Created
July 4, 2017 08:17
-
-
Save MLWave/4a3f8b0fee43d45646cf118bda4d202a to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
Embed test points in existing t-sne map
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| # Author: HJ van Veen <info@mlwave.com> | |
| # Description: Experiment to learn a tSNE transformer for new | |
| # test data with a multi-output GBM | |
| # | |
| # Idea first seen at lvdmaaten.github.io/tsne | |
| # > [...] it is not possible to embed test points in an existing | |
| # > map [...] | |
| # > A potential approach to deal with this would be to train | |
| # > a multivariate regressor to predict the map location from | |
| # > the input data. | |
| # | |
| # Part of code adapted from Fabian Pedregosa, Olivier Grisel, | |
| # Mathieu Blondel, Gael Varoquaux, | |
| # originally licensed under "BSD 3 clause (C) INRIA 2011". | |
| from sklearn import (manifold, datasets, preprocessing, model_selection, | |
| decomposition, metrics, multioutput) | |
| from xgboost import XGBRegressor | |
| import matplotlib.pyplot as plt | |
| import numpy as np | |
| # For data we use 6 different digit classes of 8x8 pixels | |
| digits = datasets.load_digits(n_class=6) | |
| X = digits.data # (1083, 64) | |
| y = digits.target # (1083, ) | |
| # Split the data into 66% train and 33% test set. | |
| X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, | |
| y, | |
| test_size=0.33, | |
| random_state=0) | |
| # First, PCA 2-D (which has .transform()) to illustrate and evaluate | |
| lens = decomposition.PCA(n_components=2, random_state=0) | |
| X_lens_train = lens.fit_transform(X_train) | |
| X_lens_test = lens.transform(X_test) | |
| # Normalize the lens within 0-1 | |
| scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler() | |
| X_lens_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_lens_train) | |
| X_lens_test = scaler.transform(X_lens_test) | |
| # Fit a model and predict the lens values from the original features | |
| model = XGBRegressor(n_estimators=2000, max_depth=20, learning_rate=0.01) | |
| model = multioutput.MultiOutputRegressor(model) | |
| model.fit(X_train, X_lens_train) | |
| preds = model.predict(X_test) | |
| # Evaluate exhaustively | |
| print("PREDICTION\t\tGROUND TRUTH") | |
| for p, g in zip(preds, X_lens_test): | |
| print(p, g) | |
| print("MAE", metrics.mean_absolute_error(X_lens_test, preds)) | |
| # Now TSNE (which has no .transform()) and a visual evaluation | |
| lens = manifold.TSNE(n_components=2, init='pca', random_state=0) | |
| X_lens_train = lens.fit_transform(X_train) | |
| # Normalize the lens within 0-1 | |
| X_lens_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_lens_train) | |
| # Fit a model and predict the lens values from the original features | |
| model.fit(X_train, X_lens_train) | |
| X_tsne = model.predict(X_test) | |
| # Visualize predictions | |
| plt.figure() | |
| for i in range(X_tsne.shape[0]): | |
| plt.text(X_tsne[i, 0], X_tsne[i, 1], str(y_test[i]), | |
| color=plt.cm.Set1(y_test[i] / 10.), | |
| fontdict={'weight': 'bold', 'size': 9}) | |
| plt.title("Predicting t-SNE transformations with GBM") | |
| plt.savefig("tsne-predictions.png") |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
In my computer (PC running Ubuntu with python 3.0) tsne-transform.py is performing much worse than
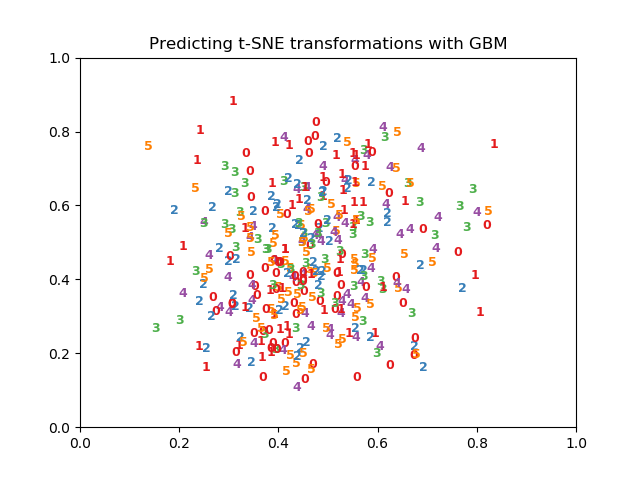
as shown in the figure at https://twitter.com/MLWave/status/882153224492527616 The following is the figure I get when running tsne-transform.py
I also tried the modified code provided by @arm_gilles to visualize errors and I can neither obtain a well separated signal as shown in https://twitter.com/arm_gilles/status/882220762328858624 The following is what I get when I run the modified tsne-transform.py by @arm_gilles
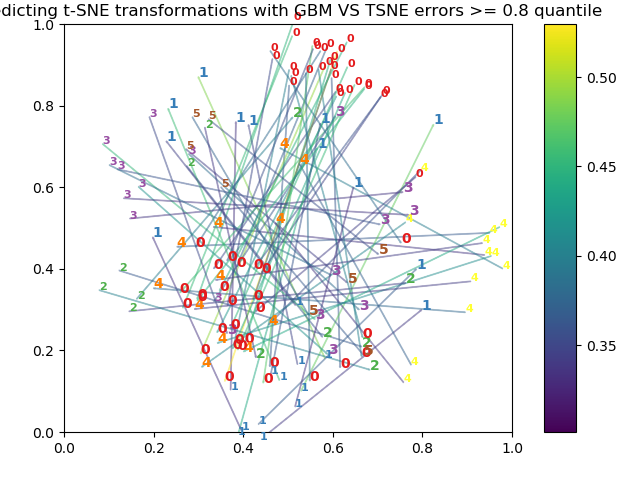
Any idea of what could be the problem?
I tried both pieces of codes many times and always get poor results. I also tried them on different Linux computers without luck.
Thanks, Joaquin