Created
September 4, 2020 06:19
-
-
Save zzjtnb/59889d26957cca3a489859e38cc85bb6 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
Ubuntu20.04 安装 Mysql
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| ### Ubuntu20.04 安装 Mysql | |
| * [1、方法一: 下载安装 MySQL(安装其他版本)](#1_MySQL_1) | |
| * [1.1 在官网下载 mysql 安装包](#11mysql_4) | |
| * [1.2 解压文件](#12_7) | |
| * [1.3 安装](#13_15) | |
| * [2、方法二:通过 apt 安装 MySQL 服务(推荐,会安装最新版)](#2apt_MySQL_65) | |
| * [2.1 初始化配置](#21__73) | |
| * [2.2 检查 mysql 服务状态](#22mysql_113) | |
| * [3.1 配置远程访问](#31_119) | |
| * [3.2 新建数据库和用户](#32_205) | |
| * [3.3mysql 服务命令](#33mysql_214) | |
| * [4、数据库操作命令](#4_231) | |
| * [4.1mysql 服务操作](#41mysql_232) | |
| * [4.2 数据库操作](#42_298) | |
| * [4.3 表操作](#43_328) | |
| * [4.4 修改表结构](#44_379) | |
| * [4.5 数据操作](#45_427) | |
| * [4.6 数据的备份与恢复](#46_444) | |
| * [4.7 卸载](#47_459) | |
| 1、方法一: 下载安装 MySQL(安装其他版本) | |
| ------------------------- | |
| 在 Ubuntu 中,默认情况下,只有最新版本的 MySQL 包含在 APT 软件包存储库中, 要安装它,只需更新服务器上的包索引并安装默认包 apt-get。 | |
| 如果因为程序兼容性问题,要安装 5.7 版本,则可以同过下载安装。 | |
| ### 1.1 在官网下载 mysql 安装包 | |
| [https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/](https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/) | |
| 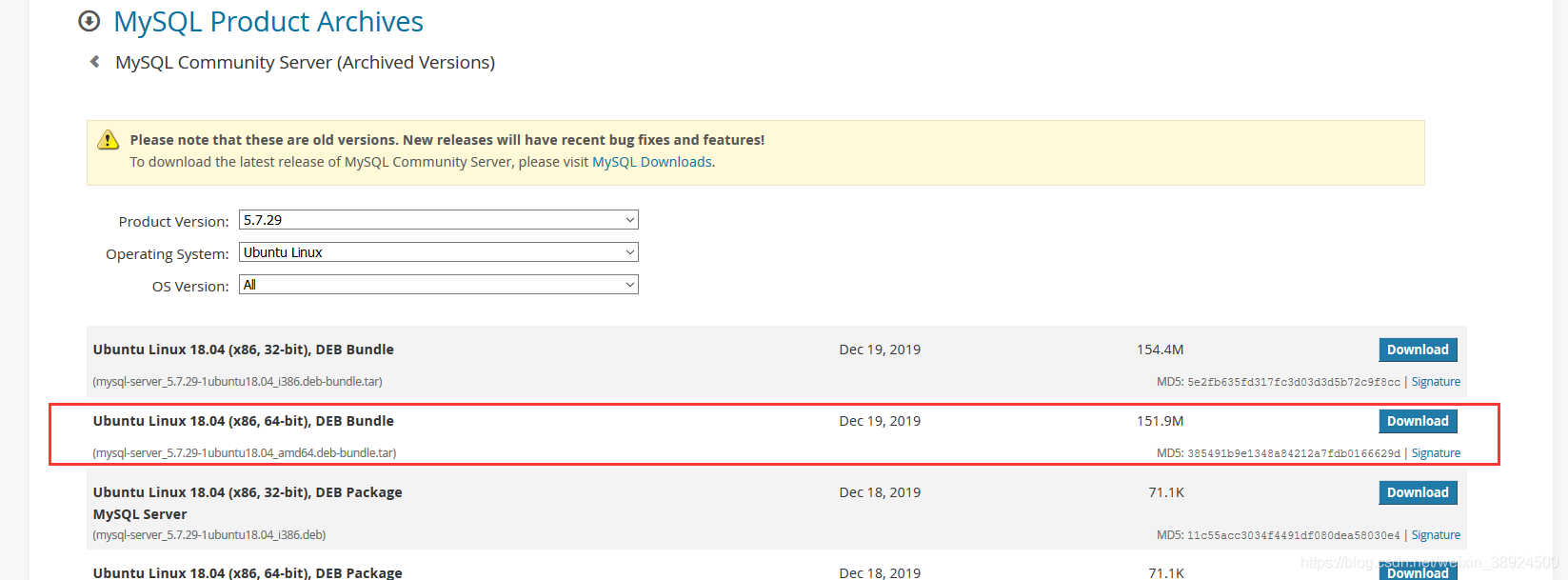 | |
| ### 1.2 解压文件 | |
| 进入你的下载文件夹下面 | |
| ```bash | |
| tar -xvf mysql-server\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb-bundle.tar | |
| ``` | |
| 解压了这个包之后会在文件夹看到多个 deb 文件 | |
| 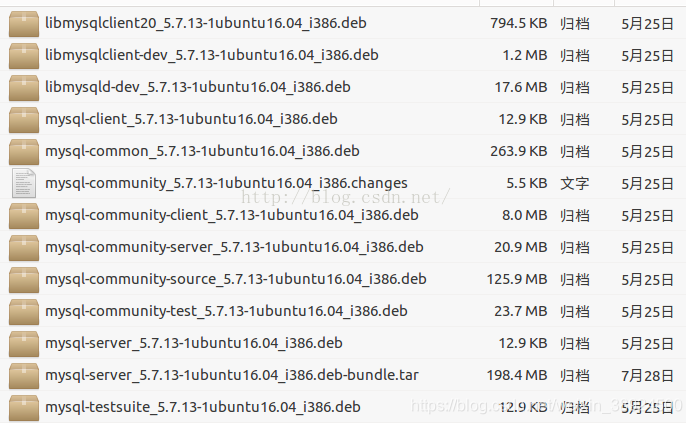 | |
| ### 1.3 安装 | |
| **安装顺序(很重要的,因为存在依赖关系)**: | |
| libmysqlclient20\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| libmysqlclient-dev\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| libmysqld-dev\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| mysql-common\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| mysql-community-source\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| mysql-community-client\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| mysql-community-server\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| mysql-server\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| 可以一次性按顺序输入安装包名字: | |
| ```bash | |
| sudo dpkg -i libmysqlclient20\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb libmysqlclient-dev\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb libmysqld-dev\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb mysql-common\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb mysql-community-source\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb mysql-community-client\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb mysql-community-server\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb mysql-server\_5.7.13-1ubuntu16.04\_i386.deb | |
| ``` | |
| 也可以一个一个来安装(这样子能够搞懂依赖的关系) | |
| 安装过程中可能缺少依赖,所以可以用: | |
| ```bash | |
| sudo apt-get install \[文件名\] | |
| ``` | |
| eg: 这里面的问题是缺少 libaio1 和 libmecab2,所以可以用: | |
| sudo apt-get install libaio1 libmecab2 | |
| 如果还是不能安装使用: | |
| ```bash | |
| sudo apt-get -f install | |
| ``` | |
| 安装完成之后: | |
| 查看 mysql 服务状态: | |
| ```bash | |
| service mysql start | |
| ``` | |
| 进入 MySQL | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql -u root -p | |
| ``` | |
| 2、方法二:通过 apt 安装 MySQL 服务(推荐,会安装最新版) | |
| ----------------------------------- | |
| ```bash | |
| #命令1 更新源 | |
| sudo apt-get update | |
| #命令2 安装mysql服务 | |
| sudo apt-get install mysql-server | |
| ``` | |
| 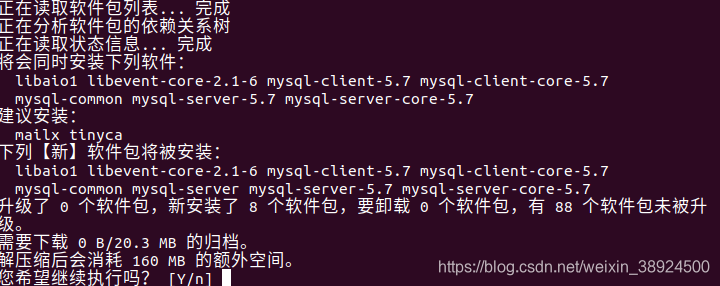 | |
| 2.1 初始化配置 | |
| --------- | |
| ```bash | |
| sudo mysql\_secure\_installation | |
| ``` | |
| 配置项较多,如下所示: | |
| ```bash | |
| #1 | |
| VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN can be used to test passwords... | |
| Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: N (选择N ,不会进行密码的强校验) | |
| #2 | |
| Please set the password for root here... | |
| New password: (输入密码) | |
| Re-enter new password: (重复输入) | |
| #3 | |
| By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, | |
| allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have | |
| a user account created for them... | |
| Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : N (选择N,不删除匿名用户) | |
| #4 | |
| Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from | |
| 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at | |
| the root password from the network... | |
| Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : N (选择N,允许root远程连接) | |
| #5 | |
| By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that | |
| anyone can access... | |
| Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : N (选择N,不删除test数据库) | |
| #6 | |
| Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes | |
| made so far will take effect immediately. | |
| Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y (选择Y,修改权限立即生效) | |
| ``` | |
| ### 2.2 检查 mysql 服务状态 | |
| ```bash | |
| systemctl status mysql.service | |
| ``` | |
| 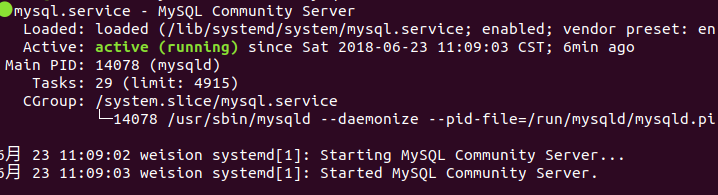 | |
| 3.1 配置远程访问 | |
| ---------- | |
| 在 Ubuntu 下 MySQL 缺省是只允许本地访问的,使用 workbench 连接工具是连不上的; | |
| 如果你要其他机器也能够访问的话,需要进行配置; | |
| **找到 bind-address 修改值为 0.0.0.0(如果需要远程访问**) | |
| ```bash | |
| sudo vi /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf #找到 bind-address 修改值为 0.0.0.0(如果需要远程访问) | |
| sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restart #重启mysql | |
| ``` | |
| ```bash | |
| sudo mysql -uroot -p | |
| ``` | |
| 输入用户密码 | |
| ```bash | |
| #切换数据库 | |
| mysql>use mysql; | |
| #查询用户表命令: | |
| mysql>select User,authentication\_string,Host from user; | |
| #查看状态 | |
| select host,user,plugin from user; | |
| ``` | |
| 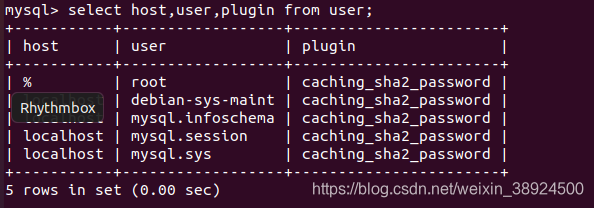 | |
| ```bash | |
| #设置权限与密码 | |
| mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql\_native\_password BY '密码'; #使用mysql\_native\_password修改加密规则 | |
| mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '密码' PASSWORD EXPIRE NEVER; #更新一下用户的密码 | |
| mysql> UPDATE user SET host = '%' WHERE user = 'root'; #允许远程访问 | |
| #刷新cache中配置 刷新权限 | |
| mysql>flush privileges; | |
| mysql>quit; | |
| ``` | |
| 如果无法更改密码使用 **flush privileges; **然后再进行更改密码,修改加密规则操作。 | |
| 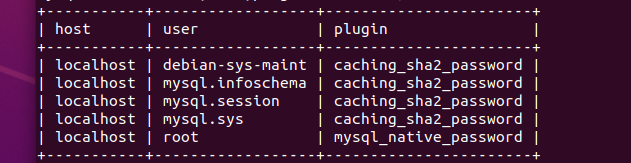 | |
| 其中** root@localhost**,localhost 就是本地访问,配置成 **%** 就是所有主机都可连接; | |
| 第二个’**密码**’为你给新增权限用户设置的密码,% 代表所有主机,也可以是具体的 ip; | |
| **注意不要直接更新密码的编码格式,而不加密码,这样会把加密密码跟新了,需要携带密码** | |
| * FLUSH PRIVILEGES; 作用是: | |
| 将当前 user 和 privilige 表中的用户信息 / 权限设置从 mysql 库 (MySQL 数据库的内置库) 中提取到内存里。 | |
| MySQL 用户数据和权限有修改后,希望在 "不重启 MySQL 服务" 的情况下直接生效,那么就需要执行这个命令。 | |
| 通常是在修改 ROOT 帐号的设置后,怕重启后无法再登录进来,那么直接 flush 之后就可以看权限设置是否生效。 | |
| 而不必冒太大风险。 | |
| * 修改密码 | |
| ```bash | |
| alter user 'root'@'%' identified with mysql\_native\_password by '密码'; | |
| ``` | |
| * 新增用户赋权并设置远程访问 | |
| mysql8 和原来的版本有点不一样,8 的安全级别更高,所以在创建远程连接用户的时候, | |
| 不能用原来的命令(同时创建用户和赋权): | |
| ```bash | |
| #必须先创建用户(密码规则:mysql8.0以上密码策略限制必须要大小写加数字特殊符号) | |
| mysql> CREATE USER 'sammy'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql\_native\_password BY 'password'; | |
| #赋权 | |
| mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON \*.\* TO 'sammy'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION; | |
| ``` | |
| * 修改加密方式: | |
| mysql8.0 引入了新特性 caching\_sha2\_password;这种密码加密方式 Navicat 12 以下客户端不支持; | |
| Navicat 12 以下客户端支持的是 mysql\_native\_password 这种加密方式; | |
| ``` | |
| update user set plugin='mysql\_native\_password' where user='root' | |
| ``` | |
| * 如果为了安全性,设置了用户验证,必须使用 sudo,才能登录,出现如下情况:(尽量不要设置 ubuntu 用户在验证,否则会很麻烦) | |
|  | |
| 解决方法: | |
| sudo vim /etc/mysql/my.cnf | |
| 添加: | |
| \[mysqld\] | |
| skip-grant-tables | |
| 保存后重启 mysql,可以正常登陆了 | |
| 这样操作后,是相当于跳过了 mysql 的密码认证。很不安全,直接就可以登录进去。 | |
| ### 3.2 新建数据库和用户 | |
| ```bash | |
| ##1 创建数据库studentService | |
| CREATE DATABASE studentService; | |
| ##2 创建用户teacher(密码admin) 并赋予其studentService数据库的远程连接权限 | |
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON teacher.\* TO studentService@% IDENTIFIED BY "admin"; | |
| ``` | |
| ### 3.3mysql 服务命令 | |
| ```bash | |
| #检查服务状态 | |
| systemctl status mysql.service | |
| 或 | |
| sudo service mysql status | |
| ``` | |
| mysql 服务启动停止 | |
| ```bash | |
| #停止 | |
| sudo service mysql stop | |
| #启动 | |
| sudo service mysql start | |
| ``` | |
| 4、数据库操作命令 | |
| --------- | |
| ### 4.1mysql 服务操作 | |
| 1、进入 mysql 数据库 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql -u root -p | |
| ``` | |
| 2、查看数据库版本 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> status; | |
| ``` | |
| 3、退出 mysql 操作 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> quit; | |
| ``` | |
| 4、启动 mysql 服务 | |
| ```bash | |
| \[root@szxdb etc\]# service mysql start | |
| ``` | |
| 5、停止 mysql 服务 | |
| ```bash | |
| \[root@szxdb etc\]# service mysql stop | |
| ``` | |
| 6、重启 mysql 服务 | |
| ```bash | |
| service mysql restart | |
| ``` | |
| 7、更改密码 :mysqladmin -u 用户名 -p 旧密码 password 新密码 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> mysqladmin -uroot -proot password 123456 | |
| ``` | |
| 8、增加新用户 :grant select on 数据库.\* to 用户名 @登录主机 identified by “密码” | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> grant all privileges on \*.\* to root@"%" identified by "pwd" with grant option; | |
| ``` | |
| 增加一个用户 test2 密码为 abc, 让他只可以在 localhost 上登录,并可以对数据库 mydb 进行查询、插入、修改、删除的操作 (localhost 指本地主机,即 MYSQL 数据库所在的那台主机),这样用户即使用知道 test2 的密码,他也无法从 internet 上直接访问数据 库,只能通过 MYSQL 主机上的 web 页来访问了。 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> grant select,insert,update,delete on mydb.\* to test2@localhost identified by "abc"; | |
| ``` | |
| 如果你不想 test2 有密码,可以再打一个命令将密码消掉。 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> grant select,insert,update,delete on mydb.\* to test2@localhost identified by ""; | |
| ``` | |
| 9、查看字符集 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> show variables like 'character%'; | |
| ``` | |
| ### 4.2 数据库操作 | |
| * 创建数据库 | |
| ```bash | |
| create database 数据库名 charset=utf8; | |
| ``` | |
| * 删除数据库 | |
| ```bash | |
| drop database 数据库名; | |
| ``` | |
| * 切换数据库 | |
| ```bash | |
| use 数据库名; | |
| ``` | |
| * 查看当前选择的数据库 | |
| ```bash | |
| select database(); | |
| ``` | |
| * 列出数据库 | |
| ```bash | |
| mysql-> show databases; | |
| ``` | |
| ### 4.3 表操作 | |
| * 查看当前数据库中所有表 | |
| ```bash | |
| show tables; | |
| ``` | |
| * 创建表 | |
| ```bash | |
| auto\_increment表示自动增长 | |
| ``` | |
| create table 表名 (列及类型); | |
| 如: | |
| create table students( | |
| id int auto\_increment primary key, | |
| sname varchar(10) not null | |
| ); | |
| * 修改表 | |
| ```bash | |
| alter table 表名 add|change|drop 列名 类型; | |
| ``` | |
| 如: | |
| alter table students add birthday datetime; | |
| * 删除表 | |
| ```bash | |
| drop table 表名; | |
| ``` | |
| * 查看表结构 | |
| ```bash | |
| desc 表名; | |
| ``` | |
| * 更改表名称 | |
| ```bash | |
| rename table 原表名 to 新表名; | |
| ``` | |
| * 查看表的创建语句 | |
| ```bash | |
| show create table '表名'; | |
| ``` | |
| ### 4.4 修改表结构 | |
| 1、更改表得的定义把某个栏位设为主键。 | |
| ```bash | |
| ALTER TABLE tab\_name ADD PRIMARY KEY (col\_name) | |
| ``` | |
| 2、把主键的定义删除 | |
| ```bash | |
| ALTER TABLE tab\_name DROP PRIMARY KEY (col\_name) | |
| ``` | |
| 3、 在 tab\_name 表中增加一个名为 col\_name 的字段且类型为 varchar(20) | |
| ```bash | |
| alter table tab\_name add col\_name varchar(20); | |
| ``` | |
| 4、在 tab\_name 中将 col\_name 字段删除 | |
| ```bash | |
| alter table tab\_name drop col\_name; | |
| ``` | |
| 5、修改字段属性,注若加上 not null 则要求原字段下没有数据 | |
| ```bash | |
| alter table tab\_name modify col\_name varchar(40) not null; | |
| ``` | |
| SQL Server200 下的写法是: | |
| ```bash | |
| Alter Table table\_name Alter Column col\_name varchar(30) not null; | |
| ``` | |
| 6、如何修改表名: | |
| ```bash | |
| alter table tab\_name rename to new\_tab\_name; | |
| ``` | |
| 7、如何修改字段名: | |
| ```bash | |
| alter table tab\_name change old\_col new\_col varchar(40); | |
| ``` | |
| 必须为当前字段指定数据类型等属性,否则不能修改 | |
| 8、 用一个已存在的表来建新表,但不包含旧表的数据 | |
| ```bash | |
| create table new\_tab\_name like old\_tab\_name; | |
| ``` | |
| ### 4.5 数据操作 | |
| * 查询 | |
| select \* from 表名 | |
| * 增加 | |
| 全列插入:insert into 表名 values(…) | |
| 缺省插入:insert into 表名 (列 1,…) values(值 1,…) | |
| 同时插入多条数据:insert into 表名 values(…),(…)…; | |
| 或 insert into 表名 (列 1,…) values(值 1,…),(值 1,…)…; | |
| 主键列是自动增长,但是在全列插入时需要占位,通常使用 0,插入成功后以实际数据为准 | |
| * 修改 | |
| update 表名 set 列 1 = 值 1,… where 条件 | |
| * 删除 | |
| delete from 表名 where 条件 | |
| * 逻辑删除,本质就是修改操作 update | |
| alter table students add isdelete bit default 0; | |
| 如果需要删除则 | |
| update students isdelete=1 where …; | |
| ### 4.6 数据的备份与恢复 | |
| 导入外部数据文本: | |
| 1\. 执行外部的 sql 脚本 | |
| 当前数据库上执行: mysql < input.sql | |
| 指定数据库上执行: mysql \[表名\] < input.sql | |
| 2\. 数据传入命令 load data local infile “\[文件名\]” into table \[表名\]; | |
| 备份数据库:(dos 下) | |
| ```bash | |
| mysqldump --opt school>school.bbb | |
| mysqldump -u \[user\] -p \[password\] databasename > filename (备份) | |
| mysql -u \[user\] -p \[password\] databasename < filename (恢复) | |
| ``` | |
| ### 4.7 卸载 | |
| 卸载 mysql | |
| ```bash | |
| dpkg --list|grep mysql #在终端中查看MySQL的依赖项 | |
| sudo apt-get remove mysql-common #卸载 | |
| sudo apt-get autoremove --purge mysql-server-8.0 | |
| ##sudo apt-get autoremove --purge mysqlxxx | |
| ``` | |
| 清理残留数据 | |
| ```bash | |
| dpkg -l |grep ^rc|awk '{print $2}' |sudo xargs dpkg -P | |
| ``` | |
| 再次查看 MySQL 的剩余依赖项: | |
| ```bash | |
| dpkg --list|grep mysql | |
| ``` | |
| 继续删除剩余依赖项,如:sudo apt-get autoremove --purge mysql-apt-config | |
| 删除原先配置文件 | |
| ```bash | |
| sudo rm -rf /etc/mysql/ /var/lib/mysql | |
| sudo apt autoremove | |
| sudo apt autoreclean(如果提示指令有误,就把reclean改成clean) | |
| ``` | |
| 参考:1.[https://blog.csdn.net/weixx3/article/details/94133847](https://blog.csdn.net/weixx3/article/details/94133847) | |
| 2.[https://blog.csdn.net/DoubleIceFire/article/details/80544516](https://blog.csdn.net/DoubleIceFire/article/details/80544516) | |
| 3.[https://blog.csdn.net/longgeaisisi/article/details/78669007](https://blog.csdn.net/longgeaisisi/article/details/78669007) |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment