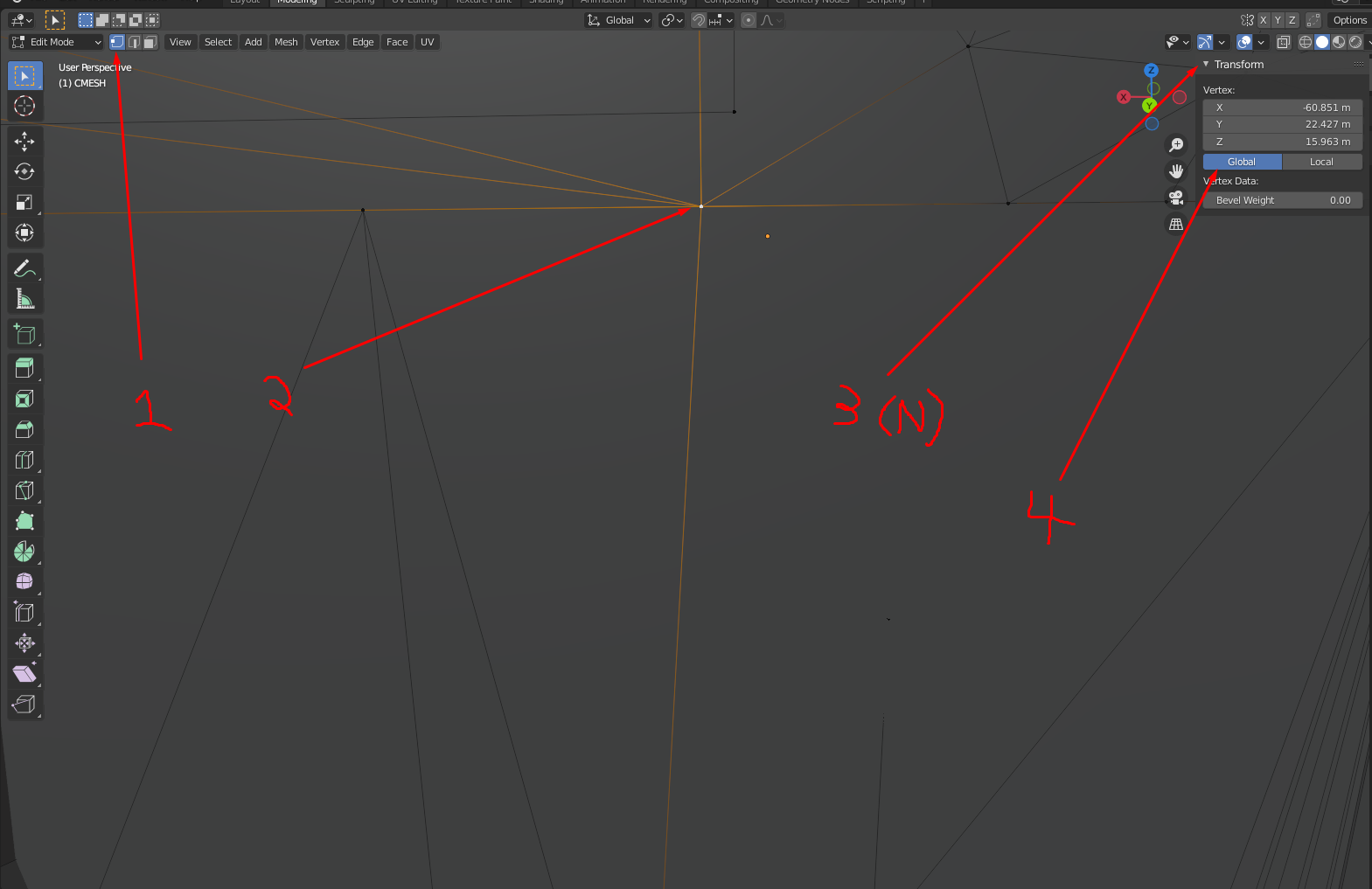
- Once you find a hole worth investigating, you can view it's coordinates by changing the selection mode to
Vertex, selecting a vertex adjacent to the hole, then opening the transform window by pressingn. You will need to switch the coordinate view toGlobalfor the coordinates to make any sense.
Rinse and repeat until you find a real stinky one.
Don't use this method, it is inferior and overly-acedemic. This information is being preserved for posterity only.
- Repeat steps 1-5 from Method 1
- Save the file as
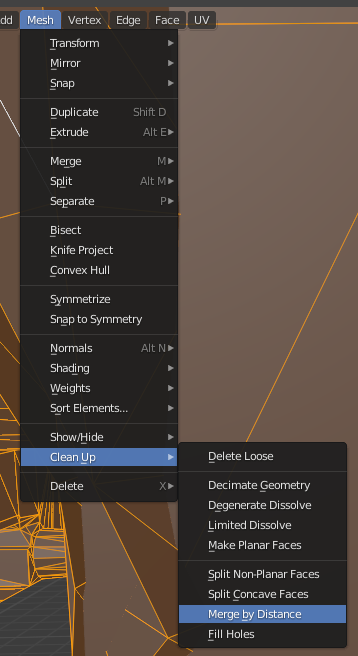
pre.blend - Select all vertices and apply "Merge by Distance:"
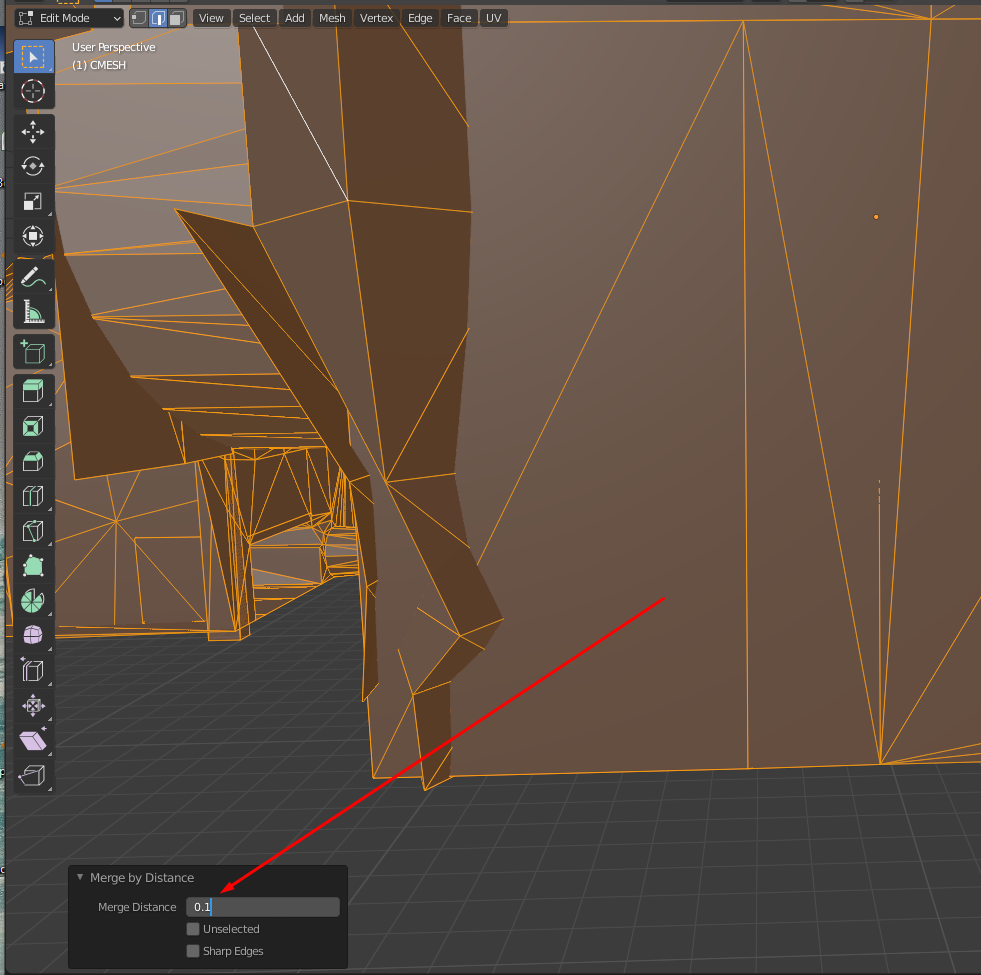
- Re-apply the "Merge By Distance" with
0.1m:
-
Save the file as
post.blend -
Using these commands:
blender --background post.blend --python test.py > post.txt
blender --background pre.blend --python test.py > pre.txt
run this python script:
import bpy
found_it = False
for ob in bpy.context.scene.objects:
if ob.data.name != "CMESH":
continue
print("location:" + str(list(ob.location)))
mesh = ob.data
for vertex in mesh.vertices:
print(list(vertex.co))
assert(not found_it)
found_it = True
assert(found_it)- Run this python script:
import math
def distance(a, b):
return math.dist(a,b)
def to_vec3(string):
string = string.replace("[", "").replace("]", "").replace("location:", "").replace(",", "")
data = [float(x) for x in string.split(" ")]
return data
def parse_file(filename):
with open(filename, "r") as file:
text = file.read()
lines = text.split("\n")
location = to_vec3(lines[5])
return(lines[5:], location)
(pre, pre_location) = parse_file("pre.txt")
(post, post_location) = parse_file("post.txt")
diff = list()
for line in pre:
if line not in post:
diff.append(line)
for line in post:
if line not in pre and line not in diff:
diff.append(line)
# print(diff)
assert pre_location == post_location
location = pre_location
diff_coords = list()
for line in diff:
coord = to_vec3(line)
coord = [location[0] + coord[0], location[1] + coord[1], location[2] + coord[2]]
diff_coords.append(coord)
for coord_a in diff_coords:
for coord_b in diff_coords:
if coord_a == coord_b:
continue
dist = distance(coord_a, coord_b)
if dist < 5.0:
diff_coords.remove(coord_b)
for coord in sorted(diff_coords):
print("%0.3f, %0.3f, %0.3f" % (coord[0], coord[1], coord[2]))- Inspect the printed coordinates for holes in your favorite hole-viewing program