- Define and describe DevOps
- Define and describe CI
- Define and describe CD
- List some common CI/CD tools
- Connect a github repo with tests to travis ci
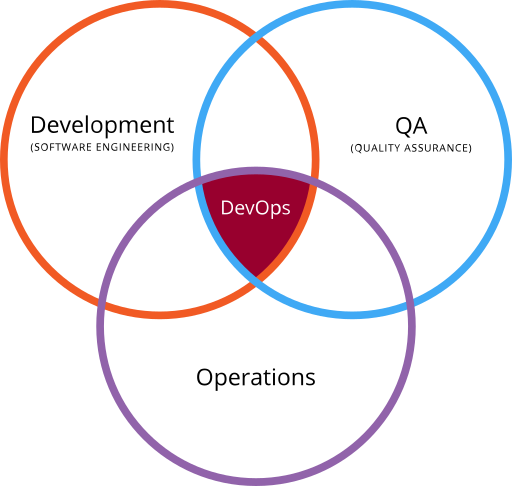
DevOps (a clipped compound of development and operations) is a culture, movement or practice that emphasizes the collaboration and communication of both software developers and other information-technology (IT) professionals while automating the process of software delivery and infrastructure changes.
It aims at establishing a culture and environment where building, testing, and releasing software can happen rapidly, frequently, and more reliably.
There is no single DevOps tool, rather a set or “DevOps toolchain” consisting of multiple tools.
- Code
- Build
- Test
- Package
- Release
- Configure
- Monitor
In software engineering, continuous integration (CI) is the practice of merging all developer working copies to a shared mainline several times a day.
The main aim of CI is to prevent integration problems, referred to as "integration hell".
Because you’re integrating so frequently, there is significantly less back-tracking to discover where things went wrong, so you can spend more time building features.
- Say goodbye to long and tense integrations
- Increase visibility which enables greater communication
- Catch issues fast and nip them in the bud
- Spend less time debugging and more time adding features
- Proceed in the confidence you’re building on a solid foundation
- Stop waiting to find out if your code’s going to work
- Reduce integration problems allowing you to deliver software more rapidly
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time.[1] It aims at building, testing, and releasing software faster and more frequently.
Continuous Delivery is the natural extension of Continuous Integration: an approach in which teams ensure that every change to the system is releasable, and that we can release any version at the push of a button. Continuous Delivery aims to make releases boring, so we can deliver frequently and get fast feedback on what users care about.
- Continuous Delivery reduces waste and makes releases boring
- Implementing CD has second-order effects that reduce the costs of software development
- Define and describe DevOps
- Define and describe CI
- Define and describe CD
- List some common CI/CD tools
- Connect a github repo with tests to travis ci